| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. The important components of the nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group ( [link] ). The nucleotide is named depending on the nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be a purine such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine such as cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
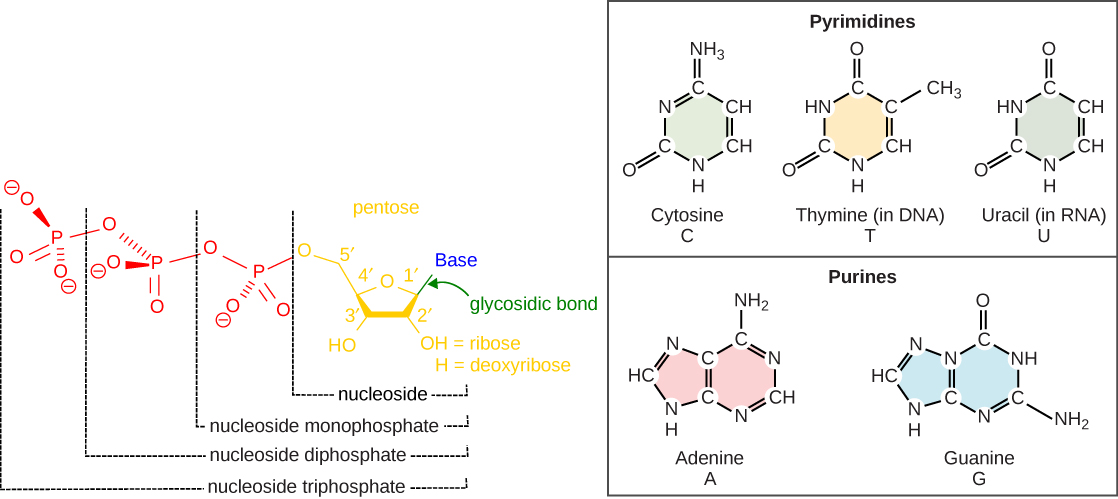
The nucleotides combine with each other by covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds or linkages. The purines have a double ring structure with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. Pyrimidines are smaller in size; they have a single six-membered ring structure. The carbon atoms of the five-carbon sugar are numbered 1', 2', 3', 4', and 5' (1' is read as “one prime”). The phosphate residue is attached to the hydroxyl group of the 5' carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the 3' carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, thereby forming a 5'-3' phosphodiester bond.
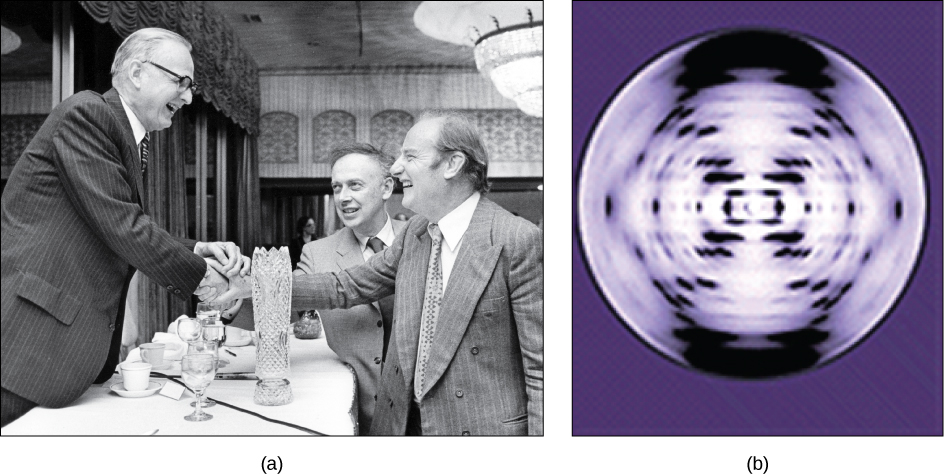
In the 1950s, Francis Crick and James Watson worked together to determine the structure of DNA at the University of Cambridge, England. Other scientists like Linus Pauling and Maurice Wilkins were also actively exploring this field. Pauling had discovered the secondary structure of proteins using X-ray crystallography. In Wilkins’ lab, researcher Rosalind Franklin was using X-ray diffraction methods to understand the structure of DNA. Watson and Crick were able to piece together the puzzle of the DNA molecule on the basis of Franklin's data because Crick had also studied X-ray diffraction ( [link] ). In 1962, James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine. Unfortunately, by then Franklin had died, and Nobel prizes are not awarded posthumously.
Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix. Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine; namely, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base pairs. The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds and cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds. The two strands are anti-parallel in nature; that is, the 3' end of one strand faces the 5' end of the other strand. The sugar and phosphate of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the nitrogenous bases are stacked inside. Each base pair is separated from the other base pair by a distance of 0.34 nm, and each turn of the helix measures 3.4 nm. Therefore, ten base pairs are present per turn of the helix. The diameter of the DNA double helix is 2 nm, and it is uniform throughout. Only the pairing between a purine and pyrimidine can explain the uniform diameter. The twisting of the two strands around each other results in the formation of uniformly spaced major and minor grooves ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?