| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although there have been significant advances in the medical sciences in recent years, doctors are still confounded by some diseases, and they are using whole-genome sequencing to get to the bottom of the problem. Whole-genome sequencing is a process that determines the DNA sequence of an entire genome. Whole-genome sequencing is a brute-force approach to problem solving when there is a genetic basis at the core of a disease. Several laboratories now provide services to sequence, analyze, and interpret entire genomes.
For example, whole-exome sequencing is a lower-cost alternative to whole genome sequencing. In exome sequencing, only the coding, exon-producing regions of the DNA are sequenced. In 2010, whole-exome sequencing was used to save a young boy whose intestines had multiple mysterious abscesses. The child had several colon operations with no relief. Finally, whole-exome sequencing was performed, which revealed a defect in a pathway that controls apoptosis (programmed cell death). A bone-marrow transplant was used to overcome this genetic disorder, leading to a cure for the boy. He was the first person to be successfully treated based on a diagnosis made by whole-exome sequencing. Today, human genome sequencing is more readily available and can be completed in a day or two for about $1000.
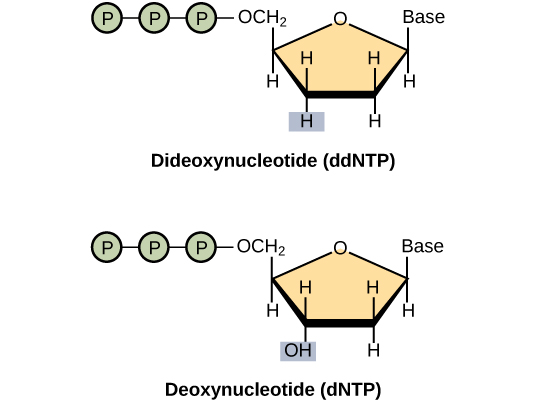
The basic sequencing technique used in all modern day sequencing projects is the chain termination method (also known as the dideoxy method), which was developed by Fred Sanger in the 1970s. The chain termination method involves DNA replication of a single-stranded template with the use of a primer and a regular deoxynucleotide (dNTP), which is a monomer, or a single unit, of DNA. The primer and dNTP are mixed with a small proportion of fluorescently labeled dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs). The ddNTPs are monomers that are missing a hydroxyl group (–OH) at the site at which another nucleotide usually attaches to form a chain ( [link] ). Each ddNTP is labeled with a different color of fluorophore. Every time a ddNTP is incorporated in the growing complementary strand, it terminates the process of DNA replication, which results in multiple short strands of replicated DNA that are each terminated at a different point during replication. When the reaction mixture is processed by gel electrophoresis after being separated into single strands, the multiple newly replicated DNA strands form a ladder because of the differing sizes. Because the ddNTPs are fluorescently labeled, each band on the gel reflects the size of the DNA strand and the ddNTP that terminated the reaction. The different colors of the fluorophore-labeled ddNTPs help identify the ddNTP incorporated at that position. Reading the gel on the basis of the color of each band on the ladder produces the sequence of the template strand ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?