| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In classical conditioning , a response called the conditioned response is associated with a stimulus that it had previously not been associated with, the conditioned stimulus. The response to the original, unconditioned stimulus is called the unconditioned response. The most cited example of classical conditioning is Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs ( [link] ). In Pavlov’s experiments, the unconditioned response was the salivation of dogs in response to the unconditioned stimulus of seeing or smelling their food. The conditioning stimulus that researchers associated with the unconditioned response was the ringing of a bell. During conditioning, every time the animal was given food, the bell was rung. This was repeated during several trials. After some time, the dog learned to associate the ringing of the bell with food and to respond by salivating. After the conditioning period was finished, the dog would respond by salivating when the bell was rung, even when the unconditioned stimulus, the food, was absent. Thus, the ringing of the bell became the conditioned stimulus and the salivation became the conditioned response. Although it is thought by some scientists that the unconditioned and conditioned responses are identical, even Pavlov discovered that the saliva in the conditioned dogs had characteristic differences when compared to the unconditioned dog.
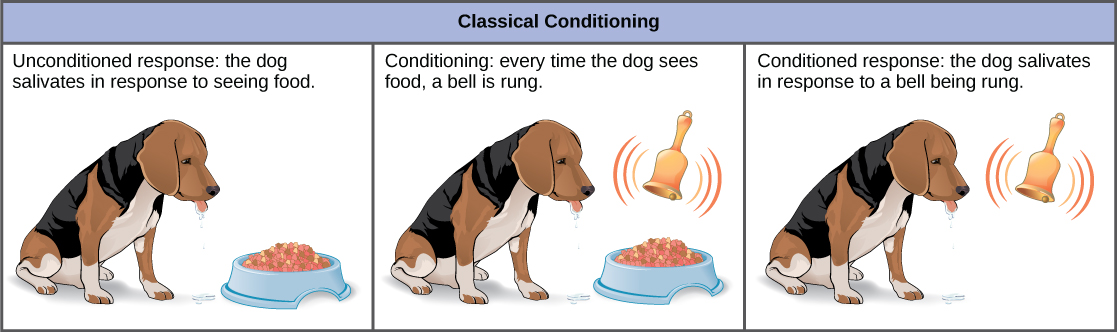
It had been thought by some scientists that this type of conditioning required multiple exposures to the paired stimulus and response, but it is now known that this is not necessary in all cases, and that some conditioning can be learned in a single pairing experiment. Classical conditioning is a major tenet of behaviorism, a branch of psychological philosophy that proposes that all actions, thoughts, and emotions of living things are behaviors that can be treated by behavior modification and changes in the environment.
In operant conditioning , the conditioned behavior is gradually modified by its consequences as the animal responds to the stimulus. A major proponent of such conditioning was psychologist B.F. Skinner, the inventor of the Skinner box. Skinner put rats in his boxes that contained a lever that would dispense food to the rat when depressed. While initially the rat would push the lever a few times by accident, it eventually associated pushing the lever with getting the food. This type of learning is an example of operant conditioning. Operant learning is the basis of most animal training. The conditioned behavior is continually modified by positive or negative reinforcement, often a reward such as food or some type of punishment, respectively. In this way, the animal is conditioned to associate a type of behavior with the punishment or reward, and, over time, can be induced to perform behaviors that they would not have done in the wild, such as the “tricks” dolphins perform at marine amusement park shows ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?