| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This video presents an overview of action potential.
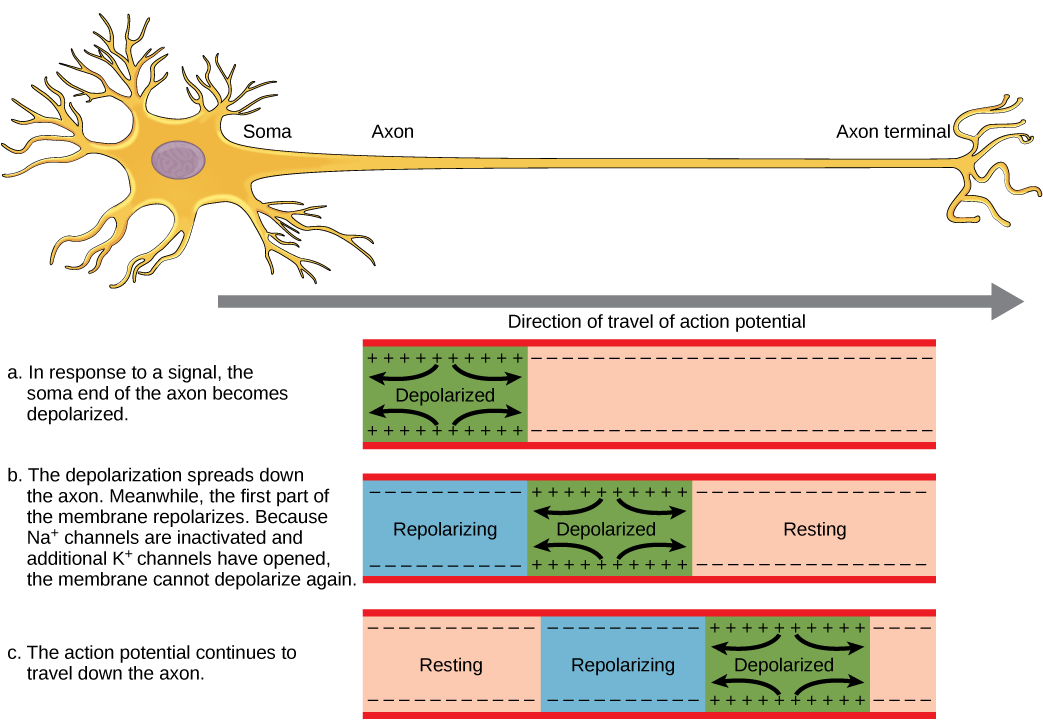
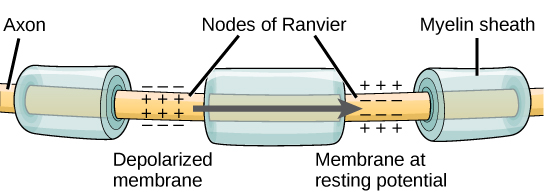
For an action potential to communicate information to another neuron, it must travel along the axon and reach the axon terminals where it can initiate neurotransmitter release. The speed of conduction of an action potential along an axon is influenced by both the diameter of the axon and the axon’s resistance to current leak. Myelin acts as an insulator that prevents current from leaving the axon; this increases the speed of action potential conduction. In demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis, action potential conduction slows because current leaks from previously insulated axon areas. The nodes of Ranvier, illustrated in [link] are gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon. These unmyelinated spaces are about one micrometer long and contain voltage gated Na + and K + channels. Flow of ions through these channels, particularly the Na + channels, regenerates the action potential over and over again along the axon. This ‘jumping’ of the action potential from one node to the next is called saltatory conduction . If nodes of Ranvier were not present along an axon, the action potential would propagate very slowly since Na + and K + channels would have to continuously regenerate action potentials at every point along the axon instead of at specific points. Nodes of Ranvier also save energy for the neuron since the channels only need to be present at the nodes and not along the entire axon.
The synapse or “gap” is the place where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. Synapses usually form between axon terminals and dendritic spines, but this is not universally true. There are also axon-to-axon, dendrite-to-dendrite, and axon-to-cell body synapses. The neuron transmitting the signal is called the presynaptic neuron, and the neuron receiving the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. Note that these designations are relative to a particular synapse—most neurons are both presynaptic and postsynaptic. There are two types of synapses: chemical and electrical.
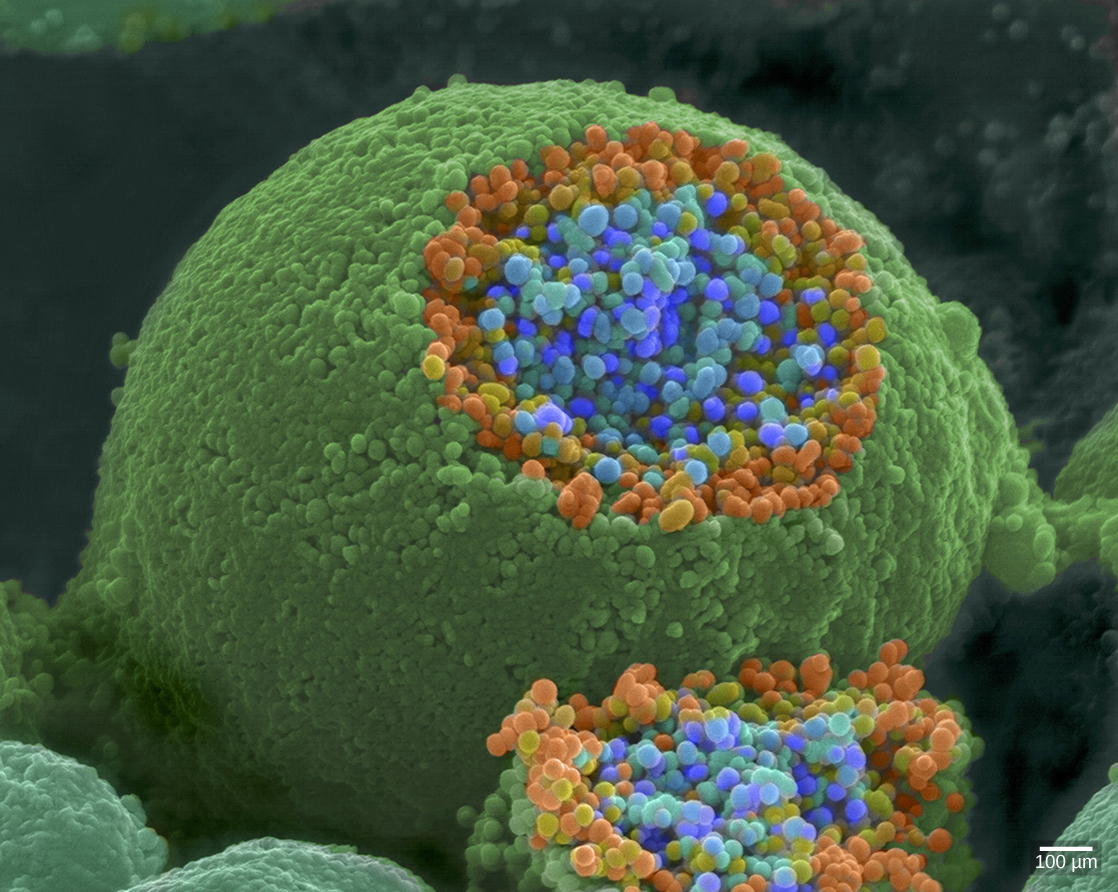
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal it depolarizes the membrane and opens voltage-gated Na + channels. Na + ions enter the cell, further depolarizing the presynaptic membrane. This depolarization causes voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels to open. Calcium ions entering the cell initiate a signaling cascade that causes small membrane-bound vesicles, called synaptic vesicles , containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse with the presynaptic membrane. Synaptic vesicles are shown in [link] , which is an image from a scanning electron microscope.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?