| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
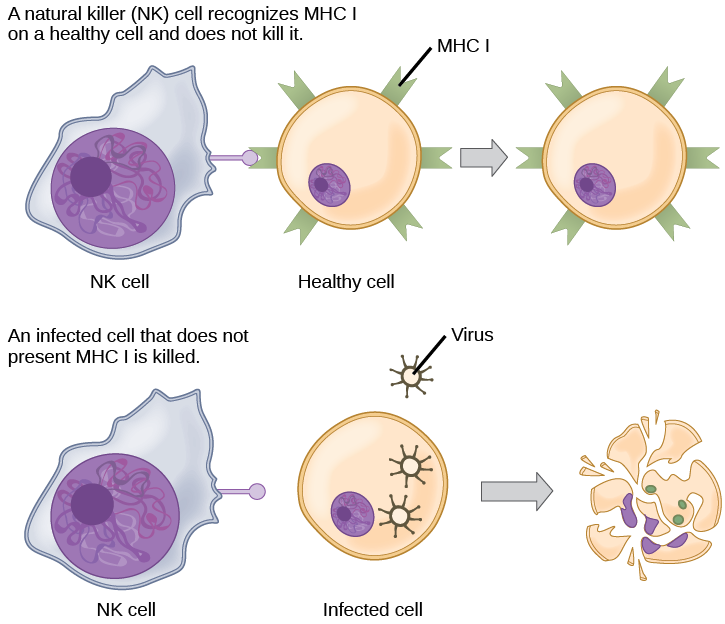
Based on what you know about MHC receptors, why do you think an organ transplanted from an incompatible donor to a recipient will be rejected?
Plasma cells and CTLs are collectively called effector cells : they represent differentiated versions of their naïve counterparts, and they are involved in bringing about the immune defense of killing pathogens and infected host cells.
The innate and adaptive immune responses discussed thus far comprise the systemic immune system (affecting the whole body), which is distinct from the mucosal immune system. Mucosal immunity is formed by mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, which functions independently of the systemic immune system, and which has its own innate and adaptive components. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) , illustrated in [link] , is a collection of lymphatic tissue that combines with epithelial tissue lining the mucosa throughout the body. This tissue functions as the immune barrier and response in areas of the body with direct contact to the external environment. The systemic and mucosal immune systems use many of the same cell types. Foreign particles that make their way to MALT are taken up by absorptive epithelial cells called M cells and delivered to APCs located directly below the mucosal tissue. M cells function in the transport described, and are located in the Peyer’s patch, a lymphoid nodule. APCs of the mucosal immune system are primarily dendritic cells, with B cells and macrophages having minor roles. Processed antigens displayed on APCs are detected by T cells in the MALT and at various mucosal induction sites, such as the tonsils, adenoids, appendix, or the mesenteric lymph nodes of the intestine. Activated T cells then migrate through the lymphatic system and into the circulatory system to mucosal sites of infection.
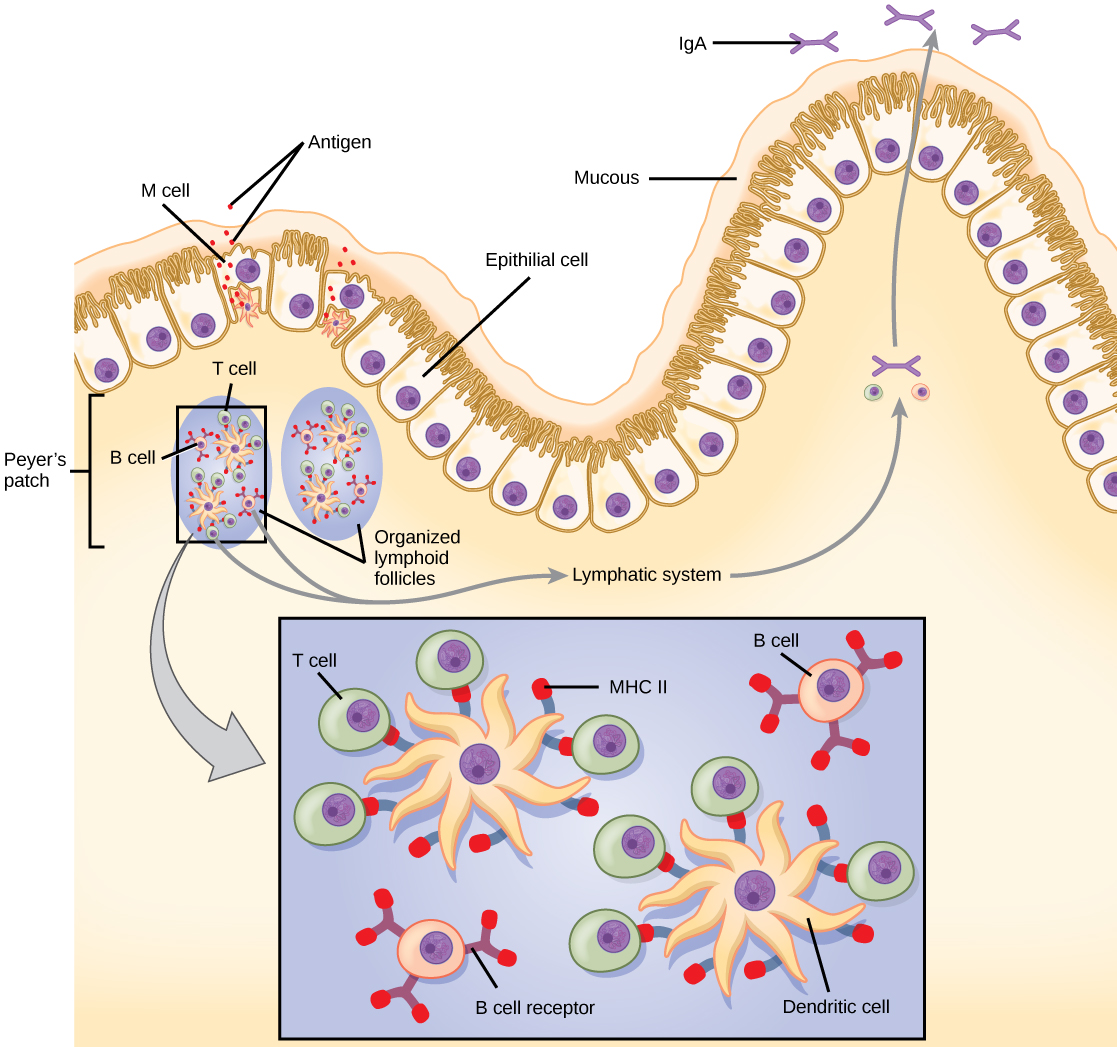
MALT is a crucial component of a functional immune system because mucosal surfaces, such as the nasal passages, are the first tissues onto which inhaled or ingested pathogens are deposited. The mucosal tissue includes the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus, and the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and urogenital tracts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?