| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Dilation and constriction of the airway are achieved through nervous control by the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. The parasympathetic system causes bronchoconstriction , whereas the sympathetic nervous system stimulates bronchodilation . Reflexes such as coughing, and the ability of the lungs to regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, also result from this autonomic nervous system control. Sensory nerve fibers arise from the vagus nerve, and from the second to fifth thoracic ganglia. The pulmonary plexus is a region on the lung root formed by the entrance of the nerves at the hilum. The nerves then follow the bronchi in the lungs and branch to innervate muscle fibers, glands, and blood vessels.
Each lung is enclosed within a cavity that is surrounded by the pleura. The pleura (plural = pleurae) is a serous membrane that surrounds the lung. The right and left pleurae, which enclose the right and left lungs, respectively, are separated by the mediastinum. The pleurae consist of two layers. The visceral pleura is the layer that is superficial to the lungs, and extends into and lines the lung fissures ( [link] ). In contrast, the parietal pleura is the outer layer that connects to the thoracic wall, the mediastinum, and the diaphragm. The visceral and parietal pleurae connect to each other at the hilum. The pleural cavity is the space between the visceral and parietal layers.
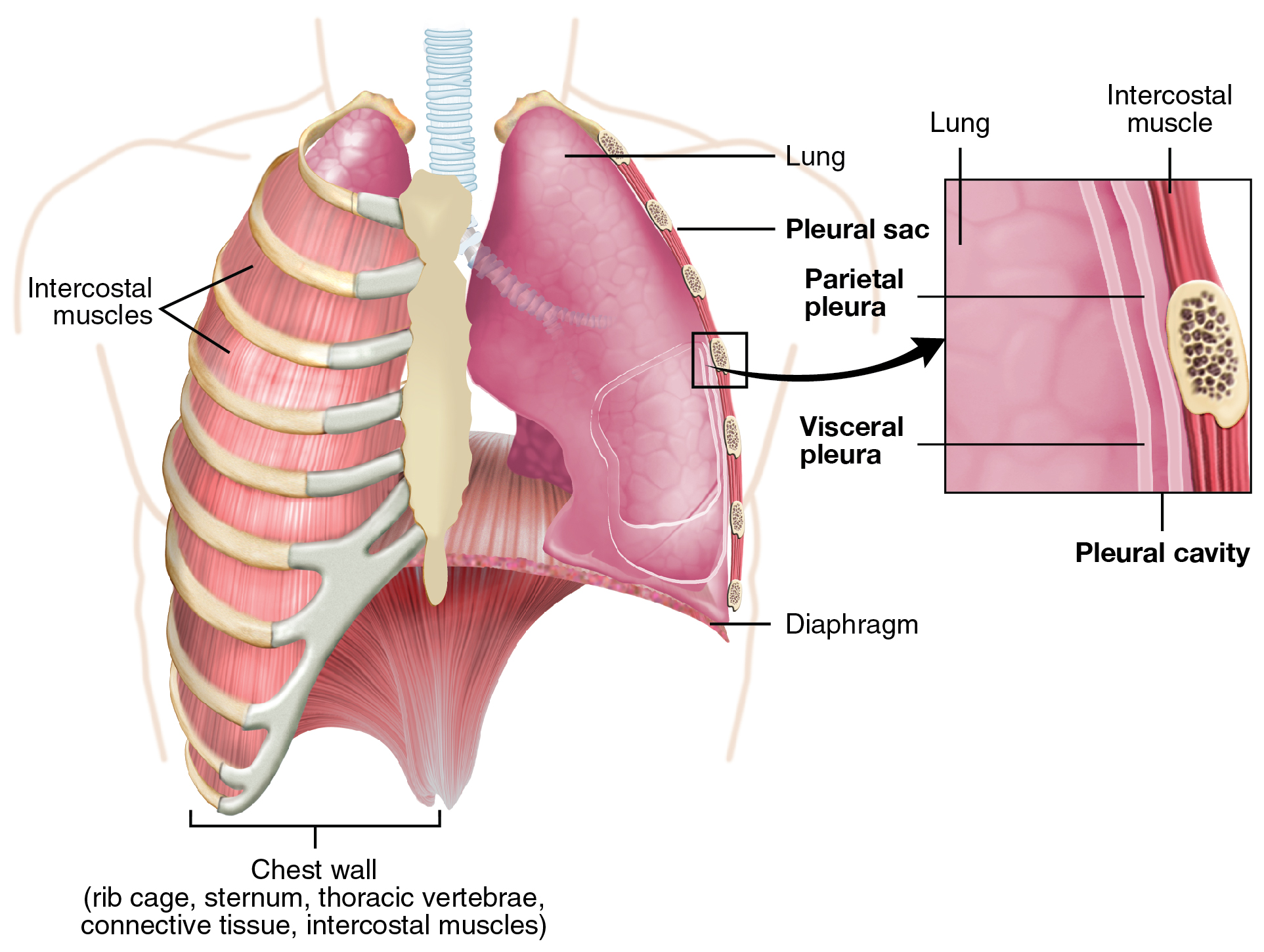
The pleurae perform two major functions: They produce pleural fluid and create cavities that separate the major organs. Pleural fluid is secreted by mesothelial cells from both pleural layers and acts to lubricate their surfaces. This lubrication reduces friction between the two layers to prevent trauma during breathing, and creates surface tension that helps maintain the position of the lungs against the thoracic wall. This adhesive characteristic of the pleural fluid causes the lungs to enlarge when the thoracic wall expands during ventilation, allowing the lungs to fill with air. The pleurae also create a division between major organs that prevents interference due to the movement of the organs, while preventing the spread of infection.
Tobacco and second-hand smoke are considered to be carcinogenic. Exposure to second-hand smoke can cause lung cancer in individuals who are not tobacco users themselves. It is estimated that the risk of developing lung cancer is increased by up to 30 percent in nonsmokers who live with an individual who smokes in the house, as compared to nonsmokers who are not regularly exposed to second-hand smoke. Children are especially affected by second-hand smoke. Children who live with an individual who smokes inside the home have a larger number of lower respiratory infections, which are associated with hospitalizations, and higher risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Second-hand smoke in the home has also been linked to a greater number of ear infections in children, as well as worsening symptoms of asthma.
The lungs are the major organs of the respiratory system and are responsible for performing gas exchange. The lungs are paired and separated into lobes; The left lung consists of two lobes, whereas the right lung consists of three lobes. Blood circulation is very important, as blood is required to transport oxygen from the lungs to other tissues throughout the body. The function of the pulmonary circulation is to aid in gas exchange. The pulmonary artery provides deoxygenated blood to the capillaries that form respiratory membranes with the alveoli, and the pulmonary veins return newly oxygenated blood to the heart for further transport throughout the body. The lungs are innervated by the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, which coordinate the bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction of the airways. The lungs are enclosed by the pleura, a membrane that is composed of visceral and parietal pleural layers. The space between these two layers is called the pleural cavity. The mesothelial cells of the pleural membrane create pleural fluid, which serves as both a lubricant (to reduce friction during breathing) and as an adhesive to adhere the lungs to the thoracic wall (to facilitate movement of the lungs during ventilation).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?