| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Even exergonic, energy-releasing reactions require a small amount of activation energy in order to proceed. However, consider endergonic reactions, which require much more energy input, because their products have more free energy than their reactants. Within the cell, where does energy to power such reactions come from? The answer lies with an energy-supplying molecule called adenosine triphosphate , or ATP . ATP is a small, relatively simple molecule ( [link] ), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. This molecule can be thought of as the primary energy currency of cells in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they need. ATP is used to power the majority of energy-requiring cellular reactions.
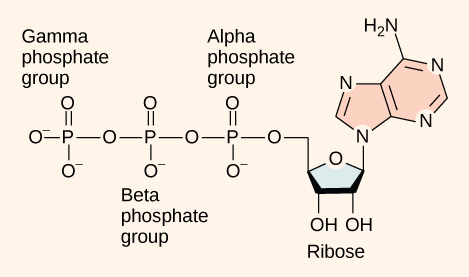
As its name suggests, adenosine triphosphate is comprised of adenosine bound to three phosphate groups ( [link] ). Adenosine is a nucleoside consisting of the nitrogenous base adenine and a five-carbon sugar, ribose. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma. Together, these chemical groups constitute an energy powerhouse. However, not all bonds within this molecule exist in a particularly high-energy state. Both bonds that link the phosphates are equally high-energy bonds ( phosphoanhydride bonds ) that, when broken, release sufficient energy to power a variety of cellular reactions and processes. These high-energy bonds are the bonds between the second and third (or beta and gamma) phosphate groups and between the first and second phosphate groups. The reason that these bonds are considered “high-energy” is because the products of such bond breaking—adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and one inorganic phosphate group (P i )—have considerably lower free energy than the reactants: ATP and a water molecule. Because this reaction takes place with the use of a water molecule, it is considered a hydrolysis reaction. In other words, ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP in the following reaction:
Like most chemical reactions, the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP is reversible. The reverse reaction regenerates ATP from ADP + P i . Indeed, cells rely on the regeneration of ATP just as people rely on the regeneration of spent money through some sort of income. Since ATP hydrolysis releases energy, ATP regeneration must require an input of free energy. The formation of ATP is expressed in this equation:
Two prominent questions remain with regard to the use of ATP as an energy source. Exactly how much free energy is released with the hydrolysis of ATP, and how is that free energy used to do cellular work? The calculated ∆G for the hydrolysis of one mole of ATP into ADP and P i is −7.3 kcal/mole (−30.5 kJ/mol). Since this calculation is true under standard conditions, it would be expected that a different value exists under cellular conditions. In fact, the ∆G for the hydrolysis of one mole of ATP in a living cell is almost double the value at standard conditions: 14 kcal/mol (−57 kJ/mol).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?