| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The law of independent assortment also indicates that a cross between yellow, wrinkled ( YYrr ) and green, round ( yyRR ) parents would yield the same F 1 and F 2 offspring as in the YYRR x yyrr cross.
The physical basis for the law of independent assortment also lies in meiosis I, in which the different homologous pairs line up in random orientations. Each gamete can contain any combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes (and therefore the genes on them) because the orientation of tetrads on the metaphase plane is random.
When more than two genes are being considered, the Punnett-square method becomes unwieldy. For instance, examining a cross involving four genes would require a 16 × 16 grid containing 256 boxes. It would be extremely cumbersome to manually enter each genotype. For more complex crosses, the forked-line and probability methods are preferred.
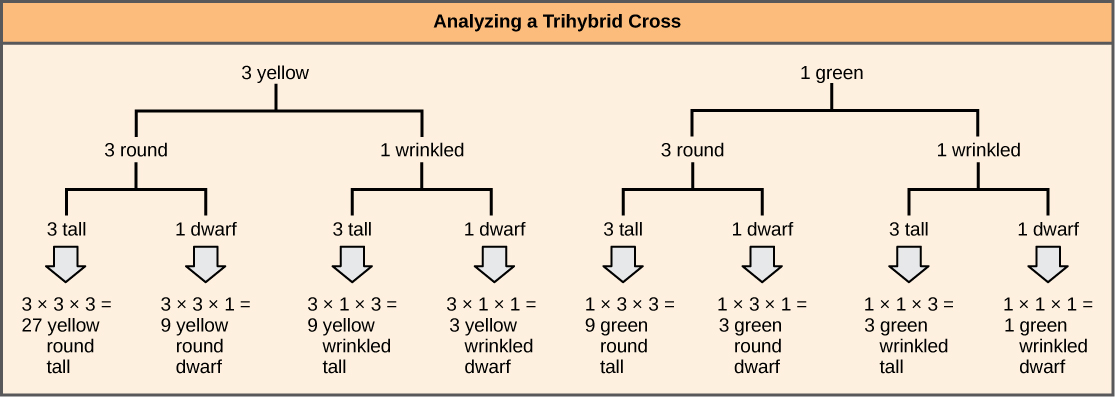
To prepare a forked-line diagram for a cross between F 1 heterozygotes resulting from a cross between AABBCC and aabbcc parents, we first create rows equal to the number of genes being considered, and then segregate the alleles in each row on forked lines according to the probabilities for individual monohybrid crosses ( [link] ). We then multiply the values along each forked path to obtain the F 2 offspring probabilities. Note that this process is a diagrammatic version of the product rule. The values along each forked pathway can be multiplied because each gene assorts independently. For a trihybrid cross, the F 2 phenotypic ratio is 27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1.
While the forked-line method is a diagrammatic approach to keeping track of probabilities in a cross, the probability method gives the proportions of offspring expected to exhibit each phenotype (or genotype) without the added visual assistance. Both methods make use of the product rule and consider the alleles for each gene separately. Earlier, we examined the phenotypic proportions for a trihybrid cross using the forked-line method; now we will use the probability method to examine the genotypic proportions for a cross with even more genes.
For a trihybrid cross, writing out the forked-line method is tedious, albeit not as tedious as using the Punnett-square method. To fully demonstrate the power of the probability method, however, we can consider specific genetic calculations. For instance, for a tetrahybrid cross between individuals that are heterozygotes for all four genes, and in which all four genes are sorting independently and in a dominant and recessive pattern, what proportion of the offspring will be expected to be homozygous recessive for all four alleles? Rather than writing out every possible genotype, we can use the probability method. We know that for each gene, the fraction of homozygous recessive offspring will be 1/4. Therefore, multiplying this fraction for each of the four genes, (1/4) × (1/4) × (1/4) × (1/4), we determine that 1/256 of the offspring will be quadruply homozygous recessive.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?