| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Gastrulation leads to the formation of the three germ layers that give rise, during further development, to the different organs in the animal body. This process is called organogenesis . Organogenesis is characterized by rapid and precise movements of the cells within the embryo.
Organs form from the germ layers through the process of differentiation. During differentiation, the embryonic stem cells express specific sets of genes which will determine their ultimate cell type. For example, some cells in the ectoderm will express the genes specific to skin cells. As a result, these cells will differentiate into epidermal cells. The process of differentiation is regulated by cellular signaling cascades.
Scientists study organogenesis extensively in the lab in fruit flies ( Drosophila ) and the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans . Drosophila have segments along their bodies, and the patterning associated with the segment formation has allowed scientists to study which genes play important roles in organogenesis along the length of the embryo at different time points. The nematode C.elegans has roughly 1000 somatic cells and scientists have studied the fate of each of these cells during their development in the nematode life cycle. There is little variation in patterns of cell lineage between individuals, unlike in mammals where cell development from the embryo is dependent on cellular cues.
In vertebrates, one of the primary steps during organogenesis is the formation of the neural system. The ectoderm forms epithelial cells and tissues, and neuronal tissues. During the formation of the neural system, special signaling molecules called growth factors signal some cells at the edge of the ectoderm to become epidermis cells. The remaining cells in the center form the neural plate. If the signaling by growth factors were disrupted, then the entire ectoderm would differentiate into neural tissue.
The neural plate undergoes a series of cell movements where it rolls up and forms a tube called the neural tube , as illustrated in [link] . In further development, the neural tube will give rise to the brain and the spinal cord.
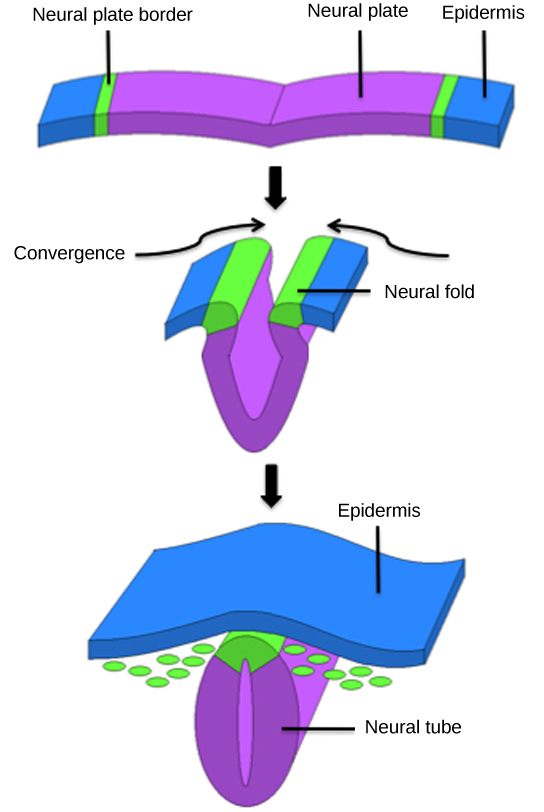
The mesoderm that lies on either side of the vertebrate neural tube will develop into the various connective tissues of the animal body. A spatial pattern of gene expression reorganizes the mesoderm into groups of cells called somites with spaces between them. The somites, illustrated in [link] will further develop into the ribs, lungs, and segmental (spine) muscle. The mesoderm also forms a structure called the notochord, which is rod-shaped and forms the central axis of the animal body.
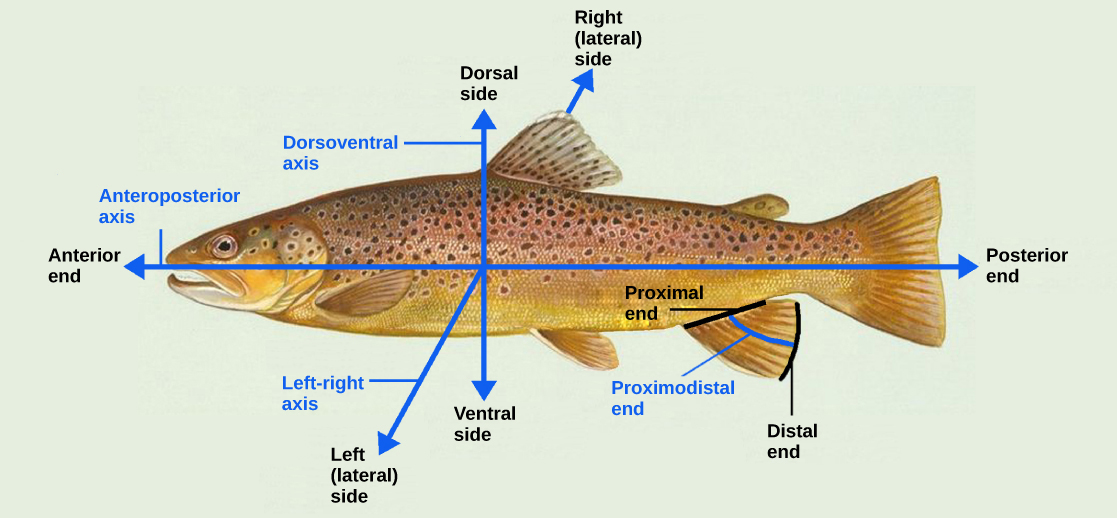
Even as the germ layers form, the ball of cells still retains its spherical shape. However, animal bodies have lateral-medial (left-right), dorsal-ventral (back-belly), and anterior-posterior (head-feet) axes, illustrated in [link] .
How are these established? In one of the most seminal experiments ever to be carried out in developmental biology, Spemann and Mangold took dorsal cells from one embryo and transplanted them into the belly region of another embryo. They found that the transplanted embryo now had two notochords: one at the dorsal site from the original cells and another at the transplanted site. This suggested that the dorsal cells were genetically programmed to form the notochord and define the axis. Since then, researchers have identified many genes that are responsible for axis formation. Mutations in these genes leads to the loss of symmetry required for organism development.
Animal bodies have externally visible symmetry. However, the internal organs are not symmetric. For example, the heart is on the left side and the liver on the right. The formation of the central left-right axis is an important process during development. This internal asymmetry is established very early during development and involves many genes. Research is still ongoing to fully understand the developmental implications of these genes.
Organogenesis is the formation of organs from the germ layers. Each germ layer gives rise to specific tissue types. The first stage is the formation of the neural system in the ectoderm. The mesoderm gives rise to somites and the notochord. Formation of vertebrate axis is another important developmental stage.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?