| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Bone , or osseous tissue , is a connective tissue that constitutes the endoskeleton. It contains specialized cells and a matrix of mineral salts and collagen fibers.
The mineral salts primarily include hydroxyapatite, a mineral formed from calcium phosphate. Calcification is the process of deposition of mineral salts on the collagen fiber matrix that crystallizes and hardens the tissue. The process of calcification only occurs in the presence of collagen fibers.
The bones of the human skeleton are classified by their shape: long bones, short bones, flat bones, sutural bones, sesamoid bones, and irregular bones ( [link] ).
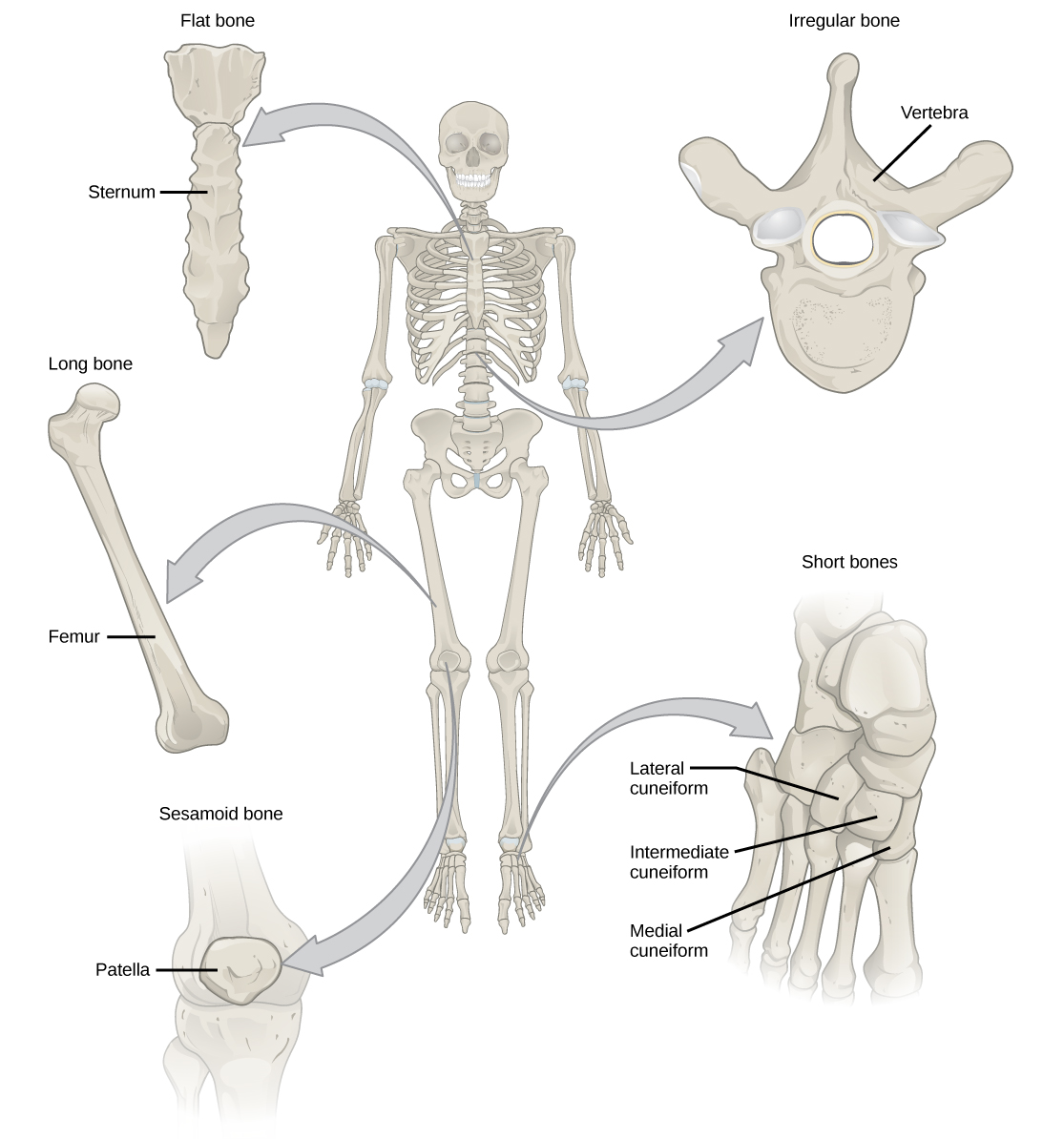
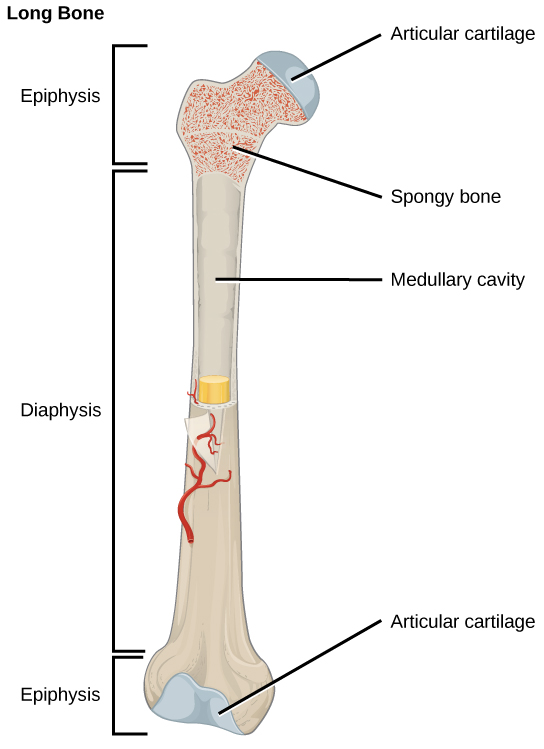
Long bones are longer than they are wide and have a shaft and two ends. The diaphysis , or central shaft, contains bone marrow in a marrow cavity. The rounded ends, the epiphyses , are covered with articular cartilage and are filled with red bone marrow, which produces blood cells ( [link] ). Most of the limb bones are long bones—for example, the femur, tibia, ulna, and radius. Exceptions to this include the patella and the bones of the wrist and ankle.
Short bones , or cuboidal bones, are bones that are the same width and length, giving them a cube-like shape. For example, the bones of the wrist (carpals) and ankle (tarsals) are short bones ( [link] ).
Flat bones are thin and relatively broad bones that are found where extensive protection of organs is required or where broad surfaces of muscle attachment are required. Examples of flat bones are the sternum (breast bone), ribs, scapulae (shoulder blades), and the roof of the skull ( [link] ).
Irregular bones are bones with complex shapes. These bones may have short, flat, notched, or ridged surfaces. Examples of irregular bones are the vertebrae, hip bones, and several skull bones.
Sesamoid bones are small, flat bones and are shaped similarly to a sesame seed. The patellae are sesamoid bones ( [link] ). Sesamoid bones develop inside tendons and may be found near joints at the knees, hands, and feet.
Sutural bones are small, flat, irregularly shaped bones. They may be found between the flat bones of the skull. They vary in number, shape, size, and position.
Bones are considered organs because they contain various types of tissue, such as blood, connective tissue, nerves, and bone tissue. Osteocytes, the living cells of bone tissue, form the mineral matrix of bones. There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy.
Compact bone (or cortical bone) forms the hard external layer of all bones and surrounds the medullary cavity, or bone marrow. It provides protection and strength to bones. Compact bone tissue consists of units called osteons or Haversian systems. Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain a mineral matrix and living osteocytes connected by canaliculi, which transport blood. They are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone. Each osteon consists of lamellae , which are layers of compact matrix that surround a central canal called the Haversian canal. The Haversian canal (osteonic canal) contains the bone’s blood vessels and nerve fibers ( [link] ). Osteons in compact bone tissue are aligned in the same direction along lines of stress and help the bone resist bending or fracturing. Therefore, compact bone tissue is prominent in areas of bone at which stresses are applied in only a few directions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?