| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Biologists strive to understand the evolutionary history and relationships of members of the animal kingdom, and all of life, for that matter. The study of phylogeny aims to determine the evolutionary relationships between phyla. Currently, most biologists divide the animal kingdom into 35 to 40 phyla. Scientists develop phylogenetic trees, which serve as hypotheses about which species have evolved from which ancestors
Recall that until recently, only morphological characteristics and the fossil record were used to determine phylogenetic relationships among animals. Scientific understanding of the distinctions and hierarchies between anatomical characteristics provided much of this knowledge. Used alone, however, this information can be misleading. Morphological characteristics may evolve multiple times, and independently, through evolutionary history. Analogous characteristics may appear similar between animals, but their underlying evolution may be very different. With the advancement of molecular technologies, modern phylogenetics is now informed by genetic and molecular analyses, in addition to traditional morphological and fossil data. With a growing understanding of genetics, the animal evolutionary tree has changed substantially and continues to change as new DNA and RNA analyses are performed on additional animal species.
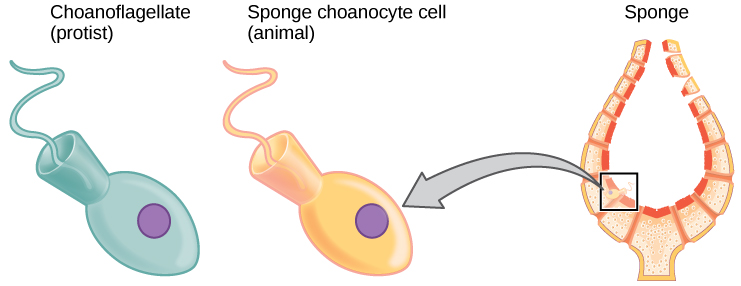
The current understanding of evolutionary relationships between animal, or Metazoa , phyla begins with the distinction between “true” animals with true differentiated tissues, called Eumetazoa , and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues (such as the sponges), called Parazoa . Both Parazoa and Eumetazoa evolved from a common ancestral organism that resembles the modern-day protists called choanoflagellates. These protist cells strongly resemble the sponge choanocyte cells today ( [link] ).
Eumetazoa are subdivided into radially symmetrical animals and bilaterally symmetrical animals, and are thus classified into clade Bilateria or Radiata, respectively. As mentioned earlier, the cnidarians and ctenophores are animal phyla with true radial symmetry. All other Eumetazoa are members of the Bilateria clade. The bilaterally symmetrical animals are further divided into deuterostomes (including chordates and echinoderms) and two distinct clades of protostomes (including ecdysozoans and lophotrochozoans) ( [link] ab). Ecdysozoa includes nematodes and arthropods; they are so named for a commonly found characteristic among the group: exoskeletal molting (termed ecdysis). Lophotrochozoa is named for two structural features, each common to certain phyla within the clade. Some lophotrochozoan phyla are characterized by a larval stage called trochophore larvae, and other phyla are characterized by the presence of a feeding structure called a lophophore.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?