| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
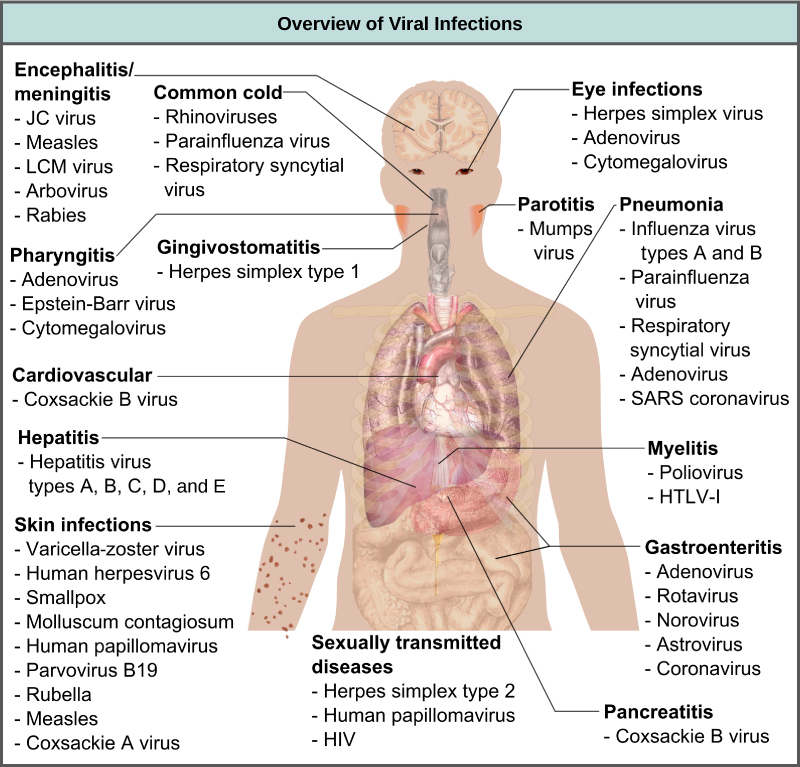
Viruses cause a variety of diseases in animals, including humans, ranging from the common cold to potentially fatal illnesses like meningitis ( [link] ). These diseases can be treated by antiviral drugs or by vaccines, but some viruses, such as HIV, are capable of both avoiding the immune response and mutating to become resistant to antiviral drugs.
While we do have limited numbers of effective antiviral drugs, such as those used to treat HIV and influenza, the primary method of controlling viral disease is by vaccination, which is intended to prevent outbreaks by building immunity to a virus or virus family ( [link] ). Vaccines may be prepared using live viruses, killed viruses, or molecular subunits of the virus. The killed viral vaccines and subunit viruses are both incapable of causing disease.
Live viral vaccines are designed in the laboratory to cause few symptoms in recipients while giving them protective immunity against future infections. Polio was one disease that represented a milestone in the use of vaccines. Mass immunization campaigns in the 1950s (killed vaccine) and 1960s (live vaccine) significantly reduced the incidence of the disease, which caused muscle paralysis in children and generated a great amount of fear in the general population when regional epidemics occurred. The success of the polio vaccine paved the way for the routine dispensation of childhood vaccines against measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox, and other diseases.
The danger of using live vaccines, which are usually more effective than killed vaccines, is the low but significant danger that these viruses will revert to their disease-causing form by back mutations . Live vaccines are usually made by attenuating (weakening) the “wild-type” (disease-causing) virus by growing it in the laboratory in tissues or at temperatures different from what the virus is accustomed to in the host. Adaptations to these new cells or temperatures induce mutations in the genomes of the virus, allowing it to grow better in the laboratory while inhibiting its ability to cause disease when reintroduced into conditions found in the host. These attenuated viruses thus still cause infection, but they do not grow very well, allowing the immune response to develop in time to prevent major disease. Back mutations occur when the vaccine undergoes mutations in the host such that it readapts to the host and can again cause disease, which can then be spread to other humans in an epidemic. This type of scenario happened as recently as 2007 in Nigeria where mutations in a polio vaccine led to an epidemic of polio in that country.
Some vaccines are in continuous development because certain viruses, such as influenza and HIV, have a high mutation rate compared to other viruses and normal host cells. With influenza, mutations in the surface molecules of the virus help the organism evade the protective immunity that may have been obtained in a previous influenza season, making it necessary for individuals to get vaccinated every year. Other viruses, such as those that cause the childhood diseases measles, mumps, and rubella, mutate so infrequently that the same vaccine is used year after year.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?