| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
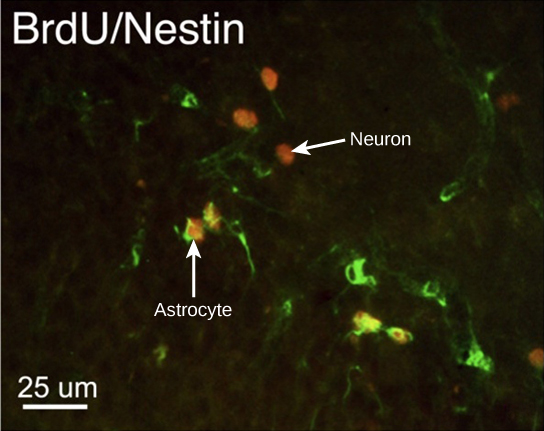
How do scientists identify new neurons? A researcher can inject a compound called bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) into the brain of an animal. While all cells will be exposed to BrdU, BrdU will only be incorporated into the DNA of newly generated cells that are in S phase. A technique called immunohistochemistry can be used to attach a fluorescent label to the incorporated BrdU, and a researcher can use fluorescent microscopy to visualize the presence of BrdU, and thus new neurons, in brain tissue. [link] is a micrograph which shows fluorescently labeled neurons in the hippocampus of a rat.
This site contains more information about neurogenesis, including an interactive laboratory simulation and a video that explains how BrdU labels new cells.
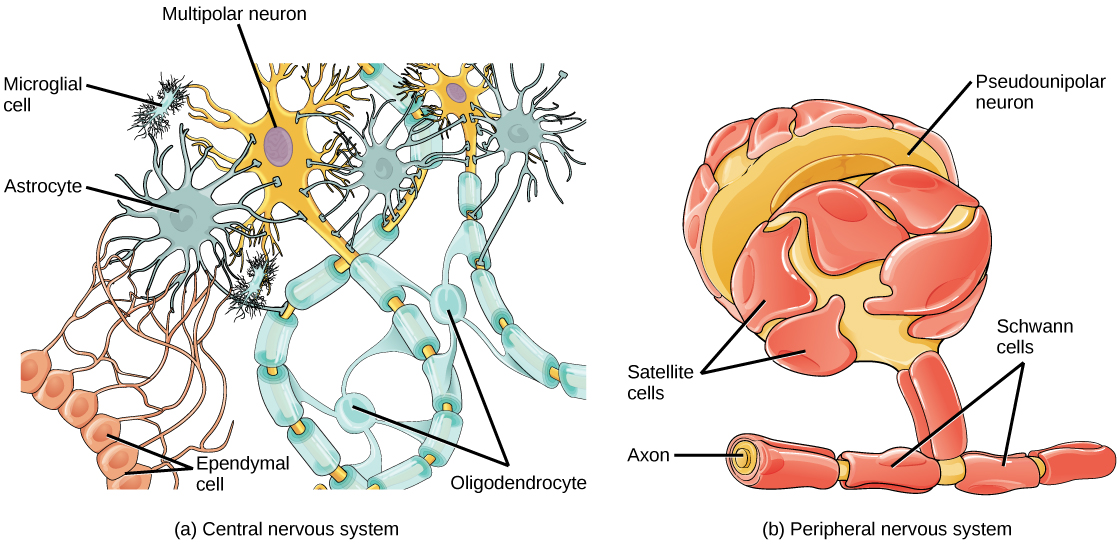
While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system, the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glia guide developing neurons to their destinations, buffer ions and chemicals that would otherwise harm neurons, and provide myelin sheaths around axons. Scientists have recently discovered that they also play a role in responding to nerve activity and modulating communication between nerve cells. When glia do not function properly, the result can be disastrous—most brain tumors are caused by mutations in glia.
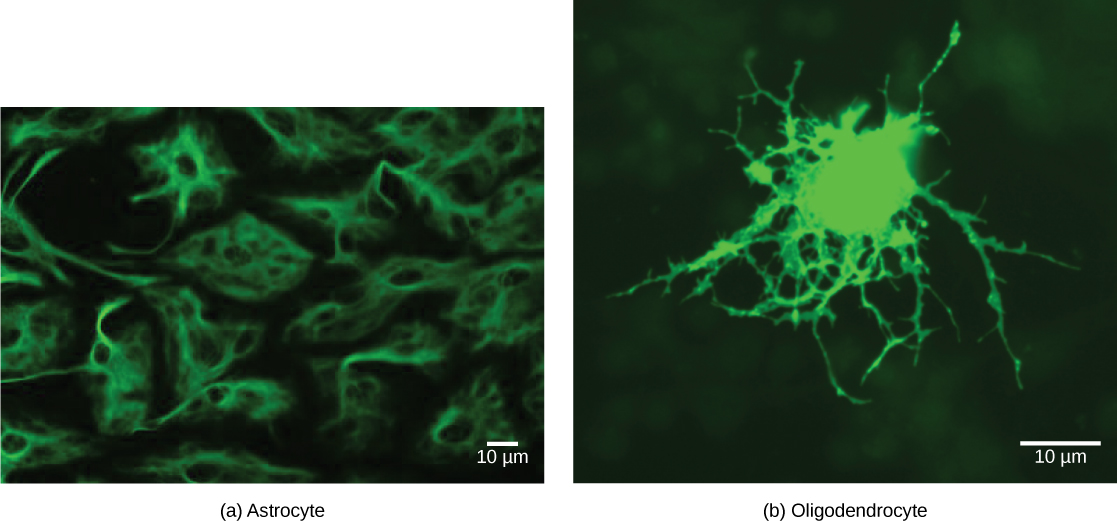
There are several different types of glia with different functions, two of which are shown in [link] . Astrocytes , shown in [link] a make contact with both capillaries and neurons in the CNS. They provide nutrients and other substances to neurons, regulate the concentrations of ions and chemicals in the extracellular fluid, and provide structural support for synapses. Astrocytes also form the blood-brain barrier—a structure that blocks entrance of toxic substances into the brain. Astrocytes, in particular, have been shown through calcium imaging experiments to become active in response to nerve activity, transmit calcium waves between astrocytes, and modulate the activity of surrounding synapses. Satellite glia provide nutrients and structural support for neurons in the PNS. Microglia scavenge and degrade dead cells and protect the brain from invading microorganisms. Oligodendrocytes , shown in [link] b form myelin sheaths around axons in the CNS. One axon can be myelinated by several oligodendrocytes, and one oligodendrocyte can provide myelin for multiple neurons. This is distinctive from the PNS where a single Schwann cell provides myelin for only one axon as the entire Schwann cell surrounds the axon. Radial glia serve as scaffolds for developing neurons as they migrate to their end destinations. Ependymal cells line fluid-filled ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. They are involved in the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which serves as a cushion for the brain, moves the fluid between the spinal cord and the brain, and is a component for the choroid plexus.
The nervous system is made up of neurons and glia. Neurons are specialized cells that are capable of sending electrical as well as chemical signals. Most neurons contain dendrites, which receive these signals, and axons that send signals to other neurons or tissues. There are four main types of neurons: unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, and pseudounipolar neurons. Glia are non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support neuronal development and signaling. There are several types of glia that serve different functions.
[link] Which of the following statements is false?
[link] B

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?