| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are called oils. If there is one double bond in the molecule, then it is known as a monounsaturated fat (e.g., olive oil), and if there is more than one double bond, then it is known as a polyunsaturated fat (e.g., canola oil).
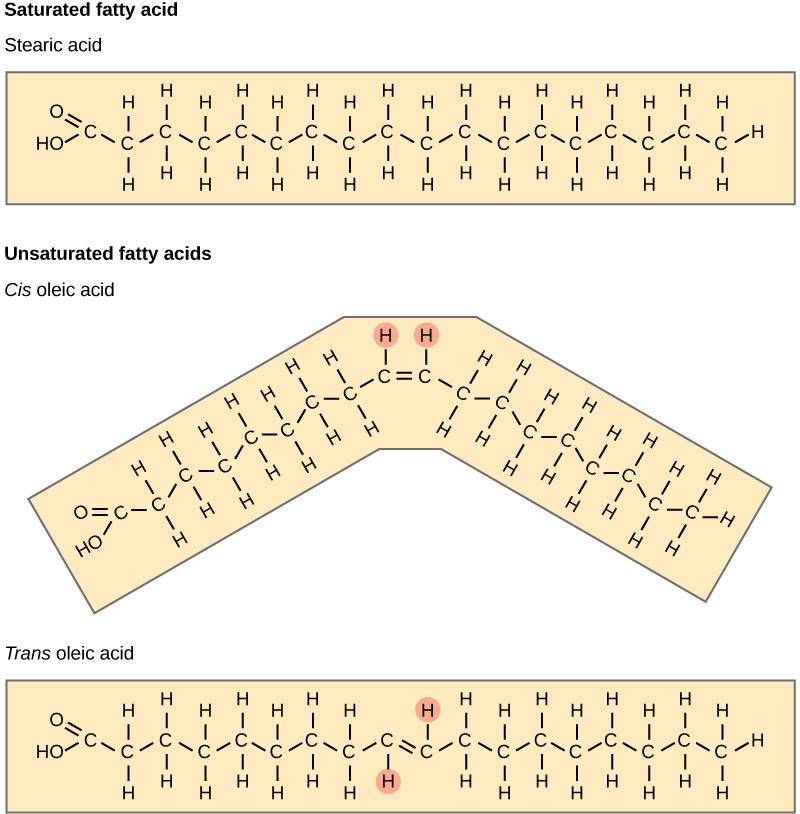
When a fatty acid has no double bonds, it is known as a saturated fatty acid because no more hydrogen may be added to the carbon atoms of the chain. A fat may contain similar or different fatty acids attached to glycerol. Long straight fatty acids with single bonds tend to get packed tightly and are solid at room temperature. Animal fats with stearic acid and palmitic acid (common in meat) and the fat with butyric acid (common in butter) are examples of saturated fats. Mammals store fats in specialized cells called adipocytes, where globules of fat occupy most of the cell’s volume. In plants, fat or oil is stored in many seeds and is used as a source of energy during seedling development. Unsaturated fats or oils are usually of plant origin and contain cis unsaturated fatty acids. Cis and trans indicate the configuration of the molecule around the double bond. If hydrogens are present in the same plane, it is referred to as a cis fat; if the hydrogen atoms are on two different planes, it is referred to as a trans fat . The cis double bond causes a bend or a “kink” that prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly, keeping them liquid at room temperature ( [link] ). Olive oil, corn oil, canola oil, and cod liver oil are examples of unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats help to lower blood cholesterol levels whereas saturated fats contribute to plaque formation in the arteries.
In the food industry, oils are artificially hydrogenated to make them semi-solid and of a consistency desirable for many processed food products. Simply speaking, hydrogen gas is bubbled through oils to solidify them. During this hydrogenation process, double bonds of the cis - conformation in the hydrocarbon chain may be converted to double bonds in the trans- conformation.
Margarine, some types of peanut butter, and shortening are examples of artificially hydrogenated trans fats. Recent studies have shown that an increase in trans fats in the human diet may lead to an increase in levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol, which in turn may lead to plaque deposition in the arteries, resulting in heart disease. Many fast food restaurants have recently banned the use of trans fats, and food labels are required to display the trans fat content.
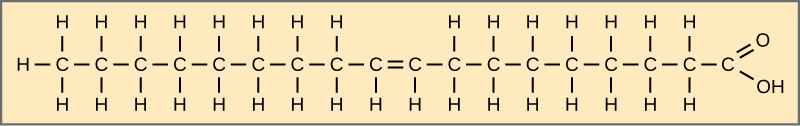
Essential fatty acids are fatty acids required but not synthesized by the human body. Consequently, they have to be supplemented through ingestion via the diet. Omega -3 fatty acids (like that shown in [link] ) fall into this category and are one of only two known for humans (the other being omega-6 fatty acid). These are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are called omega-3 because the third carbon from the end of the hydrocarbon chain is connected to its neighboring carbon by a double bond.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?