| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Pregnancy begins with the fertilization of an egg and continues through to the birth of the individual. The length of time of gestation varies among animals, but is very similar among the great apes: human gestation is 266 days, while chimpanzee gestation is 237 days, a gorilla’s is 257 days, and orangutan gestation is 260 days long. The fox has a 57-day gestation. Dogs and cats have similar gestations averaging 60 days. The longest gestation for a land mammal is an African elephant at 640 days. The longest gestations among marine mammals are the beluga and sperm whales at 460 days.
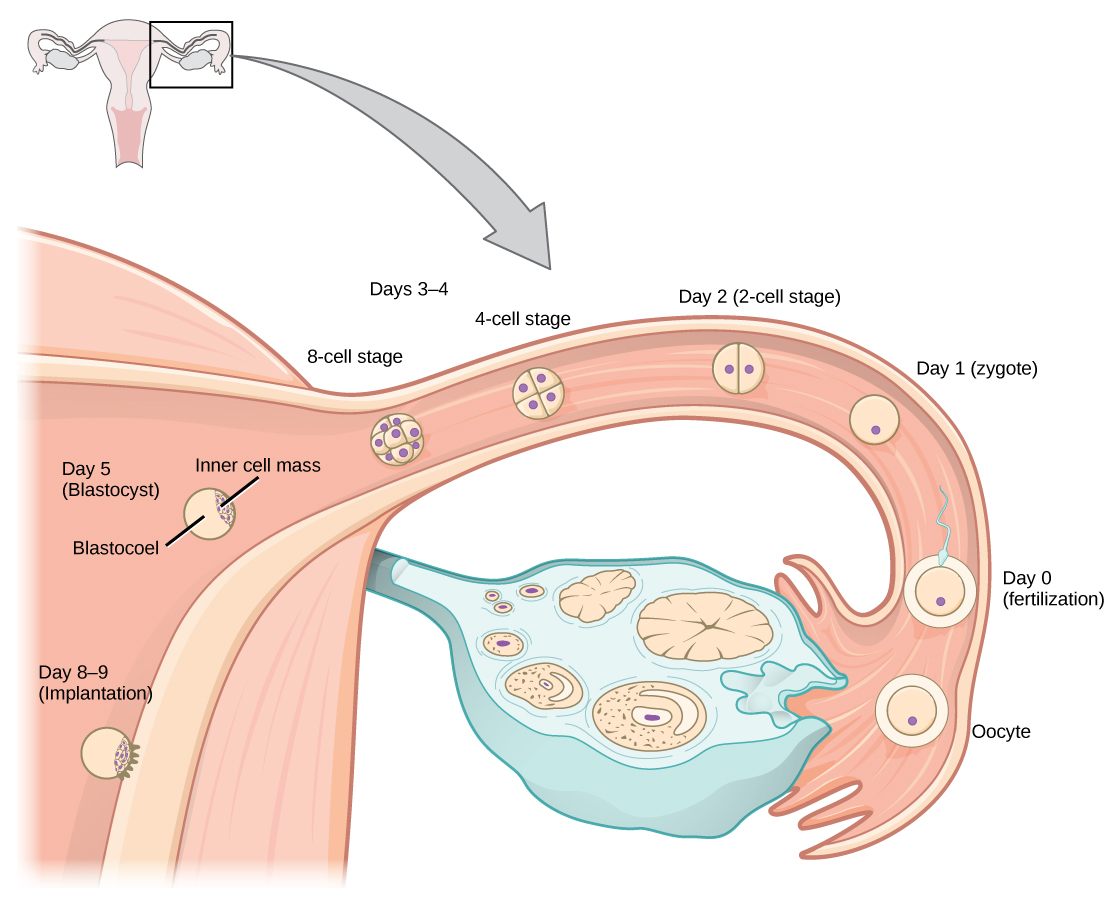
Twenty-four hours before fertilization, the egg has finished meiosis and becomes a mature oocyte. When fertilized (at conception) the egg becomes known as a zygote. The zygote travels through the oviduct to the uterus ( [link] ). The developing embryo must implant into the wall of the uterus within seven days, or it will deteriorate and die. The outer layers of the zygote (blastocyst) grow into the endometrium by digesting the endometrial cells, and wound healing of the endometrium closes up the blastocyst into the tissue. Another layer of the blastocyst, the chorion, begins releasing a hormone called human beta chorionic gonadotropin ( β -HCG) which makes its way to the corpus luteum and keeps that structure active. This ensures adequate levels of progesterone that will maintain the endometrium of the uterus for the support of the developing embryo. Pregnancy tests determine the level of β -HCG in urine or serum. If the hormone is present, the test is positive.
The gestation period is divided into three equal periods or trimesters. During the first two to four weeks of the first trimester, nutrition and waste are handled by the endometrial lining through diffusion. As the trimester progresses, the outer layer of the embryo begins to merge with the endometrium, and the placenta forms. This organ takes over the nutrient and waste requirements of the embryo and fetus, with the mother’s blood passing nutrients to the placenta and removing waste from it. Chemicals from the fetus, such as bilirubin, are processed by the mother’s liver for elimination. Some of the mother’s immunoglobulins will pass through the placenta, providing passive immunity against some potential infections.
Internal organs and body structures begin to develop during the first trimester. By five weeks, limb buds, eyes, the heart, and liver have been basically formed. By eight weeks, the term fetus applies, and the body is essentially formed, as shown in [link] . The individual is about five centimeters (two inches) in length and many of the organs, such as the lungs and liver, are not yet functioning. Exposure to any toxins is especially dangerous during the first trimester, as all of the body’s organs and structures are going through initial development. Anything that affects that development can have a severe effect on the fetus’ survival.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?