| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If you are new to astronomy, you have probably reached the end of our brief tour in this chapter with mixed emotions. On the one hand, you may be fascinated by some of the new ideas you’ve read about and you may be eager to learn more. On the other hand, you may be feeling a bit overwhelmed by the number of topics we have covered, and the number of new words and ideas we have introduced. Learning astronomy is a little like learning a new language: at first it seems there are so many new expressions that you’ll never master them all, but with practice, you soon develop facility with them.
At this point you may also feel a bit small and insignificant, dwarfed by the cosmic scales of distance and time. But, there is another way to look at what you have learned from our first glimpses of the cosmos. Let us consider the history of the universe from the Big Bang to today and compress it, for easy reference, into a single year. (We have borrowed this idea from Carl Sagan’s 1997 Pulitzer Prize-winning book, The Dragons of Eden .)
On this scale, the Big Bang happened at the first moment of January 1, and this moment, when you are reading this chapter would be the end of the very last second of December 31. When did other events in the development of the universe happen in this “cosmic year?” Our solar system formed around September 10, and the oldest rocks we can date on Earth go back to the third week in September ( [link] ).
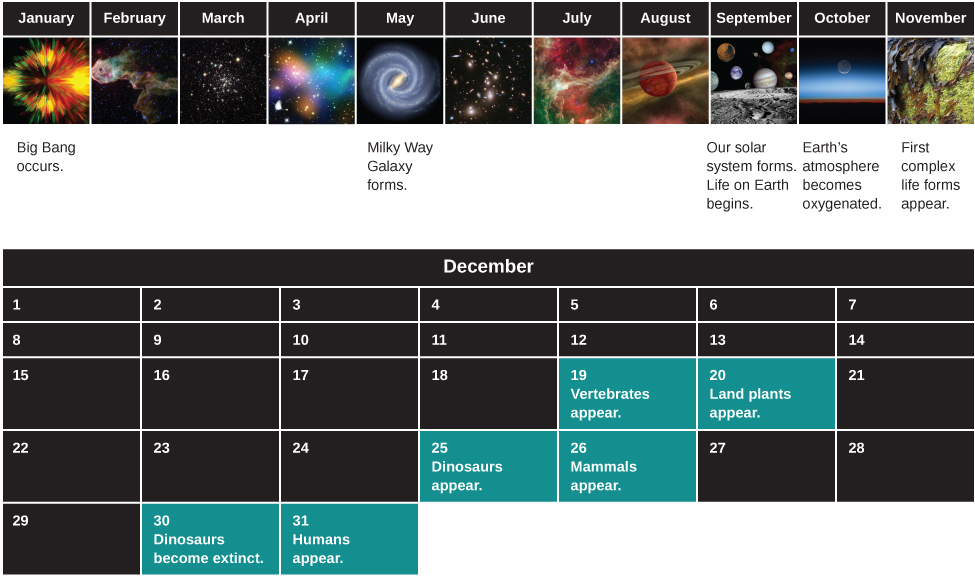
Where does the origin of human beings fall during the course of this cosmic year? The answer turns out to be the evening of December 31. The invention of the alphabet doesn’t occur until the fiftieth second of 11:59 p.m. on December 31. And the beginnings of modern astronomy are a mere fraction of a second before the New Year. Seen in a cosmic context, the amount of time we have had to study the stars is minute, and our success in piecing together as much of the story as we have is remarkable.
Certainly our attempts to understand the universe are not complete. As new technologies and new ideas allow us to gather more and better data about the cosmos, our present picture of astronomy will very likely undergo many changes. Still, as you read our current progress report on the exploration of the universe, take a few minutes every once in a while just to savor how much you have already learned.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?