| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
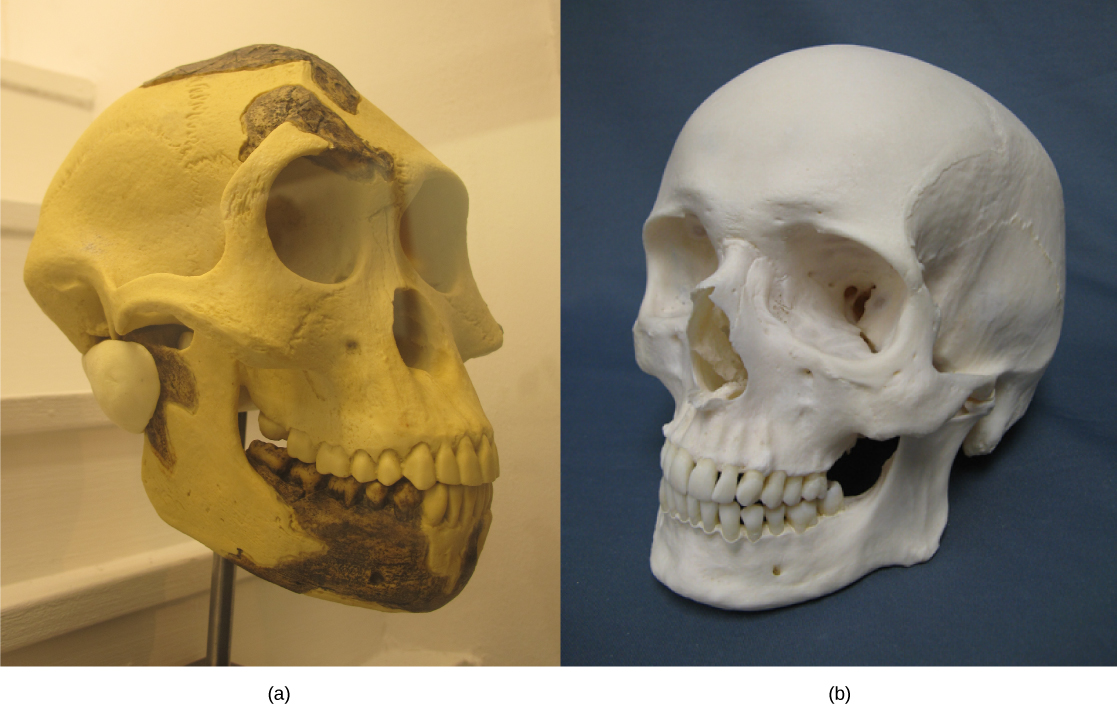
Australopithecus africanus lived between 2 and 3 million years ago. It had a slender build and was bipedal, but had robust arm bones and, like other early hominids, may have spent significant time in trees. Its brain was larger than that of A . afarensis at 500 cubic centimeters, which is slightly less than one-third the size of modern human brains. Two other species, Australopithecus bahrelghazali and Australopithecus garhi , have been added to the roster of australopiths in recent years.
The australopiths had a relatively slender build and teeth that were suited for soft food. In the past several years, fossils of hominids of a different body type have been found and dated to approximately 2.5 million years ago. These hominids, of the genus Paranthropus , were relatively large and had large grinding teeth. Their molars showed heavy wear, suggesting that they had a coarse and fibrous vegetarian diet as opposed to the partially carnivorous diet of the australopiths. Paranthropus includes Paranthropus robustus of South Africa, and Paranthropus aethiopicus and Paranthropus boisei of East Africa. The hominids in this genus went extinct more than 1 million years ago and are not thought to be ancestral to modern humans, but rather members of an evolutionary branch on the hominin tree that left no descendants.
The human genus, Homo , first appeared between 2.5 and 3 million years ago. For many years, fossils of a species called H . habilis were the oldest examples in the genus Homo , but in 2010, a new species called Homo gautengensis was discovered and may be older. Compared to A . africanus , H . habilis had a number of features more similar to modern humans. H . habilis had a jaw that was less prognathic than the australopiths and a larger brain, at 600–750 cubic centimeters. However, H . habilis retained some features of older hominin species, such as long arms. The name H . habilis means “handy man,” which is a reference to the stone tools that have been found with its remains.
Visit this site for a video about Smithsonian paleontologist Briana Pobiner explaining the link between hominin eating of meat and evolutionary trends.
H . erectus appeared approximately 1.8 million years ago ( [link] ). It is believed to have originated in East Africa and was the first hominin species to migrate out of Africa. Fossils of H . erectus have been found in India, China, Java, and Europe, and were known in the past as “Java Man” or “Peking Man.” H . erectus had a number of features that were more similar to modern humans than those of H . habilis . H . erectus was larger in size than earlier hominins, reaching heights up to 1.85 meters and weighing up to 65 kilograms, which are sizes similar to those of modern humans. Its degree of sexual dimorphism was less than earlier species, with males being 20 to 30 percent larger than females, which is close to the size difference seen in our species. H . erectus had a larger brain than earlier species at 775–1,100 cubic centimeters, which compares to the 1,130–1,260 cubic centimeters seen in modern human brains. H . erectus also had a nose with downward-facing nostrils similar to modern humans, rather than the forward facing nostrils found in other primates. Longer, downward-facing nostrils allow for the warming of cold air before it enters the lungs and may have been an adaptation to colder climates. Artifacts found with fossils of H . erectus suggest that it was the first hominin to use fire, hunt, and have a home base. H . erectus is generally thought to have lived until about 50,000 years ago.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?