| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
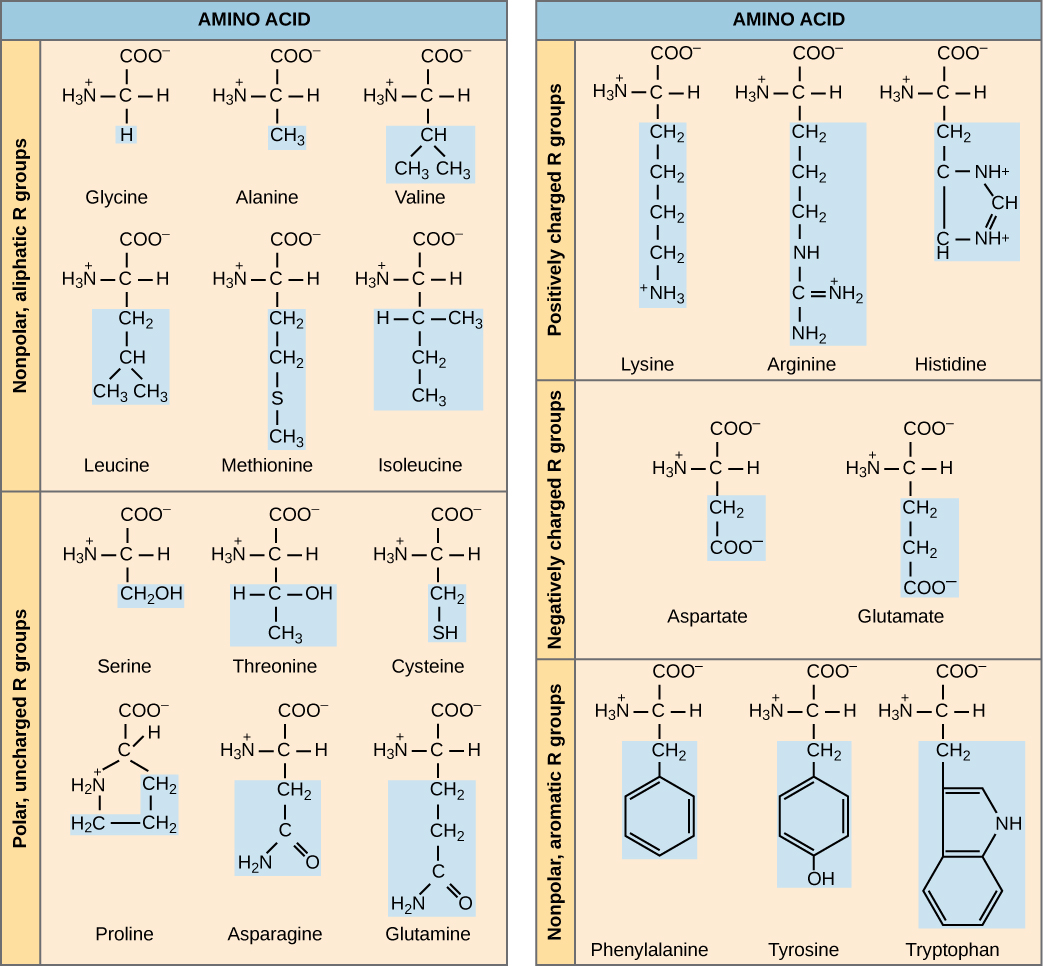
The cellular process of transcription generates messenger RNA (mRNA), a mobile molecular copy of one or more genes with an alphabet of A, C, G, and uracil (U). Translation of the mRNA template converts nucleotide-based genetic information into a protein product. Protein sequences consist of 20 commonly occurring amino acids; therefore, it can be said that the protein alphabet consists of 20 letters ( [link] ). Each amino acid is defined by a three-nucleotide sequence called the triplet codon. Different amino acids have different chemistries (such as acidic versus basic, or polar and nonpolar) and different structural constraints. Variation in amino acid sequence gives rise to enormous variation in protein structure and function.
The flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to mRNA to protein is described by the Central Dogma ( [link] ), which states that genes specify the sequence of mRNAs, which in turn specify the sequence of proteins. The decoding of one molecule to another is performed by specific proteins and RNAs. Because the information stored in DNA is so central to cellular function, it makes intuitive sense that the cell would make mRNA copies of this information for protein synthesis, while keeping the DNA itself intact and protected. The copying of DNA to RNA is relatively straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mRNA strand for every nucleotide read in the DNA strand. The translation to protein is a bit more complex because three mRNA nucleotides correspond to one amino acid in the polypeptide sequence. However, the translation to protein is still systematic and colinear , such that nucleotides 1 to 3 correspond to amino acid 1, nucleotides 4 to 6 correspond to amino acid 2, and so on.
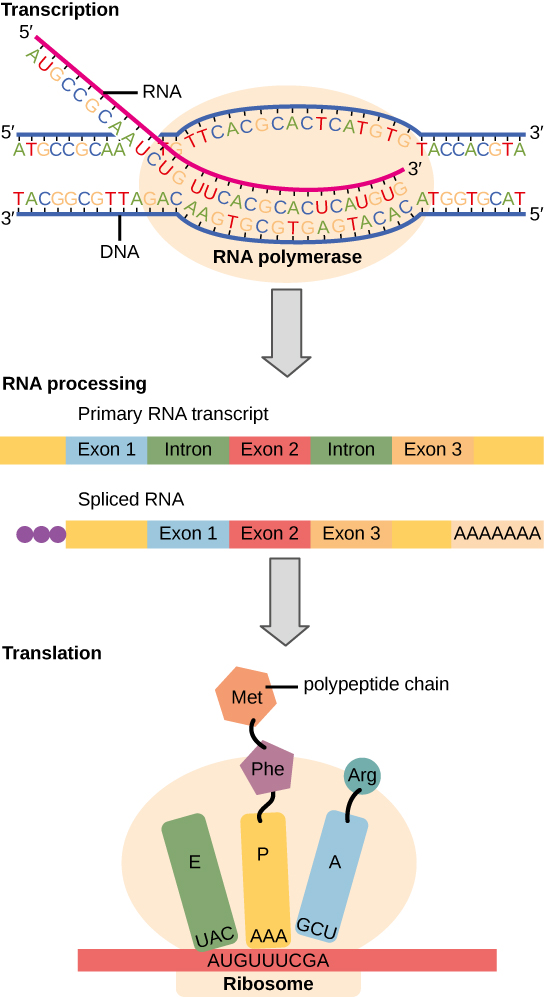
Given the different numbers of “letters” in the mRNA and protein “alphabets,” scientists theorized that combinations of nucleotides corresponded to single amino acids. Nucleotide doublets would not be sufficient to specify every amino acid because there are only 16 possible two-nucleotide combinations (4 2 ). In contrast, there are 64 possible nucleotide triplets (4 3 ), which is far more than the number of amino acids. Scientists theorized that amino acids were encoded by nucleotide triplets and that the genetic code was degenerate . In other words, a given amino acid could be encoded by more than one nucleotide triplet. This was later confirmed experimentally; Francis Crick and Sydney Brenner used the chemical mutagen proflavin to insert one, two, or three nucleotides into the gene of a virus. When one or two nucleotides were inserted, protein synthesis was completely abolished. When three nucleotides were inserted, the protein was synthesized and functional. This demonstrated that three nucleotides specify each amino acid. These nucleotide triplets are called codons . The insertion of one or two nucleotides completely changed the triplet reading frame , thereby altering the message for every subsequent amino acid ( [link] ). Though insertion of three nucleotides caused an extra amino acid to be inserted during translation, the integrity of the rest of the protein was maintained.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?