| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
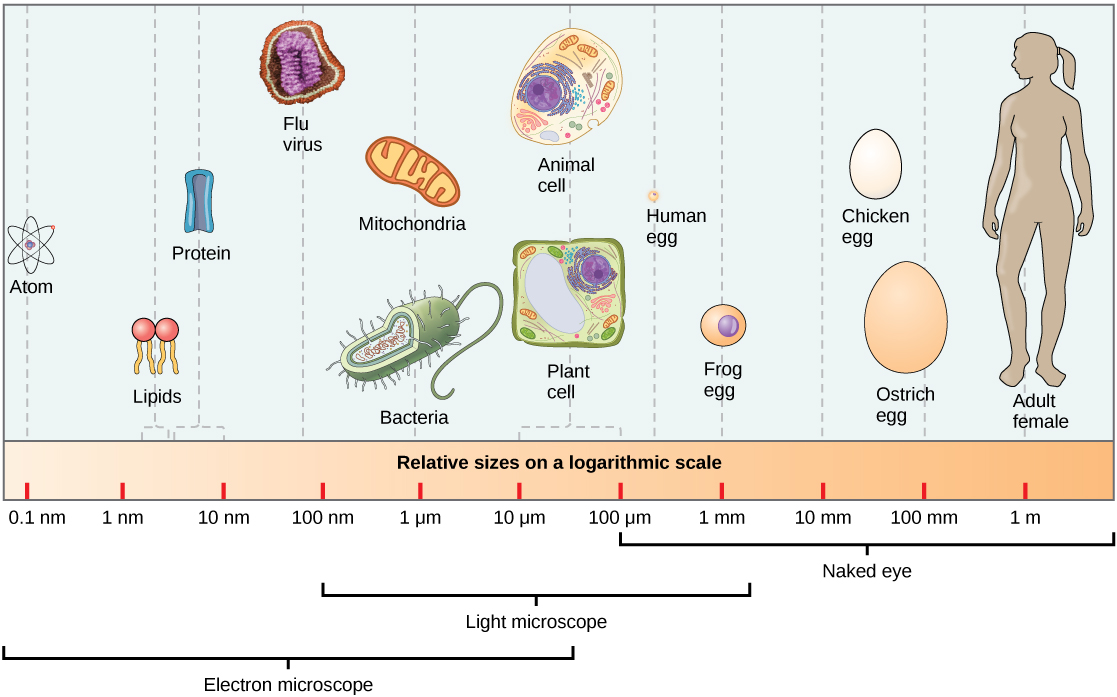
At 0.1 to 5.0 μm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm ( [link] ). The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly diffuse to other parts of the cell. Similarly, any wastes produced within a prokaryotic cell can quickly diffuse out. This is not the case in eukaryotic cells, which have developed different structural adaptations to enhance intracellular transport.
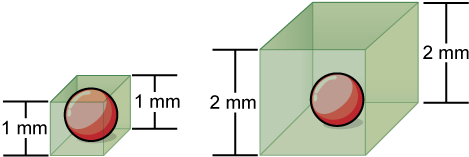
Small size, in general, is necessary for all cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Let’s examine why that is so. First, we’ll consider the area and volume of a typical cell. Not all cells are spherical in shape, but most tend to approximate a sphere. You may remember from your high school geometry course that the formula for the surface area of a sphere is 4πr 2 , while the formula for its volume is 4πr 3 /3. Thus, as the radius of a cell increases, its surface area increases as the square of its radius, but its volume increases as the cube of its radius (much more rapidly). Therefore, as a cell increases in size, its surface area-to-volume ratio decreases. This same principle would apply if the cell had the shape of a cube ( [link] ). If the cell grows too large, the plasma membrane will not have sufficient surface area to support the rate of diffusion required for the increased volume. In other words, as a cell grows, it becomes less efficient. One way to become more efficient is to divide; another way is to develop organelles that perform specific tasks. These adaptations lead to the development of more sophisticated cells called eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. What advantages might small cell size confer on a cell? What advantages might large cell size have?
Prokaryotes are predominantly single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA that is not membrane-bound. Most have peptidoglycan cell walls and many have polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1 to 5.0 μm.
As a cell increases in size, its surface area-to-volume ratio decreases. If the cell grows too large, the plasma membrane will not have sufficient surface area to support the rate of diffusion required for the increased volume.
[link] Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. What advantages might small cell size confer on a cell? What advantages might large cell size have?
[link] Substances can diffuse more quickly through small cells. Small cells have no need for organelles and therefore do not need to expend energy getting substances across organelle membranes. Large cells have organelles that can separate cellular processes, enabling them to build molecules that are more complex.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?