| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm. It runs parallel to the radius, which is the lateral bone of the forearm ( [link] ). The proximal end of the ulna resembles a crescent wrench with its large, C-shaped trochlear notch . This region articulates with the trochlea of the humerus as part of the elbow joint. The inferior margin of the trochlear notch is formed by a prominent lip of bone called the coronoid process of the ulna . Just below this on the anterior ulna is a roughened area called the ulnar tuberosity . To the lateral side and slightly inferior to the trochlear notch is a small, smooth area called the radial notch of the ulna . This area is the site of articulation between the proximal radius and the ulna, forming the proximal radioulnar joint . The posterior and superior portions of the proximal ulna make up the olecranon process , which forms the bony tip of the elbow.
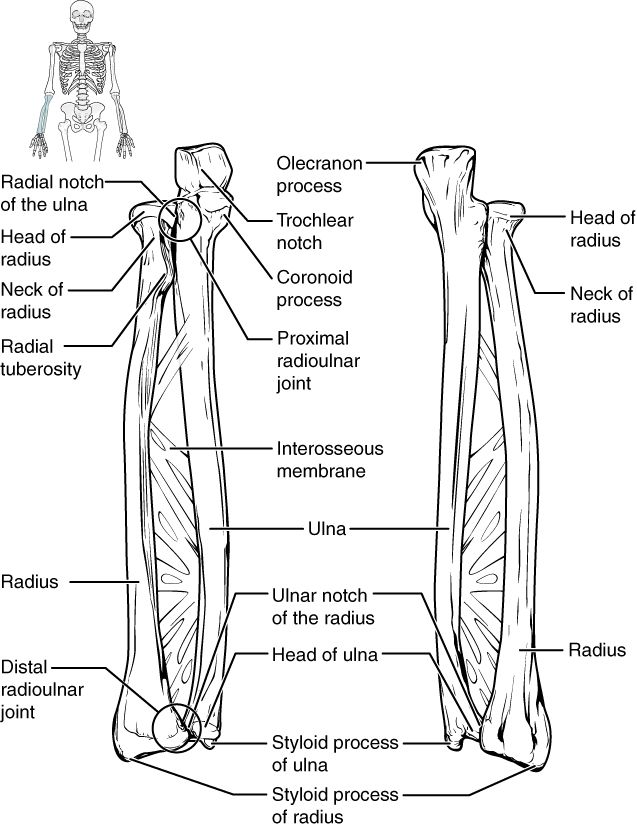
More distal is the shaft of the ulna . The lateral side of the shaft forms a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna . This is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm , a sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the ulna and radius bones. The small, rounded area that forms the distal end is the head of the ulna . Projecting from the posterior side of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna , a short bony projection. This serves as an attachment point for a connective tissue structure that unites the distal ends of the ulna and radius.
In the anatomical position, with the elbow fully extended and the palms facing forward, the arm and forearm do not form a straight line. Instead, the forearm deviates laterally by 5–15 degrees from the line of the arm. This deviation is called the carrying angle. It allows the forearm and hand to swing freely or to carry an object without hitting the hip. The carrying angle is larger in females to accommodate their wider pelvis.
The radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm (see [link] ). The head of the radius is a disc-shaped structure that forms the proximal end. The small depression on the surface of the head articulates with the capitulum of the humerus as part of the elbow joint, whereas the smooth, outer margin of the head articulates with the radial notch of the ulna at the proximal radioulnar joint. The neck of the radius is the narrowed region immediately below the expanded head. Inferior to this point on the medial side is the radial tuberosity , an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point. The shaft of the radius is slightly curved and has a small ridge along its medial side. This ridge forms the interosseous border of the radius , which, like the similar border of the ulna, is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane that unites the two forearm bones. The distal end of the radius has a smooth surface for articulation with two carpal bones to form the radiocarpal joint or wrist joint ( [link] and [link] ). On the medial side of the distal radius is the ulnar notch of the radius . This shallow depression articulates with the head of the ulna, which together form the distal radioulnar joint . The lateral end of the radius has a pointed projection called the styloid process of the radius . This provides attachment for ligaments that support the lateral side of the wrist joint. Compared to the styloid process of the ulna, the styloid process of the radius projects more distally, thereby limiting the range of movement for lateral deviations of the hand at the wrist joint.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?