| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The tibia (shin bone) is the medial bone of the leg and is larger than the fibula, with which it is paired ( [link] ). The tibia is the main weight-bearing bone of the lower leg and the second longest bone of the body, after the femur. The medial side of the tibia is located immediately under the skin, allowing it to be easily palpated down the entire length of the medial leg.
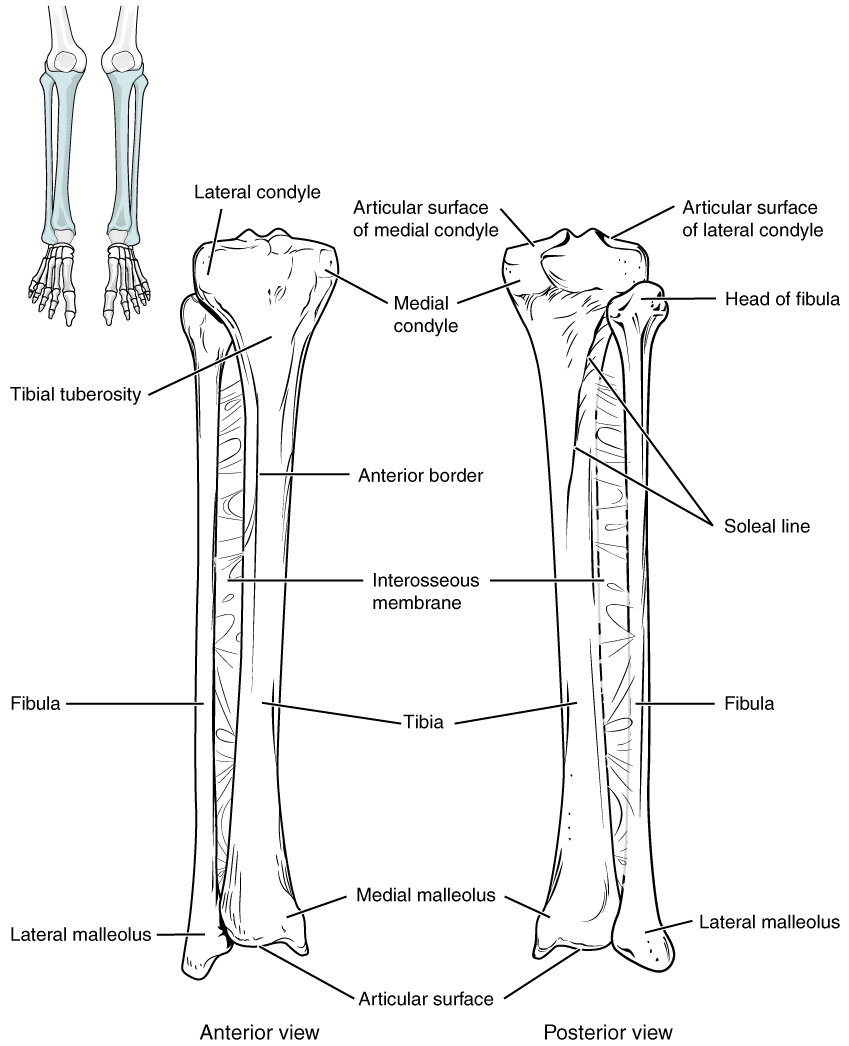
The proximal end of the tibia is greatly expanded. The two sides of this expansion form the medial condyle of the tibia and the lateral condyle of the tibia . The tibia does not have epicondyles. The top surface of each condyle is smooth and flattened. These areas articulate with the medial and lateral condyles of the femur to form the knee joint . Between the articulating surfaces of the tibial condyles is the intercondylar eminence , an irregular, elevated area that serves as the inferior attachment point for two supporting ligaments of the knee.
The tibial tuberosity is an elevated area on the anterior side of the tibia, near its proximal end. It is the final site of attachment for the muscle tendon associated with the patella. More inferiorly, the shaft of the tibia becomes triangular in shape. The anterior apex of
MH this triangle forms the anterior border of the tibia , which begins at the tibial tuberosity and runs inferiorly along the length of the tibia. Both the anterior border and the medial side of the triangular shaft are located immediately under the skin and can be easily palpated along the entire length of the tibia. A small ridge running down the lateral side of the tibial shaft is the interosseous border of the tibia . This is for the attachment of the interosseous membrane of the leg , the sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the tibia and fibula bones. Located on the posterior side of the tibia is the soleal line , a diagonally running, roughened ridge that begins below the base of the lateral condyle, and runs down and medially across the proximal third of the posterior tibia. Muscles of the posterior leg attach to this line.
The large expansion found on the medial side of the distal tibia is the medial malleolus (“little hammer”). This forms the large bony bump found on the medial side of the ankle region. Both the smooth surface on the inside of the medial malleolus and the smooth area at the distal end of the tibia articulate with the talus bone of the foot as part of the ankle joint. On the lateral side of the distal tibia is a wide groove called the fibular notch . This area articulates with the distal end of the fibula, forming the distal tibiofibular joint .
The fibula is the slender bone located on the lateral side of the leg (see [link] ). The fibula does not bear weight. It serves primarily for muscle attachments and thus is largely surrounded by muscles. Only the proximal and distal ends of the fibula can be palpated.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?