| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
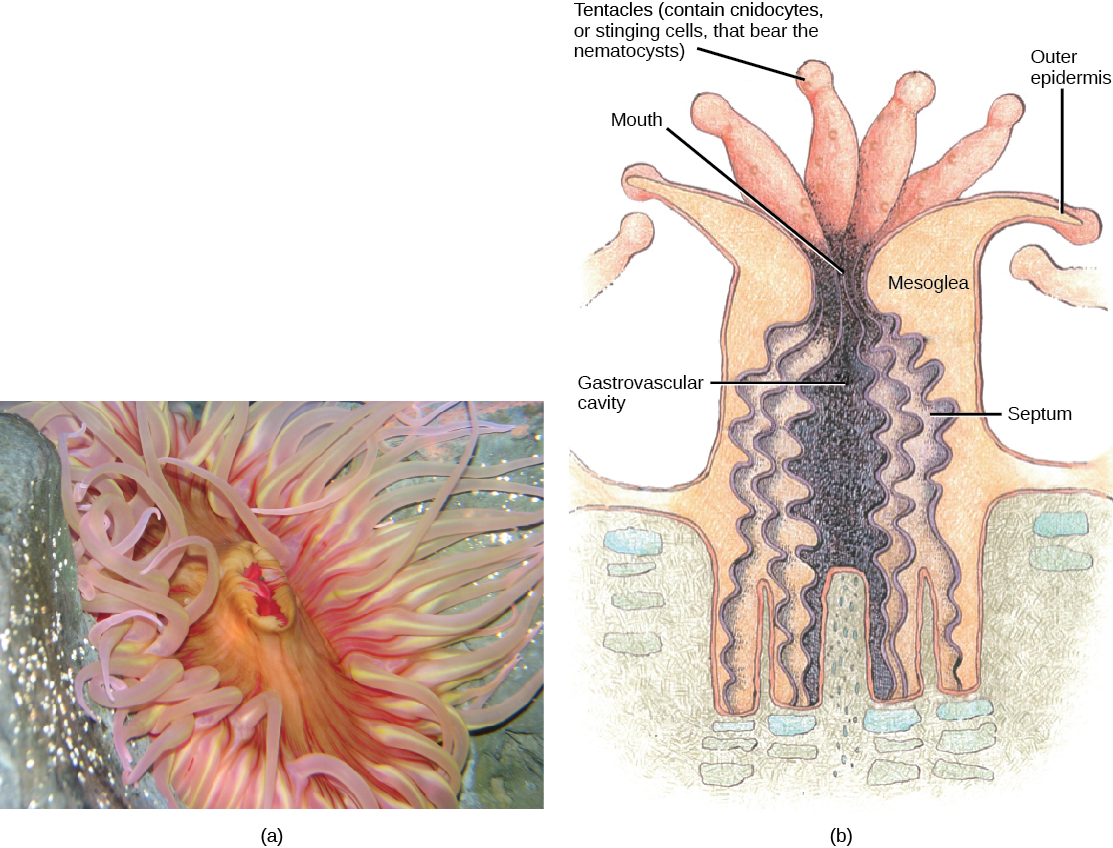
The mouth of a sea anemone is surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. The slit-like mouth opening and pharynx are lined by a groove called a siphonophore . The pharynx is the muscular part of the digestive system that serves to ingest as well as egest food, and may extend for up to two-thirds the length of the body before opening into the gastrovascular cavity. This cavity is divided into several chambers by longitudinal septa called mesenteries. Each mesentery consists of one ectodermal and one endodermal cell layer with the mesoglea sandwiched in between. Mesenteries do not divide the gastrovascular cavity completely, and the smaller cavities coalesce at the pharyngeal opening. The adaptive benefit of the mesenteries appears to be an increase in surface area for absorption of nutrients and gas exchange.
Sea anemones feed on small fish and shrimp, usually by immobilizing their prey using the cnidocytes. Some sea anemones establish a mutualistic relationship with hermit crabs by attaching to the crab’s shell. In this relationship, the anemone gets food particles from prey caught by the crab, and the crab is protected from the predators by the stinging cells of the anemone. Anemone fish, or clownfish, are able to live in the anemone since they are immune to the toxins contained within the nematocysts.
Anthozoans remain polypoid throughout their lives and can reproduce asexually by budding or fragmentation, or sexually by producing gametes. Both gametes are produced by the polyp, which can fuse to give rise to a free-swimming planula larva. The larva settles on a suitable substratum and develops into a sessile polyp.
Class Scyphozoa includes all the jellies and is exclusively a marine class of animals with about 200 known species. The defining characteristic of this class is that the medusa is the prominent stage in the life cycle, although there is a polyp stage present. Members of this species range from 2 to 40 cm in length but the largest scyphozoan species, Cyanea capillata , can reach a size of 2 m across. Scyphozoans display a characteristic bell-like morphology ( [link] ).
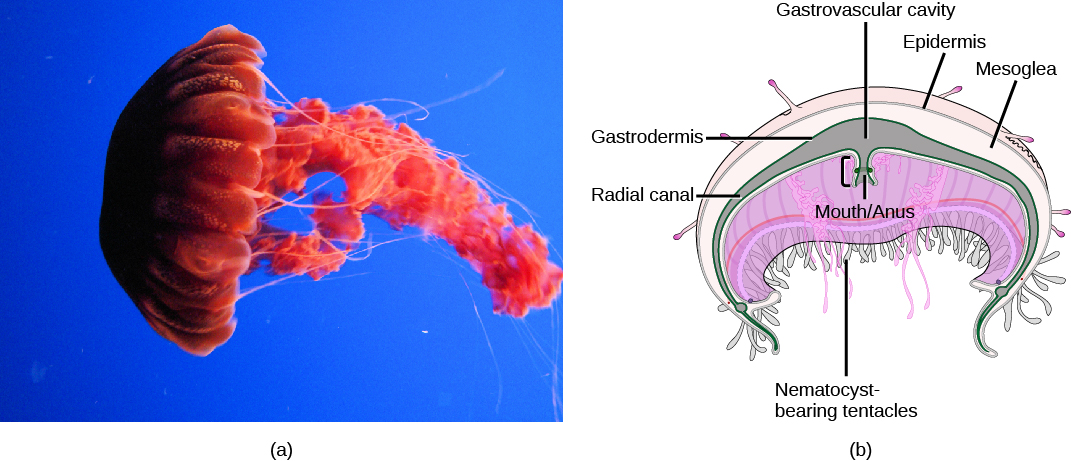
In the jellyfish, a mouth opening is present on the underside of the animal, surrounded by tentacles bearing nematocysts. Scyphozoans live most of their life cycle as free-swimming, solitary carnivores. The mouth leads to the gastrovascular cavity, which may be sectioned into four interconnected sacs, called diverticuli. In some species, the digestive system may be further branched into radial canals. Like the septa in anthozoans, the branched gastrovascular cells serve two functions: to increase the surface area for nutrient absorption and diffusion; thus, more cells are in direct contact with the nutrients in the gastrovascular cavity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?