| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The diencephalon is the one region of the adult brain that retains its name from embryologic development. The etymology of the word diencephalon translates to “through brain.” It is the connection between the cerebrum and the rest of the nervous system, with one exception. The rest of the brain, the spinal cord, and the PNS all send information to the cerebrum through the diencephalon. Output from the cerebrum passes through the diencephalon. The single exception is the system associated with olfaction , or the sense of smell, which connects directly with the cerebrum. In the earliest vertebrate species, the cerebrum was not much more than olfactory bulbs that received peripheral information about the chemical environment (to call it smell in these organisms is imprecise because they lived in the ocean).
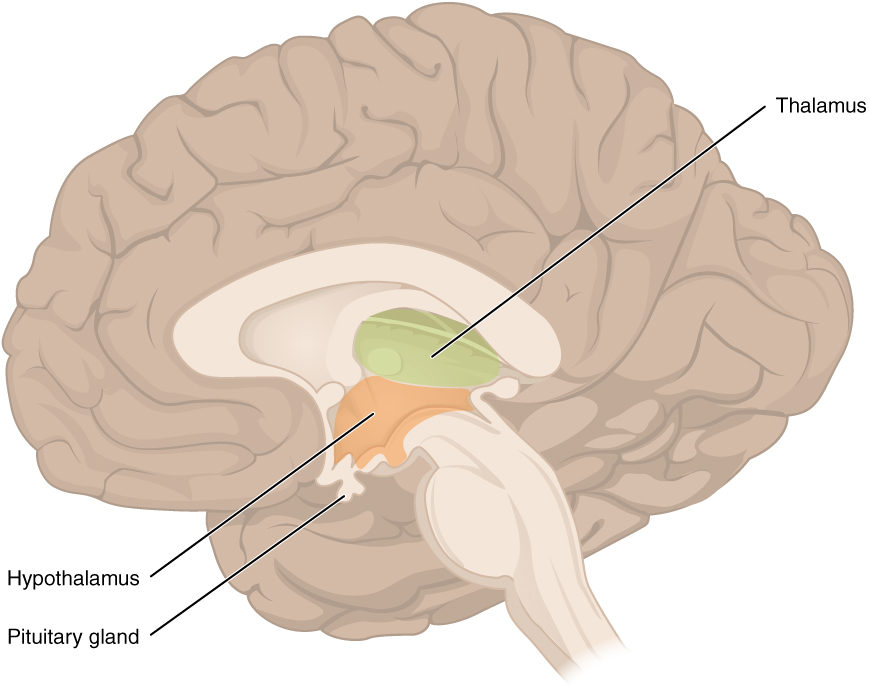
The diencephalon is deep beneath the cerebrum and constitutes the walls of the third ventricle. The diencephalon can be described as any region of the brain with “thalamus” in its name. The two major regions of the diencephalon are the thalamus itself and the hypothalamus ( [link] ). There are other structures, such as the epithalamus , which contains the pineal gland, or the subthalamus , which includes the subthalamic nucleus that is part of the basal nuclei.
The thalamus is a collection of nuclei that relay information between the cerebral cortex and the periphery, spinal cord, or brain stem. All sensory information, except for the sense of smell, passes through the thalamus before processing by the cortex. Axons from the peripheral sensory organs, or intermediate nuclei, synapse in the thalamus, and thalamic neurons project directly to the cerebrum. It is a requisite synapse in any sensory pathway, except for olfaction. The thalamus does not just pass the information on, it also processes that information. For example, the portion of the thalamus that receives visual information will influence what visual stimuli are important, or what receives attention.
The cerebrum also sends information down to the thalamus, which usually communicates motor commands. This involves interactions with the cerebellum and other nuclei in the brain stem. The cerebrum interacts with the basal nuclei, which involves connections with the thalamus. The primary output of the basal nuclei is to the thalamus, which relays that output to the cerebral cortex. The cortex also sends information to the thalamus that will then influence the effects of the basal nuclei.
Inferior and slightly anterior to the thalamus is the hypothalamus , the other major region of the diencephalon. The hypothalamus is a collection of nuclei that are largely involved in regulating homeostasis. The hypothalamus is the executive region in charge of the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system through its regulation of the anterior pituitary gland. Other parts of the hypothalamus are involved in memory and emotion as part of the limbic system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?