| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a type of epithelium that appears to be stratified but instead consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and differently sized columnar cells. In pseudostratified epithelium, nuclei of neighboring cells appear at different levels rather than clustered in the basal end. The arrangement gives the appearance of stratification; but in fact all the cells are in contact with the basal lamina, although some do not reach the apical surface. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is found in the respiratory tract, where some of these cells have cilia.
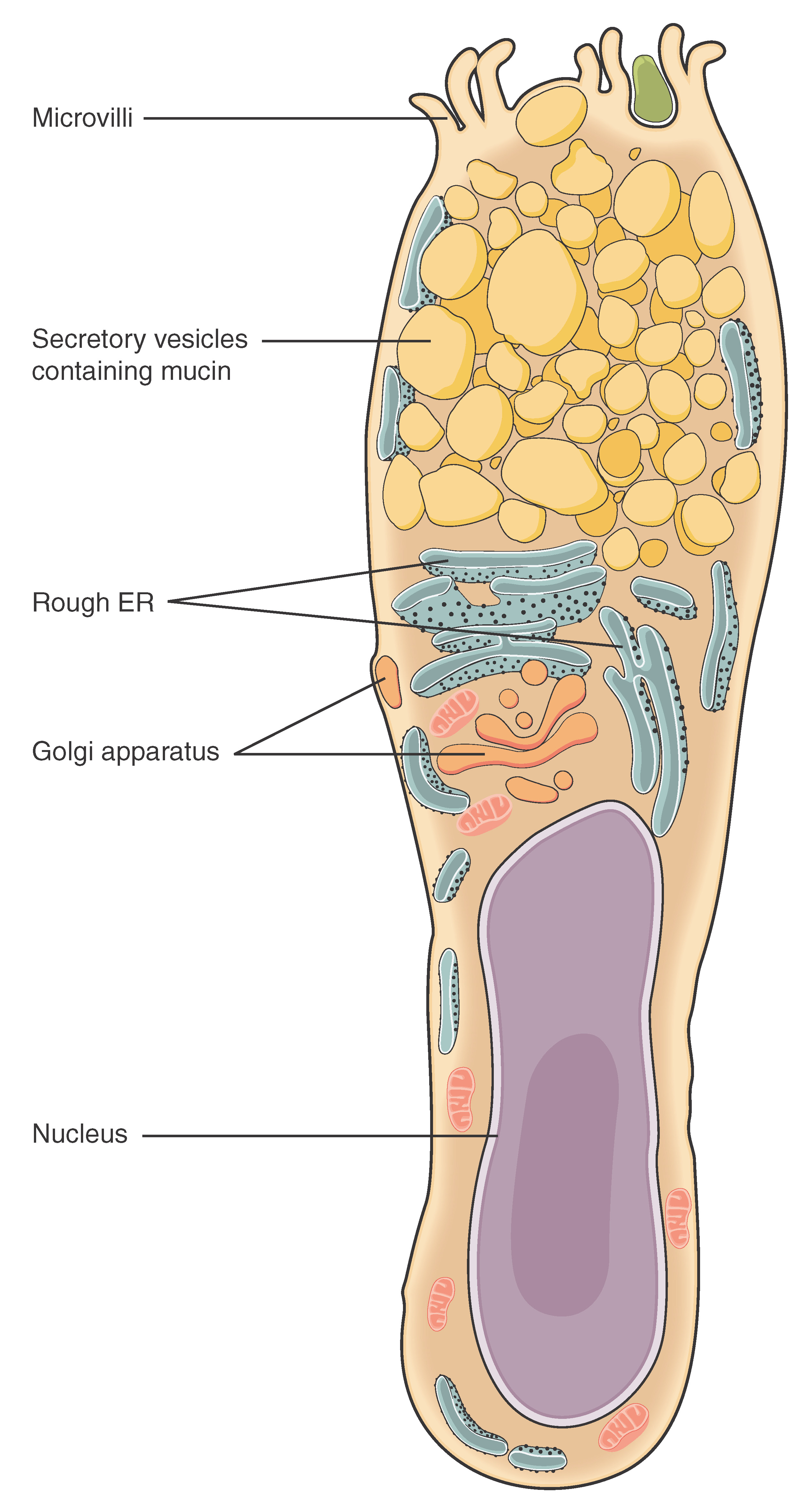
Both simple and pseudostratified columnar epithelia are heterogeneous epithelia because they include additional types of cells interspersed among the epithelial cells. For example, a goblet cell is a mucous-secreting unicellular “gland” interspersed between the columnar epithelial cells of mucous membranes ( [link] ).
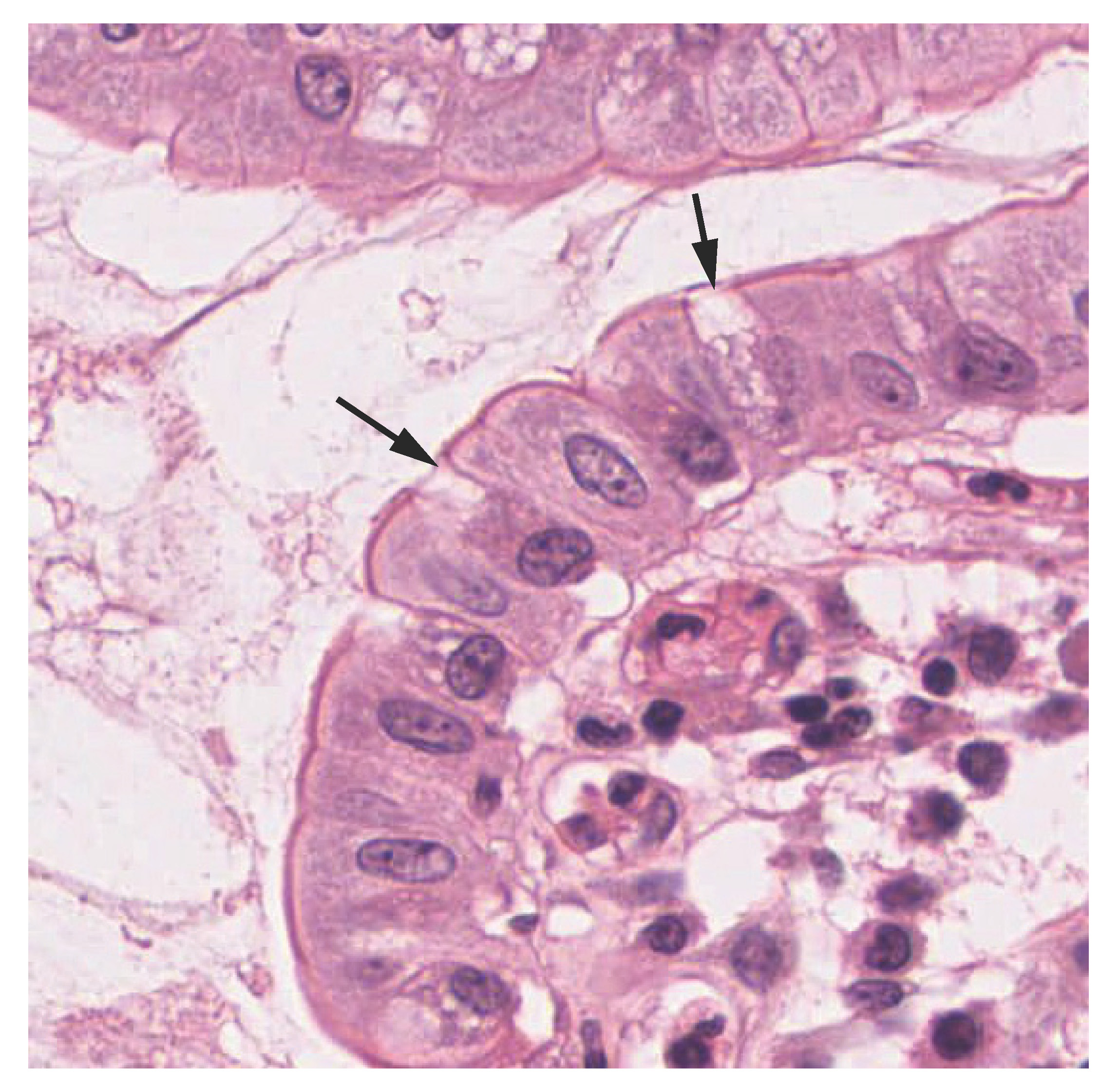
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail.
A stratified epithelium consists of several stacked layers of cells. This epithelium protects against physical and chemical wear and tear. The stratified epithelium is named by the shape of the most apical layer of cells, closest to the free space. Stratified squamous epithelium is the most common type of stratified epithelium in the human body. The apical cells are squamous, whereas the basal layer contains either columnar or cuboidal cells. The top layer may be covered with dead cells filled with keratin. Mammalian skin is an example of this dry, keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. The lining of the mouth cavity is an example of an unkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. Stratified cuboidal epithelium and stratified columnar epithelium can also be found in certain glands and ducts, but are uncommon in the human body.
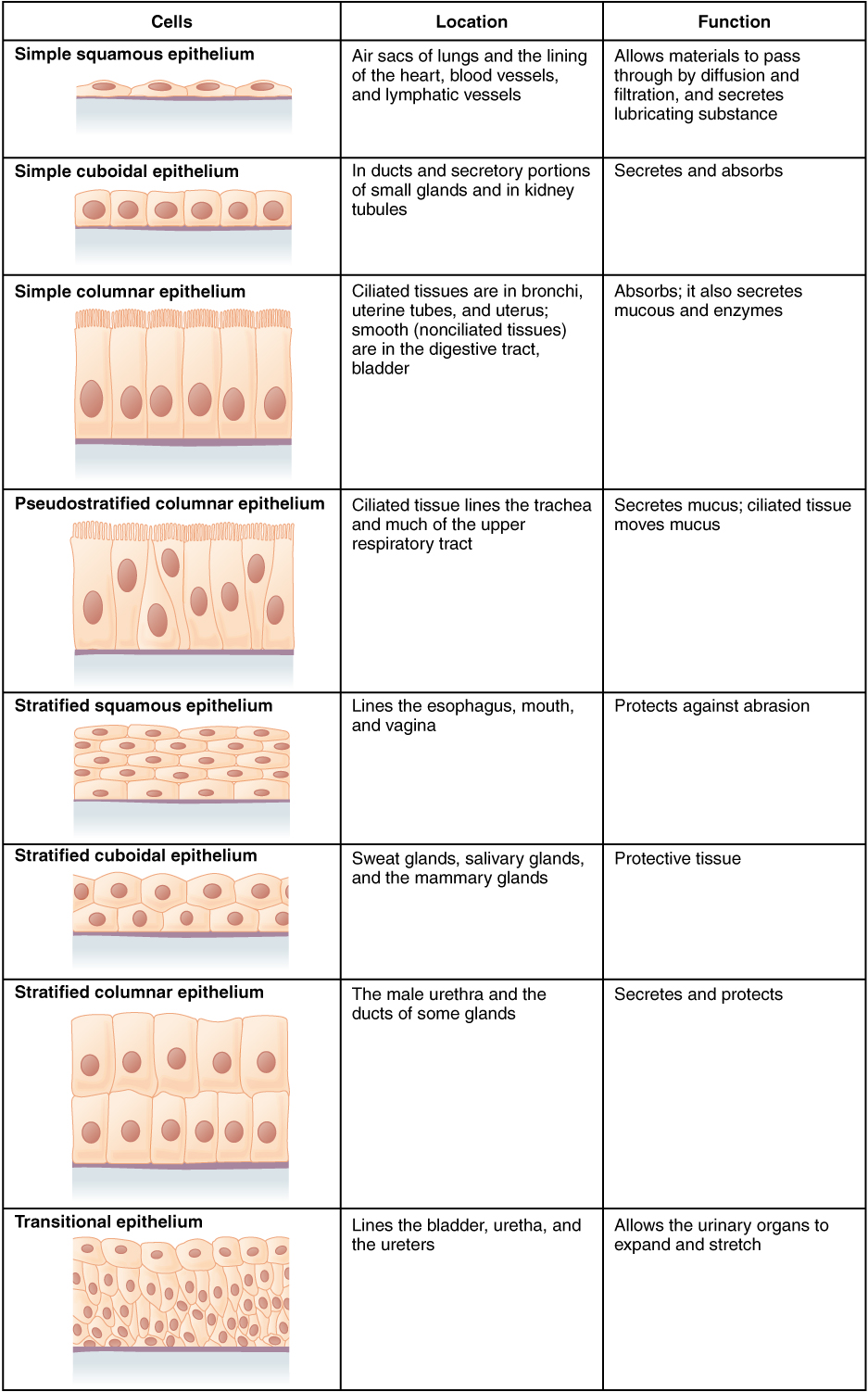
Another kind of stratified epithelium is transitional epithelium , so-called because of the gradual changes in the shapes of the apical cells as the bladder fills with urine. It is found only in the urinary system, specifically the ureters and urinary bladder. When the bladder is empty, this epithelium is convoluted and has cuboidal apical cells with convex, umbrella shaped, apical surfaces. As the bladder fills with urine, this epithelium loses its convolutions and the apical cells transition from cuboidal to squamous. It appears thicker and more multi-layered when the bladder is empty, and more stretched out and less stratified when the bladder is full and distended. [link] summarizes the different categories of epithelial cell tissue cells.
Watch this video to find out more about the anatomy of epithelial tissues. Where in the body would one find non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?