| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
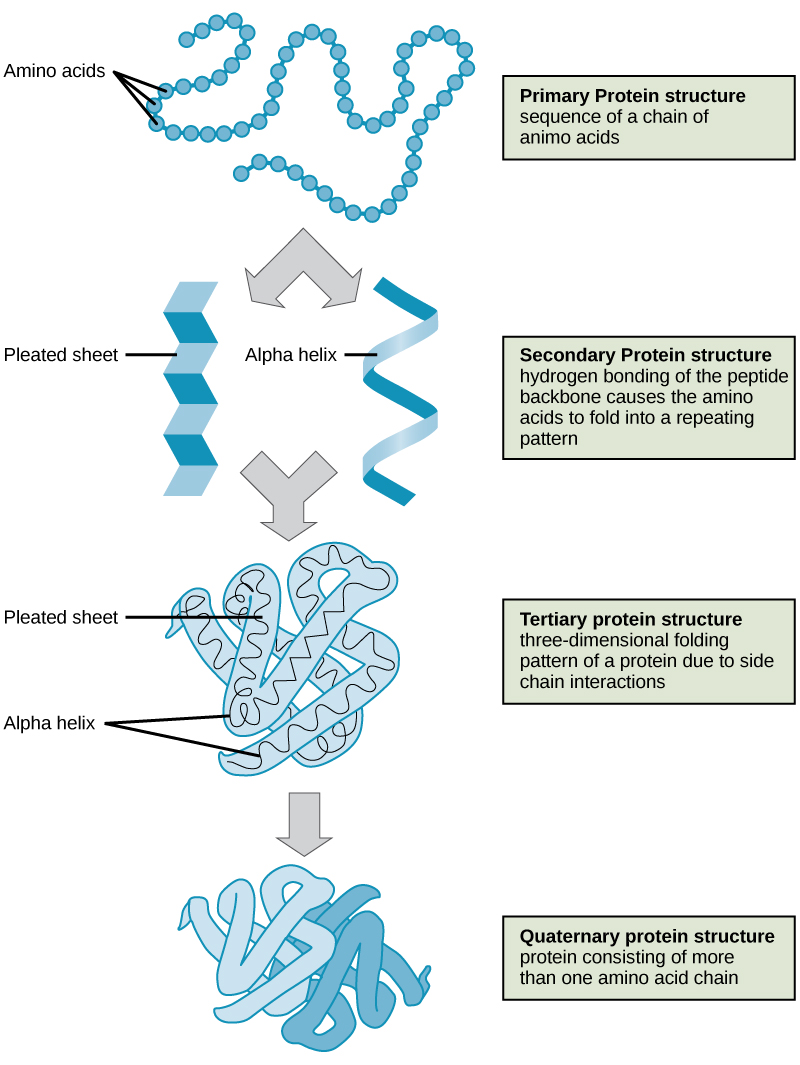
The four levels of protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) are illustrated in [link] .
Each protein has its own unique sequence and shape that are held together by chemical interactions. If the protein is subject to changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals, the protein structure may change, losing its shape without losing its primary sequence in what is known as denaturation. Denaturation is often reversible because the primary structure of the polypeptide is conserved in the process if the denaturing agent is removed, allowing the protein to resume its function. Sometimes denaturation is irreversible, leading to loss of function. One example of irreversible protein denaturation is when an egg is fried. The albumin protein in the liquid egg white is denatured when placed in a hot pan. Not all proteins are denatured at high temperatures; for instance, bacteria that survive in hot springs have proteins that function at temperatures close to boiling. The stomach is also very acidic, has a low pH, and denatures proteins as part of the digestion process; however, the digestive enzymes of the stomach retain their activity under these conditions.
Protein folding is critical to its function. It was originally thought that the proteins themselves were responsible for the folding process. Only recently was it found that often they receive assistance in the folding process from protein helpers known as chaperones (or chaperonins) that associate with the target protein during the folding process. They act by preventing aggregation of polypeptides that make up the complete protein structure, and they disassociate from the protein once the target protein is folded.
For an additional perspective on proteins, view this animation called “Biomolecules: The Proteins.”
Proteins are a class of macromolecules that perform a diverse range of functions for the cell. They help in metabolism by providing structural support and by acting as enzymes, carriers, or hormones. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. Each amino acid has a central carbon that is linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R group or side chain. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids, each of which differs in the R group. Each amino acid is linked to its neighbors by a peptide bond. A long chain of amino acids is known as a polypeptide.
Proteins are organized at four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and (optional) quaternary. The primary structure is the unique sequence of amino acids. The local folding of the polypeptide to form structures such as the α helix and β -pleated sheet constitutes the secondary structure. The overall three-dimensional structure is the tertiary structure. When two or more polypeptides combine to form the complete protein structure, the configuration is known as the quaternary structure of a protein. Protein shape and function are intricately linked; any change in shape caused by changes in temperature or pH may lead to protein denaturation and a loss in function.
[link] Which categories of amino acid would you expect to find on the surface of a soluble protein, and which would you expect to find in the interior? What distribution of amino acids would you expect to find in a protein embedded in a lipid bilayer?
[link] Polar and charged amino acid residues (the remainder after peptide bond formation) are more likely to be found on the surface of soluble proteins where they can interact with water, and nonpolar (e.g., amino acid side chains) are more likely to be found in the interior where they are sequestered from water. In membrane proteins, nonpolar and hydrophobic amino acid side chains associate with the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids, while polar and charged amino acid side chains interact with the polar head groups or with the aqueous solution. However, there are exceptions. Sometimes, positively and negatively charged amino acid side chains interact with one another in the interior of a protein, and polar or charged amino acid side chains that interact with a ligand can be found in the ligand binding pocket.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?