| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

The human skeleton is an endoskeleton that consists of 206 bones in the adult. It has five main functions: providing support to the body, storing minerals and lipids, producing blood cells, protecting internal organs, and allowing for movement. The skeletal system in vertebrates is divided into the axial skeleton (which consists of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage), and the appendicular skeleton (which consists of the shoulders, limb bones, the pectoral girdle, and the pelvic girdle).
Visit the interactive body site to build a virtual skeleton: select "skeleton" and click through the activity to place each bone.
The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body and includes the bones of the skull, ossicles of the middle ear, hyoid bone of the throat, vertebral column, and the thoracic cage (ribcage) ( [link] ). The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain, the spinal cord, and the organs in the ventral body cavity. It provides a surface for the attachment of muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk, performs respiratory movements, and stabilizes parts of the appendicular skeleton.
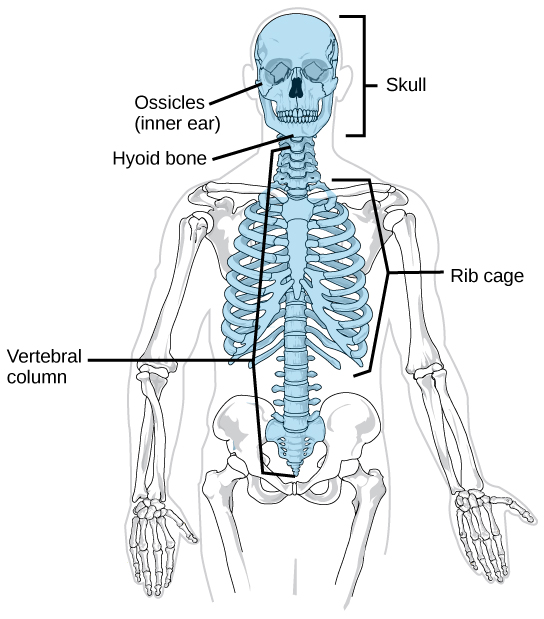
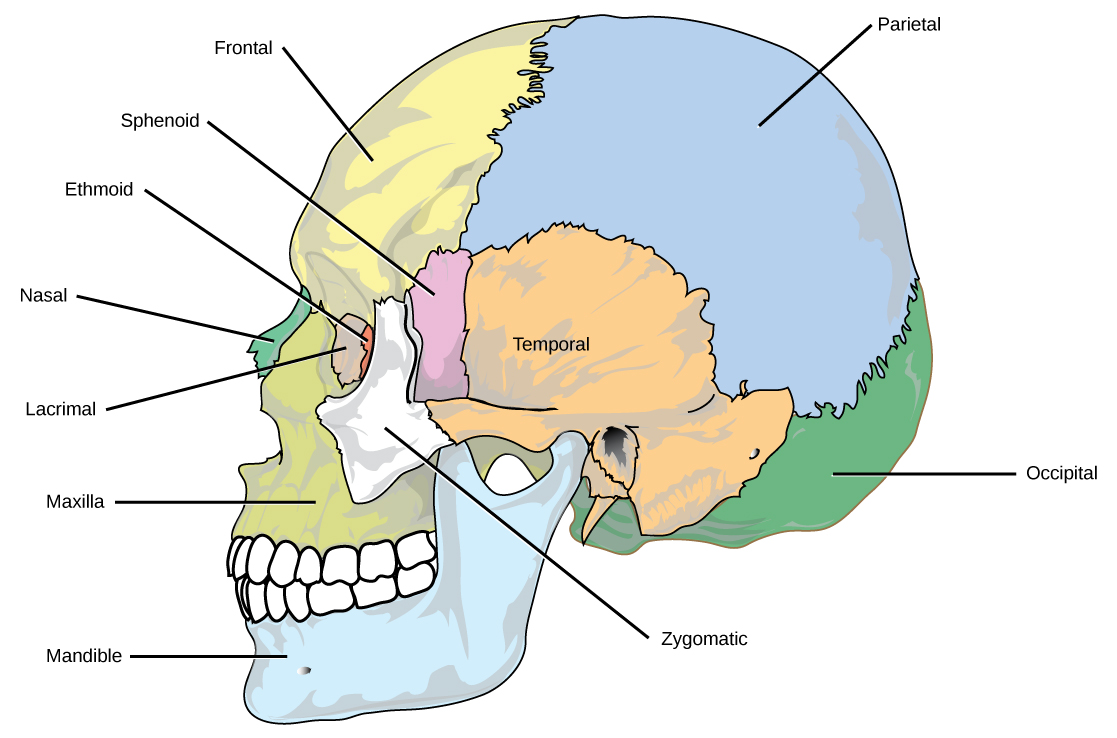
The bones of the skull support the structures of the face and protect the brain. The skull consists of 22 bones, which are divided into two categories: cranial bones and facial bones. The cranial bones are eight bones that form the cranial cavity, which encloses the brain and serves as an attachment site for the muscles of the head and neck. The eight cranial bones are the frontal bone, two parietal bones, two temporal bones, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, and the ethmoid bone. Although the bones developed separately in the embryo and fetus, in the adult, they are tightly fused with connective tissue and adjoining bones do not move ( [link] ).
The auditory ossicles of the middle ear transmit sounds from the air as vibrations to the fluid-filled cochlea. The auditory ossicles consist of six bones: two malleus bones, two incus bones, and two stapes on each side. These are the smallest bones in the body and are unique to mammals.
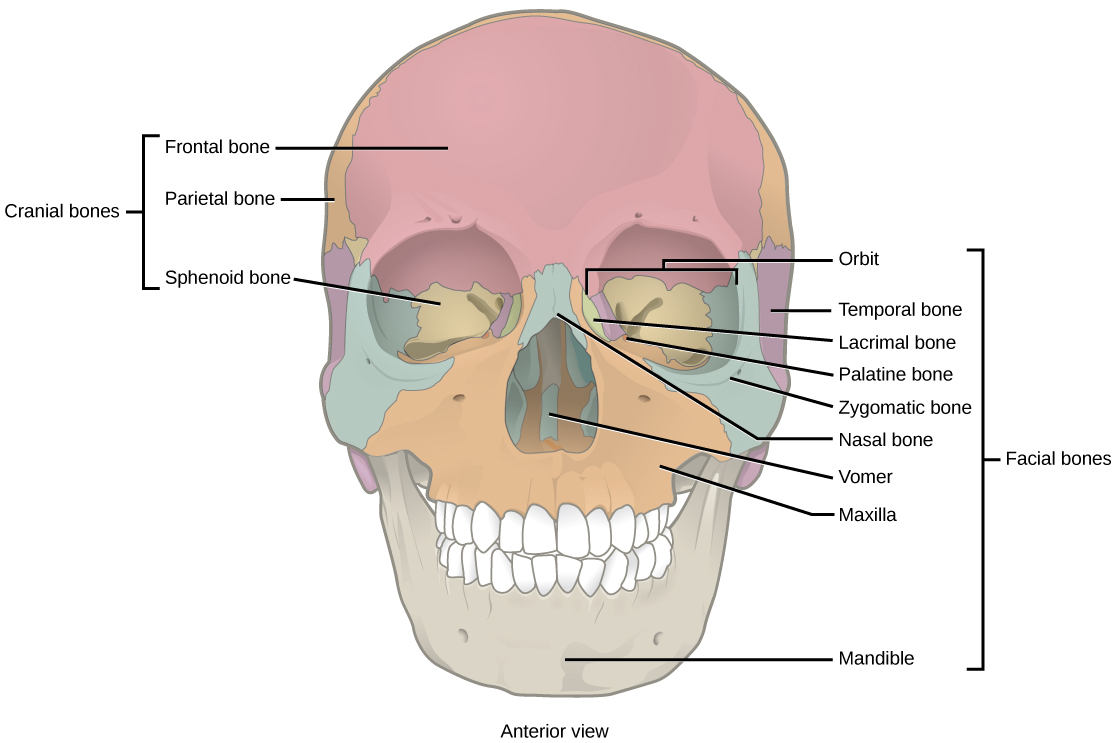
Fourteen facial bones form the face, provide cavities for the sense organs (eyes, mouth, and nose), protect the entrances to the digestive and respiratory tracts, and serve as attachment points for facial muscles. The 14 facial bones are the nasal bones, the maxillary bones, zygomatic bones, palatine, vomer, lacrimal bones, the inferior nasal conchae, and the mandible. All of these bones occur in pairs except for the mandible and the vomer ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?