| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Recall that the heart’s contraction cycle follows a dual pattern of circulation—the pulmonary and systemic circuits—because of the pairs of chambers that pump blood into the circulation. In order to develop a more precise understanding of cardiac function, it is first necessary to explore the internal anatomical structures in more detail.
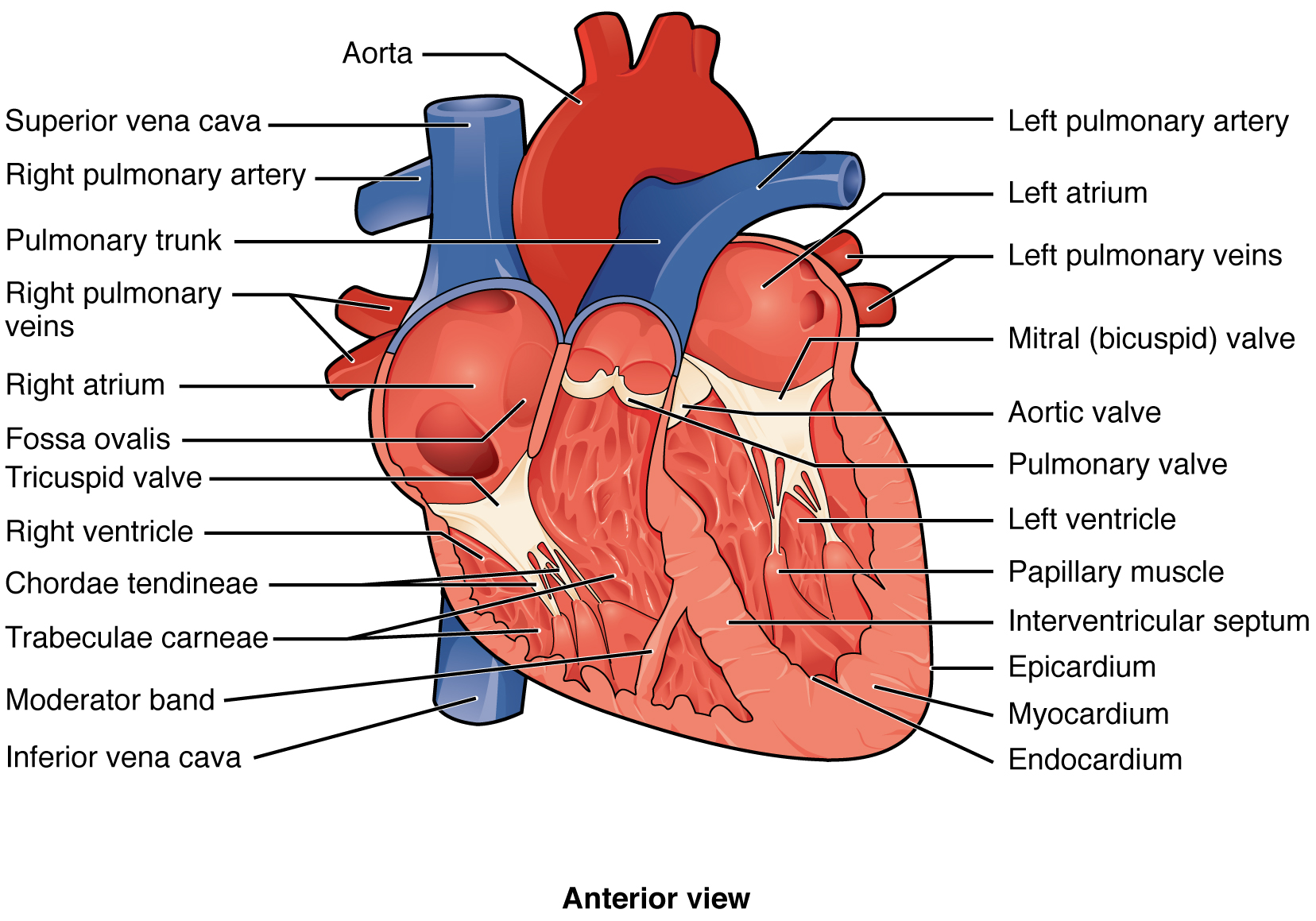
The word septum is derived from the Latin for “something that encloses;” in this case, a septum (plural = septa) refers to a wall or partition that divides the heart into chambers. The septa are physical extensions of the myocardium lined with endocardium. Located between the two atria is the interatrial septum . Normally in an adult heart, the interatrial septum bears an oval-shaped depression known as the fossa ovalis , a remnant of an opening in the fetal heart known as the foramen ovale . The foramen ovale allowed blood in the fetal heart to pass directly from the right atrium to the left atrium, allowing some blood to bypass the pulmonary circuit. Within seconds after birth, a flap of tissue known as the septum primum that previously acted as a valve closes the foramen ovale and establishes the typical cardiac circulation pattern.
Between the two ventricles is a second septum known as the interventricular septum . Unlike the interatrial septum, the interventricular septum is normally intact after its formation during fetal development. It is substantially thicker than the interatrial septum, since the ventricles generate far greater pressure when they contract.
The septum between the atria and ventricles is known as the atrioventricular septum . It is marked by the presence of four openings that allow blood to move from the atria into the ventricles and from the ventricles into the pulmonary trunk and aorta. Located in each of these openings between the atria and ventricles is a valve , a specialized structure that ensures one-way flow of blood. The valves between the atria and ventricles are known generically as atrioventricular valves . The valves at the openings that lead to the pulmonary trunk and aorta are known generically as semilunar valves . The interventricular septum is visible in [link] . In this figure, the atrioventricular septum has been removed to better show the bicupid and tricuspid valves; the interatrial septum is not visible, since its location is covered by the aorta and pulmonary trunk. Since these openings and valves structurally weaken the atrioventricular septum, the remaining tissue is heavily reinforced with dense connective tissue called the cardiac skeleton , or skeleton of the heart. It includes four rings that surround the openings between the atria and ventricles, and the openings to the pulmonary trunk and aorta, and serve as the point of attachment for the heart valves. The cardiac skeleton also provides an important boundary in the heart electrical conduction system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?