| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
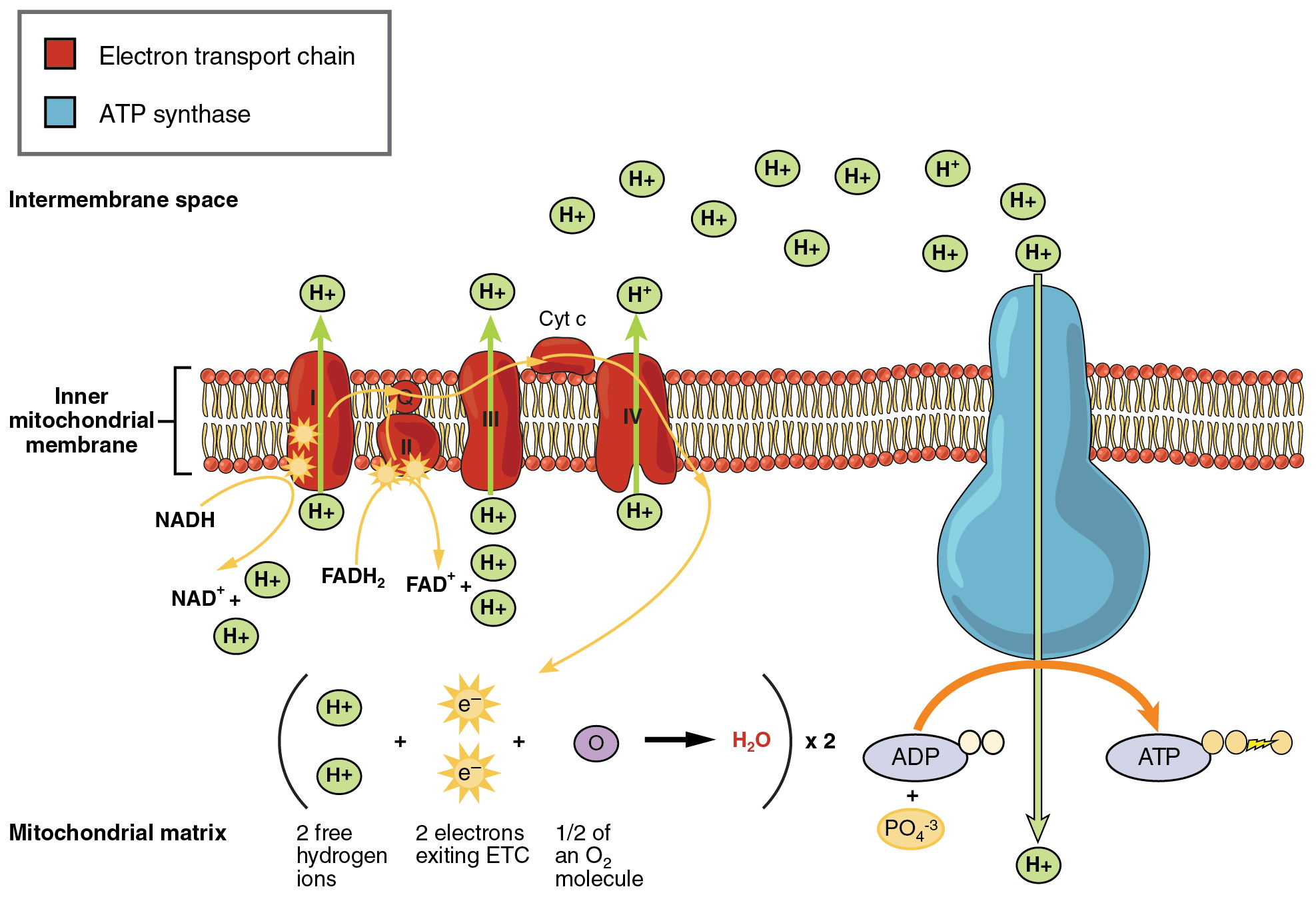
The electron transport chain (ETC) uses the NADH and FADH 2 produced by the Krebs cycle to generate ATP. Electrons from NADH and FADH 2 are transferred through protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane by a series of enzymatic reactions. The electron transport chain consists of a series of four enzyme complexes (Complex I – Complex IV) and two coenzymes (ubiquinone and Cytochrome c), which act as electron carriers and proton pumps used to transfer H + ions into the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes ( [link] ). The ETC couples the transfer of electrons between a donor (like NADH) and an electron acceptor (like O 2 ) with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, enabling the process of oxidative phosphorylation . In the presence of oxygen, energy is passed, stepwise, through the electron carriers to collect gradually the energy needed to attach a phosphate to ADP and produce ATP. The role of molecular oxygen, O 2 , is as the terminal electron acceptor for the ETC. This means that once the electrons have passed through the entire ETC, they must be passed to another, separate molecule. These electrons, O 2 , and H + ions from the matrix combine to form new water molecules. This is the basis for your need to breathe in oxygen. Without oxygen, electron flow through the ETC ceases.
Watch this video to learn about the electron transport chain.
The electrons released from NADH and FADH 2 are passed along the chain by each of the carriers, which are reduced when they receive the electron and oxidized when passing it on to the next carrier. Each of these reactions releases a small amount of energy, which is used to pump H + ions across the inner membrane. The accumulation of these protons in the space between the membranes creates a proton gradient with respect to the mitochondrial matrix.
Also embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane is an amazing protein pore complex called ATP synthase . Effectively, it is a turbine that is powered by the flow of H + ions across the inner membrane down a gradient and into the mitochondrial matrix. As the H + ions traverse the complex, the shaft of the complex rotates. This rotation enables other portions of ATP synthase to encourage ADP and P i to create ATP. In accounting for the total number of ATP produced per glucose molecule through aerobic respiration, it is important to remember the following points:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?