| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
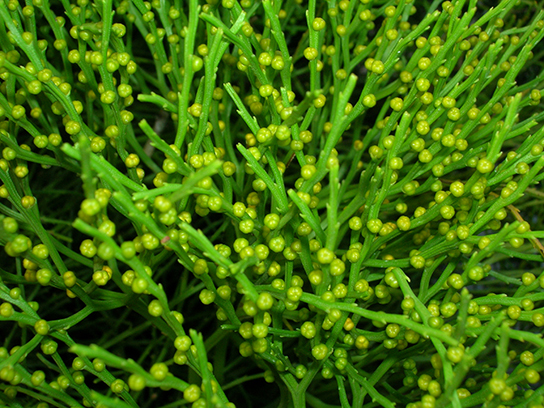
While most ferns form large leaves and branching roots, the whisk ferns , Class Psilotopsida, lack both roots and leaves, probably lost by reduction. Photosynthesis takes place in their green stems, and small yellow knobs form at the tip of the branch stem and contain the sporangia. Whisk ferns were considered an early pterophytes. However, recent comparative DNA analysis suggests that this group may have lost both vascular tissue and roots through evolution, and is more closely related to ferns.

With their large fronds, ferns are the most readily recognizable seedless vascular plants. They are considered the most advanced seedless vascular plants and display characteristics commonly observed in seed plants. More than 20,000 species of ferns live in environments ranging from tropics to temperate forests. Although some species survive in dry environments, most ferns are restricted to moist, shaded places. Ferns made their appearance in the fossil record during the Devonian period and expanded during the Carboniferous.
The dominant stage of the lifecycle of a fern is the sporophyte, which consists of large compound leaves called fronds. Fronds fulfill a double role; they are photosynthetic organs that also carry reproductive organs. The stem may be buried underground as a rhizome, from which adventitious roots grow to absorb water and nutrients from the soil; or, they may grow above ground as a trunk in tree ferns ( [link] ). Adventitious organs are those that grow in unusual places, such as roots growing from the side of a stem.

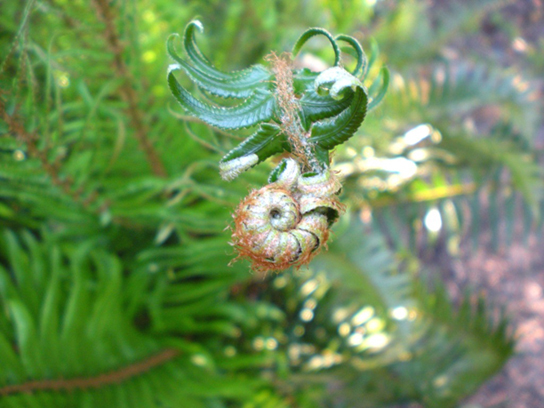
The tip of a developing fern frond is rolled into a crozier, or fiddlehead ( [link] a and [link] b ). Fiddleheads unroll as the frond develops.


The lifecycle of a fern is depicted in [link] .
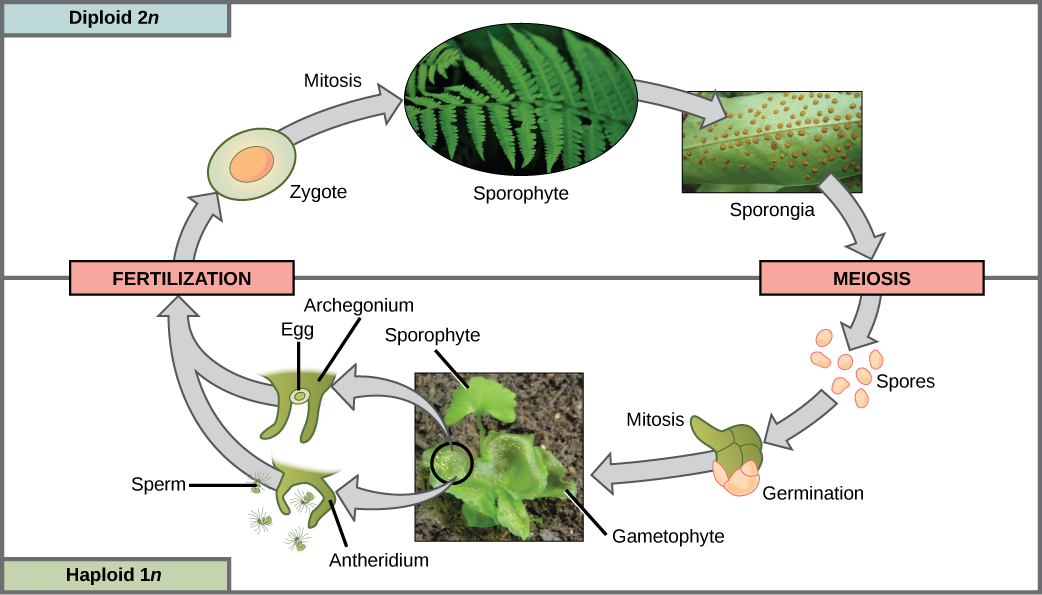
Which of the following statements about the fern life cycle is false?
To see an animation of the lifecycle of a fern and to test your knowledge, go to the website .
Most ferns produce the same type of spores and are therefore homosporous. The diploid sporophyte is the most conspicuous stage of the lifecycle. On the underside of its mature fronds, sori (singular, sorus) form as small clusters where sporangia develop ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?