| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In addition to the lymph nodes, the spleen is a major secondary lymphoid organ ( [link] ). It is about 12 cm (5 in) long and is attached to the lateral border of the stomach via the gastrosplenic ligament. The spleen is a fragile organ without a strong capsule, and is dark red due to its extensive vascularization. The spleen is sometimes called the “filter of the blood” because of its extensive vascularization and the presence of macrophages and dendritic cells that remove microbes and other materials from the blood, including dying red blood cells. The spleen also functions as the location of immune responses to blood-borne pathogens.
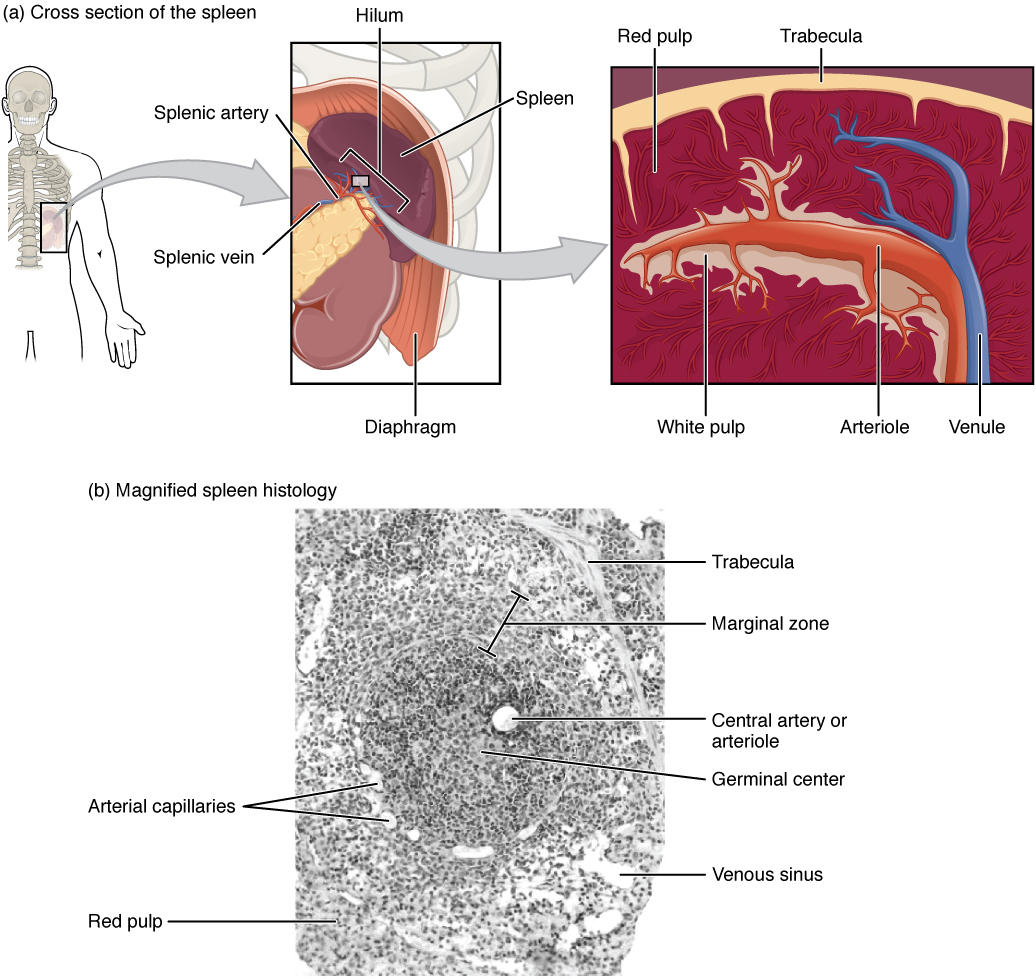
The spleen is also divided by trabeculae of connective tissue, and within each splenic nodule is an area of red pulp, consisting of mostly red blood cells, and white pulp, which resembles the lymphoid follicles of the lymph nodes. Upon entering the spleen, the splenic artery splits into several arterioles (surrounded by white pulp) and eventually into sinusoids. Blood from the capillaries subsequently collects in the venous sinuses and leaves via the splenic vein. The red pulp consists of reticular fibers with fixed macrophages attached, free macrophages, and all of the other cells typical of the blood, including some lymphocytes. The white pulp surrounds a central arteriole and consists of germinal centers of dividing B cells surrounded by T cells and accessory cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells. Thus, the red pulp primarily functions as a filtration system of the blood, using cells of the relatively nonspecific immune response, and white pulp is where adaptive T and B cell responses are mounted.
The other lymphoid tissues, the lymphoid nodules , have a simpler architecture than the spleen and lymph nodes in that they consist of a dense cluster of lymphocytes without a surrounding fibrous capsule. These nodules are located in the respiratory and digestive tracts, areas routinely exposed to environmental pathogens.
Tonsils are lymphoid nodules located along the inner surface of the pharynx and are important in developing immunity to oral pathogens ( [link] ). The tonsil located at the back of the throat, the pharyngeal tonsil, is sometimes referred to as the adenoid when swollen. Such swelling is an indication of an active immune response to infection. Histologically, tonsils do not contain a complete capsule, and the epithelial layer invaginates deeply into the interior of the tonsil to form tonsillar crypts. These structures, which accumulate all sorts of materials taken into the body through eating and breathing, actually “encourage” pathogens to penetrate deep into the tonsillar tissues where they are acted upon by numerous lymphoid follicles and eliminated. This seems to be the major function of tonsils—to help children’s bodies recognize, destroy, and develop immunity to common environmental pathogens so that they will be protected in their later lives. Tonsils are often removed in those children who have recurring throat infections, especially those involving the palatine tonsils on either side of the throat, whose swelling may interfere with their breathing and/or swallowing.
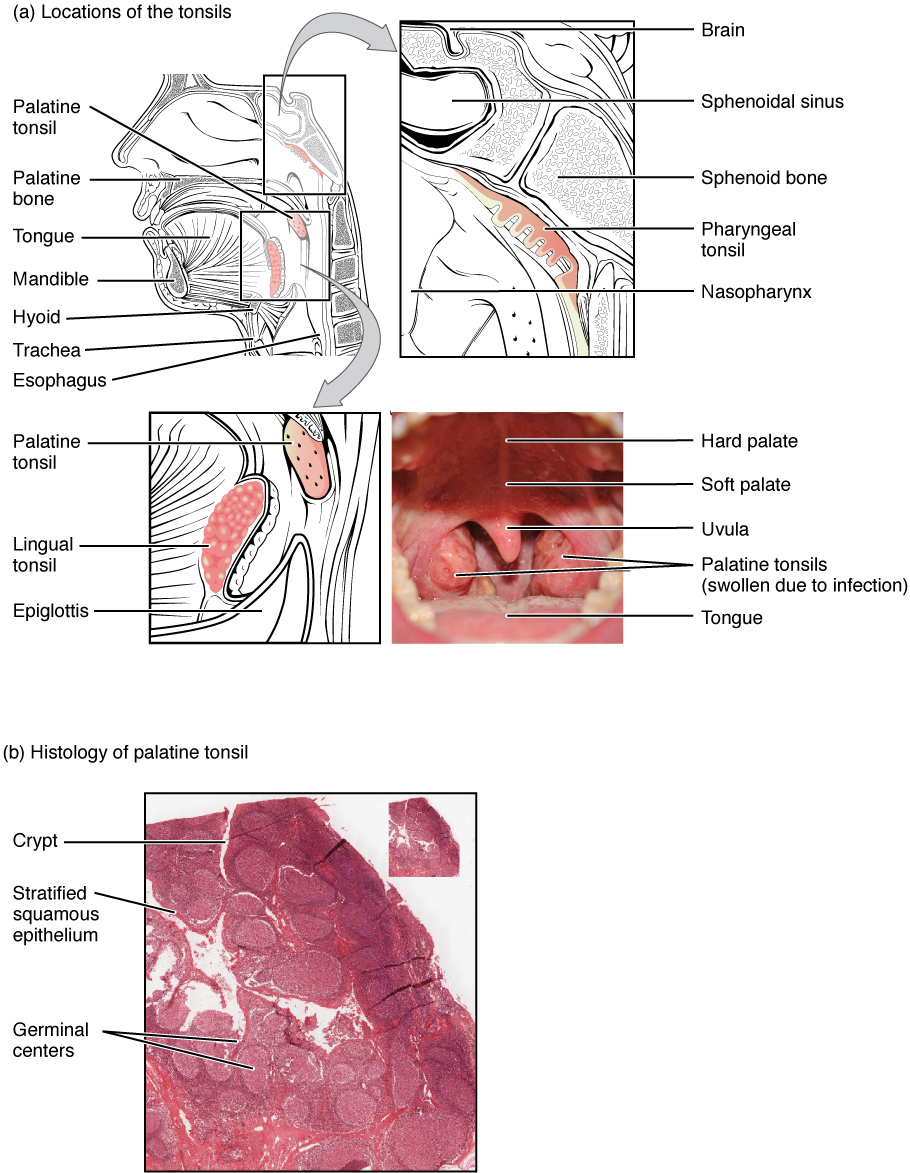
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail.
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) consists of an aggregate of lymphoid follicles directly associated with the mucous membrane epithelia. MALT makes up dome-shaped structures found underlying the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, breast tissue, lungs, and eyes. Peyer’s patches, a type of MALT in the small intestine, are especially important for immune responses against ingested substances ( [link] ). Peyer’s patches contain specialized endothelial cells called M (or microfold) cells that sample material from the intestinal lumen and transport it to nearby follicles so that adaptive immune responses to potential pathogens can be mounted.
_Nodule.jpg)
Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) consists of lymphoid follicular structures with an overlying epithelial layer found along the bifurcations of the bronchi, and between bronchi and arteries. They also have the typically less-organized structure of other lymphoid nodules. These tissues, in addition to the tonsils, are effective against inhaled pathogens.
The lymphatic system is a series of vessels, ducts, and trunks that remove interstitial fluid from the tissues and return it the blood. The lymphatics are also used to transport dietary lipids and cells of the immune system. Cells of the immune system all come from the hematopoietic system of the bone marrow. Primary lymphoid organs, the bone marrow and thymus gland, are the locations where lymphocytes of the adaptive immune system proliferate and mature. Secondary lymphoid organs are site in which mature lymphocytes congregate to mount immune responses. Many immune system cells use the lymphatic and circulatory systems for transport throughout the body to search for and then protect against pathogens.
Visit this website for an overview of the lymphatic system. What are the three main components of the lymphatic system?
The three main components are the lymph vessels, the lymph nodes, and the lymph.
Visit this website to learn about the many different cell types in the immune system and their very specialized jobs. What is the role of the dendritic cell in infection by HIV?
The dendritic cell transports the virus to a lymph node.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?