| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
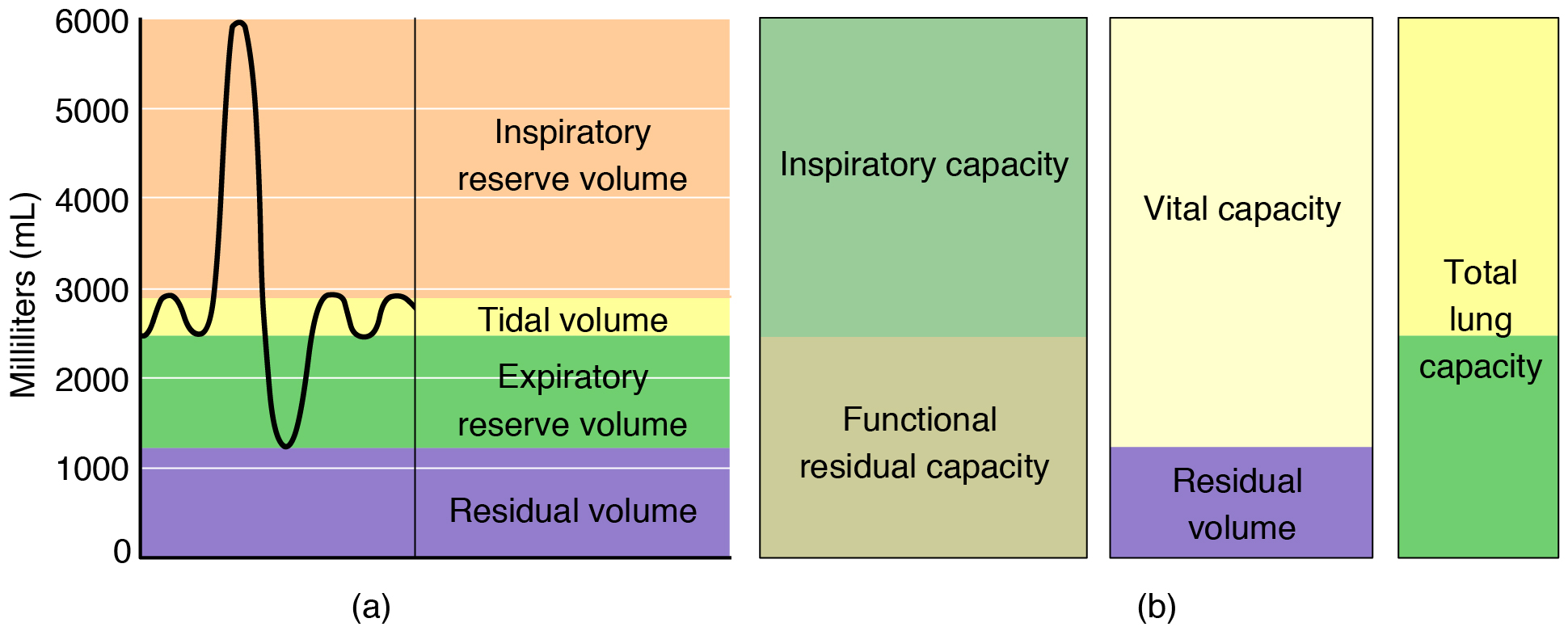
Respiratory capacity is the combination of two or more selected volumes, which further describes the amount of air in the lungs during a given time. For example, total lung capacity (TLC) is the sum of all of the lung volumes (TV, ERV, IRV, and RV), which represents the total amount of air a person can hold in the lungs after a forceful inhalation. TLC is about 6000 mL air for men, and about 4200 mL for women. Vital capacity (VC) is the amount of air a person can move into or out of his or her lungs, and is the sum of all of the volumes except residual volume (TV, ERV, and IRV), which is between 4000 and 5000 milliliters. Inspiratory capacity (IC) is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled past a normal tidal expiration, is the sum of the tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see [link] ).
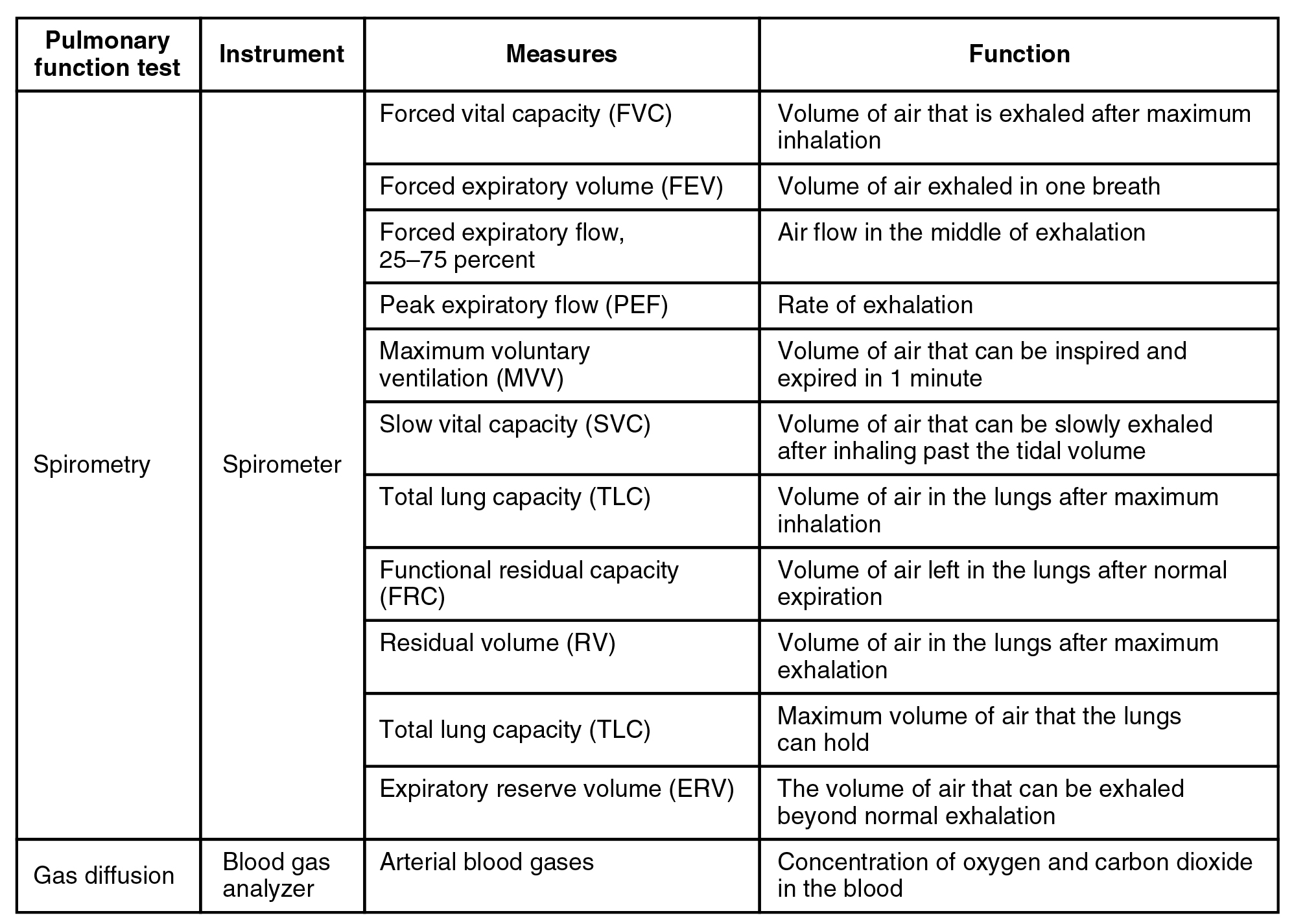
Watch this video to learn more about lung volumes and spirometers. Explain how spirometry test results can be used to diagnose respiratory diseases or determine the effectiveness of disease treatment.
In addition to the air that creates respiratory volumes, the respiratory system also contains anatomical dead space , which is air that is present in the airway that never reaches the alveoli and therefore never participates in gas exchange. Alveolar dead space involves air found within alveoli that are unable to function, such as those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow. Total dead space is the anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space together, and represents all of the air in the respiratory system that is not being used in the gas exchange process.
Breathing usually occurs without thought, although at times you can consciously control it, such as when you swim under water, sing a song, or blow bubbles. The respiratory rate is the total number of breaths, or respiratory cycles, that occur each minute. Respiratory rate can be an important indicator of disease, as the rate may increase or decrease during an illness or in a disease condition. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to changes in carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH levels in the blood.
The normal respiratory rate of a child decreases from birth to adolescence. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?