| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
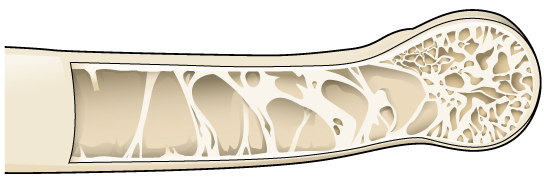
Other modifications that reduce weight include the lack of a urinary bladder. Birds possess a cloaca, a structure that allows water to be reabsorbed from waste back into the bloodstream. Uric acid is not expelled as a liquid but is concentrated into urate salts, which are expelled along with fecal matter. In this way, water is not held in the urinary bladder, which would increase body weight. Most bird species only possess one ovary rather than two, further reducing body mass.
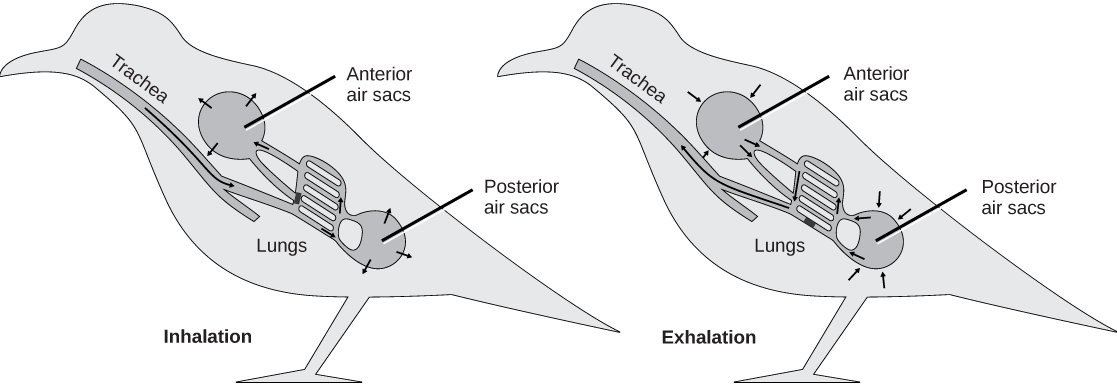
The air sacs that extend into bones to form pneumatic bones also join with the lungs and function in respiration. Unlike mammalian lungs in which air flows in two directions, as it is breathed in and out, airflow through bird lungs travels in one direction ( [link] ). Air sacs allow for this unidirectional airflow, which also creates a cross-current exchange system with the blood. In a cross-current or counter-current system, the air flows in one direction and the blood flows in the opposite direction, creating a very efficient means of gas exchange.
The evolutionary history of birds is still somewhat unclear. Due to the fragility of bird bones, they do not fossilize as well as other vertebrates. Birds are diapsids, meaning they have two fenestrations or openings in their skulls. Birds belong to a group of diapsids called the archosaurs, which also includes crocodiles and dinosaurs. It is commonly accepted that birds evolved from dinosaurs.
Dinosaurs (including birds) are further subdivided into two groups, the Saurischia (“lizard like”) and the Ornithischia (“bird like”). Despite the names of these groups, it was not the bird-like dinosaurs that gave rise to modern birds. Rather, Saurischia diverged into two groups: One included the long-necked herbivorous dinosaurs, such as Apatosaurus. The second group, bipedal predators called theropods , includes birds. This course of evolution is suggested by similarities between theropod fossils and birds, specifically in the structure of the hip and wrist bones, as well as the presence of the wishbone, formed by the fusing of the clavicles.
One important fossil of an animal intermediate to dinosaurs and birds is Archaeopteryx , which is from the Jurassic period ( [link] ). Archaeopteryx is important in establishing the relationship between birds and dinosaurs, because it is an intermediate fossil, meaning it has characteristics of both dinosaurs and birds. Some scientists propose classifying it as a bird, but others prefer to classify it as a dinosaur. The fossilized skeleton of Archaeopteryx looks like that of a dinosaur, and it had teeth whereas birds do not, but it also had feathers modified for flight, a trait associated only with birds among modern animals. Fossils of older feathered dinosaurs exist, but the feathers do not have the characteristics of flight feathers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?