| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
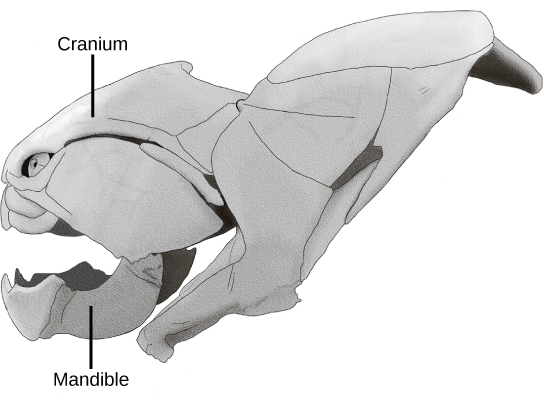
A cranium is a bony, cartilaginous, or fibrous structure surrounding the brain, jaw, and facial bones ( [link] ). Most bilaterally symmetrical animals have a head; of these, those that have a cranium compose the clade Craniata . Craniata includes the hagfishes (Myxini), which have a cranium but lack a backbone, and all of the organisms called “vertebrates.”
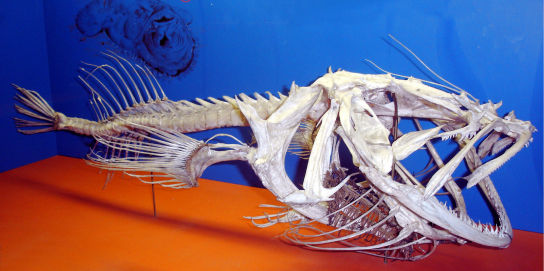
Vertebrates are members of the clade Vertebrata . Vertebrates display the four characteristic features of the chordates; however, members of this group also share derived characteristics that distinguish them from invertebrate chordates. Vertebrata is named for the vertebral column , composed of vertebrae, a series of separate bones joined together as a backbone ( [link] ). In adult vertebrates, the vertebral column replaces the notochord, which is only seen in the embryonic stage.
Based on molecular analysis, vertebrates appear to be more closely related to lancelets (cephalochordates) than to tunicates (urochordates) among the invertebrate chordates. This evidence suggests that the cephalochordates diverged from Urochordata and the vertebrates subsequently diverged from the cephalochordates. This hypothesis is further supported by the discovery of a fossil in China from the genus Haikouella . This organism seems to be an intermediate form between cephalochordates and vertebrates. The Haikouella fossils are about 530 million years old and appear similar to modern lancelets. These organisms had a brain and eyes, as do vertebrates, but lack the skull found in craniates. Chen, J. Y., Huang, D. Y., and Li, C. W., “An early Cambrian craniate-like chordate,” Nature 402 (1999): 518–522, doi:10.1038/990080. This evidence suggests that vertebrates arose during the Cambrian explosion. Recall that the “Cambrian explosion” is the name given to a relatively brief span of time during the Cambrian period during which many animal groups appeared and rapidly diversified. Most modern animal phyla originated during the Cambrian explosion.
Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with more than 62,000 living species. Vertebrates are grouped based on anatomical and physiological traits. More than one classification and naming scheme is used for these animals. Here we will consider the traditional groups Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia, which constitute classes in the subphylum Vertebrata. Many modern authors classify birds within Reptilia, which correctly reflects their evolutionary heritage. We consider them separately only for convenience. Further, we will consider hagfishes and lampreys together as jawless fishes, the agnathans, although emerging classification schemes separate them into chordate jawless fishes (the hagfishes) and vertebrate jawless fishes (the lampreys).
Animals that possess jaws are known as gnathostomes, which means “jawed mouth.” Gnathostomes include fishes and tetrapods—amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Tetrapods can be further divided into two groups: amphibians and amniotes. Amniotes are animals whose eggs are adapted for terrestrial living, and this group includes mammals, reptiles, and birds. Amniotic embryos, developing in either an externally shed egg or an egg carried by the female, are provided with a water-retaining environment and are protected by amniotic membranes.
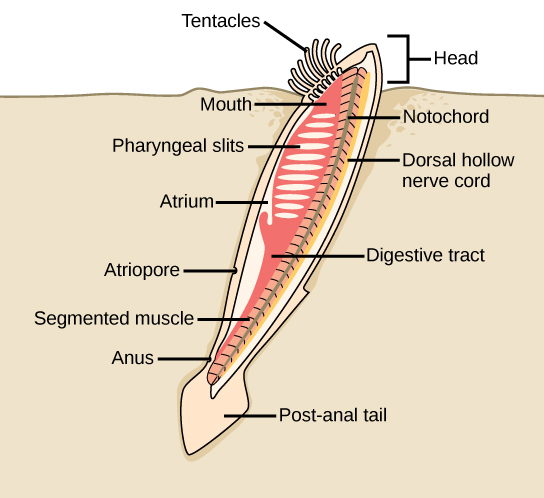
The characteristic features of Chordata are a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. Chordata contains two clades of invertebrates: Urochordata (tunicates) and Cephalochordata (lancelets), together with the vertebrates in Vertebrata. Most tunicates live on the ocean floor and are suspension feeders. Lancelets are suspension feeders that feed on phytoplankton and other microorganisms. Vertebrata is named for the vertebral column, which is a feature of almost all members of this clade.
[link] Which of the following statements about common features of chordates is true?
[link] A

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?