| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
While electrical synapses are fewer in number than chemical synapses, they are found in all nervous systems and play important and unique roles. The mode of neurotransmission in electrical synapses is quite different from that in chemical synapses. In an electrical synapse, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are very close together and are actually physically connected by channel proteins forming gap junctions. Gap junctions allow current to pass directly from one cell to the next. In addition to the ions that carry this current, other molecules, such as ATP, can diffuse through the large gap junction pores.
There are key differences between chemical and electrical synapses. Because chemical synapses depend on the release of neurotransmitter molecules from synaptic vesicles to pass on their signal, there is an approximately one millisecond delay between when the axon potential reaches the presynaptic terminal and when the neurotransmitter leads to opening of postsynaptic ion channels. Additionally, this signaling is unidirectional. Signaling in electrical synapses, in contrast, is virtually instantaneous (which is important for synapses involved in key reflexes), and some electrical synapses are bidirectional. Electrical synapses are also more reliable as they are less likely to be blocked, and they are important for synchronizing the electrical activity of a group of neurons. For example, electrical synapses in the thalamus are thought to regulate slow-wave sleep, and disruption of these synapses can cause seizures.
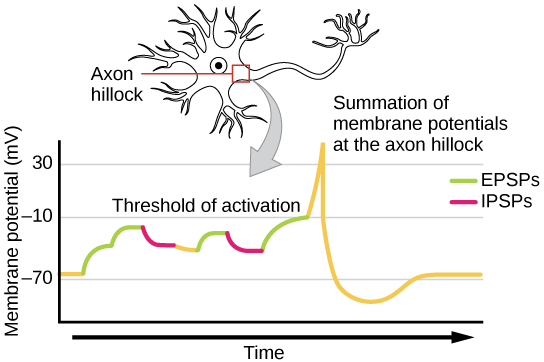
Sometimes a single EPSP is strong enough to induce an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron, but often multiple presynaptic inputs must create EPSPs around the same time for the postsynaptic neuron to be sufficiently depolarized to fire an action potential. This process is called summation and occurs at the axon hillock, as illustrated in [link] . Additionally, one neuron often has inputs from many presynaptic neurons—some excitatory and some inhibitory—so IPSPs can cancel out EPSPs and vice versa. It is the net change in postsynaptic membrane voltage that determines whether the postsynaptic cell has reached its threshold of excitation needed to fire an action potential. Together, synaptic summation and the threshold for excitation act as a filter so that random “noise” in the system is not transmitted as important information.
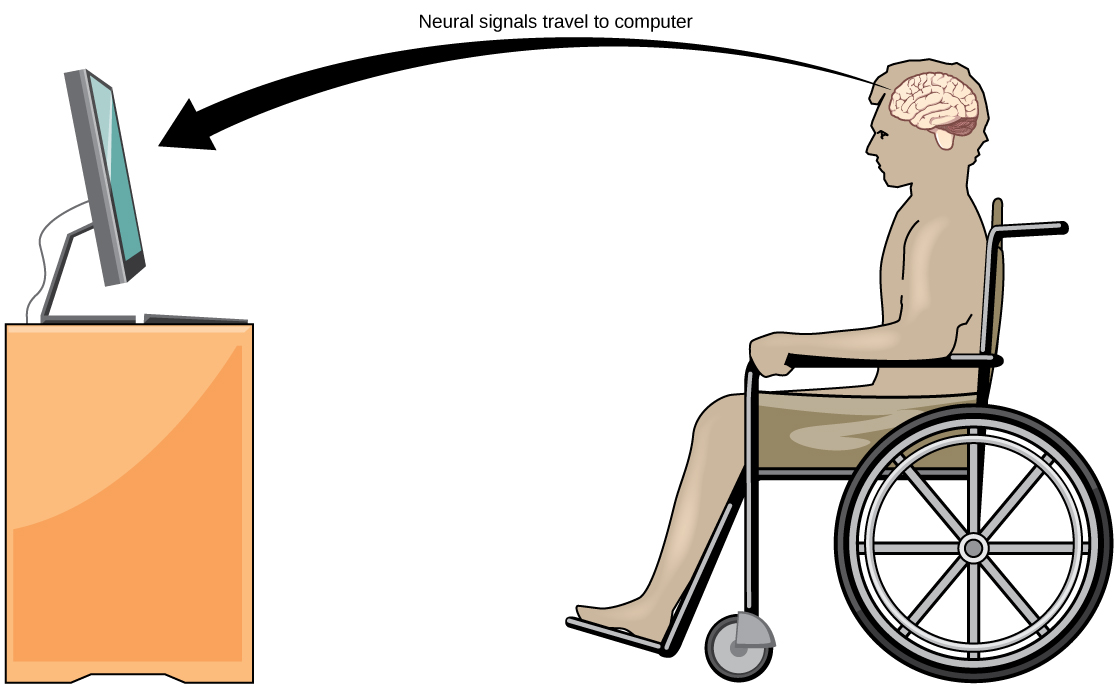
A relatively new line of research for helping paralyzed patients, including those with ALS, to communicate and retain a degree of self-sufficiency is called brain-computer interface (BCI) technology and is illustrated in [link] . This technology sounds like something out of science fiction: it allows paralyzed patients to control a computer using only their thoughts. There are several forms of BCI. Some forms use EEG recordings from electrodes taped onto the skull. These recordings contain information from large populations of neurons that can be decoded by a computer. Other forms of BCI require the implantation of an array of electrodes smaller than a postage stamp in the arm and hand area of the motor cortex. This form of BCI, while more invasive, is very powerful as each electrode can record actual action potentials from one or more neurons. These signals are then sent to a computer, which has been trained to decode the signal and feed it to a tool—such as a cursor on a computer screen. This means that a patient with ALS can use e-mail, read the Internet, and communicate with others by thinking of moving his or her hand or arm (even though the paralyzed patient cannot make that bodily movement). Recent advances have allowed a paralyzed locked-in patient who suffered a stroke 15 years ago to control a robotic arm and even to feed herself coffee using BCI technology.
Despite the amazing advancements in BCI technology, it also has limitations. The technology can require many hours of training and long periods of intense concentration for the patient; it can also require brain surgery to implant the devices.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?