| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Fats (or triglycerides) within the body are ingested as food or synthesized by adipocytes or hepatocytes from carbohydrate precursors ( [link] ). Lipid metabolism entails the oxidation of fatty acids to either generate energy or synthesize new lipids from smaller constituent molecules. Lipid metabolism is associated with carbohydrate metabolism, as products of glucose (such as acetyl CoA) can be converted into lipids.
_Is_Broken_Down_Into_Monoglycerides_(b).jpg)
Lipid metabolism begins in the intestine where ingested triglycerides are broken down into smaller chain fatty acids and subsequently into monoglyceride molecules (see [link] b ) by pancreatic lipases , enzymes that break down fats after they are emulsified by bile salts . When food reaches the small intestine in the form of chyme, a digestive hormone called cholecystokinin (CCK) is released by intestinal cells in the intestinal mucosa. CCK stimulates the release of pancreatic lipase from the pancreas and stimulates the contraction of the gallbladder to release stored bile salts into the intestine. CCK also travels to the brain, where it can act as a hunger suppressant.
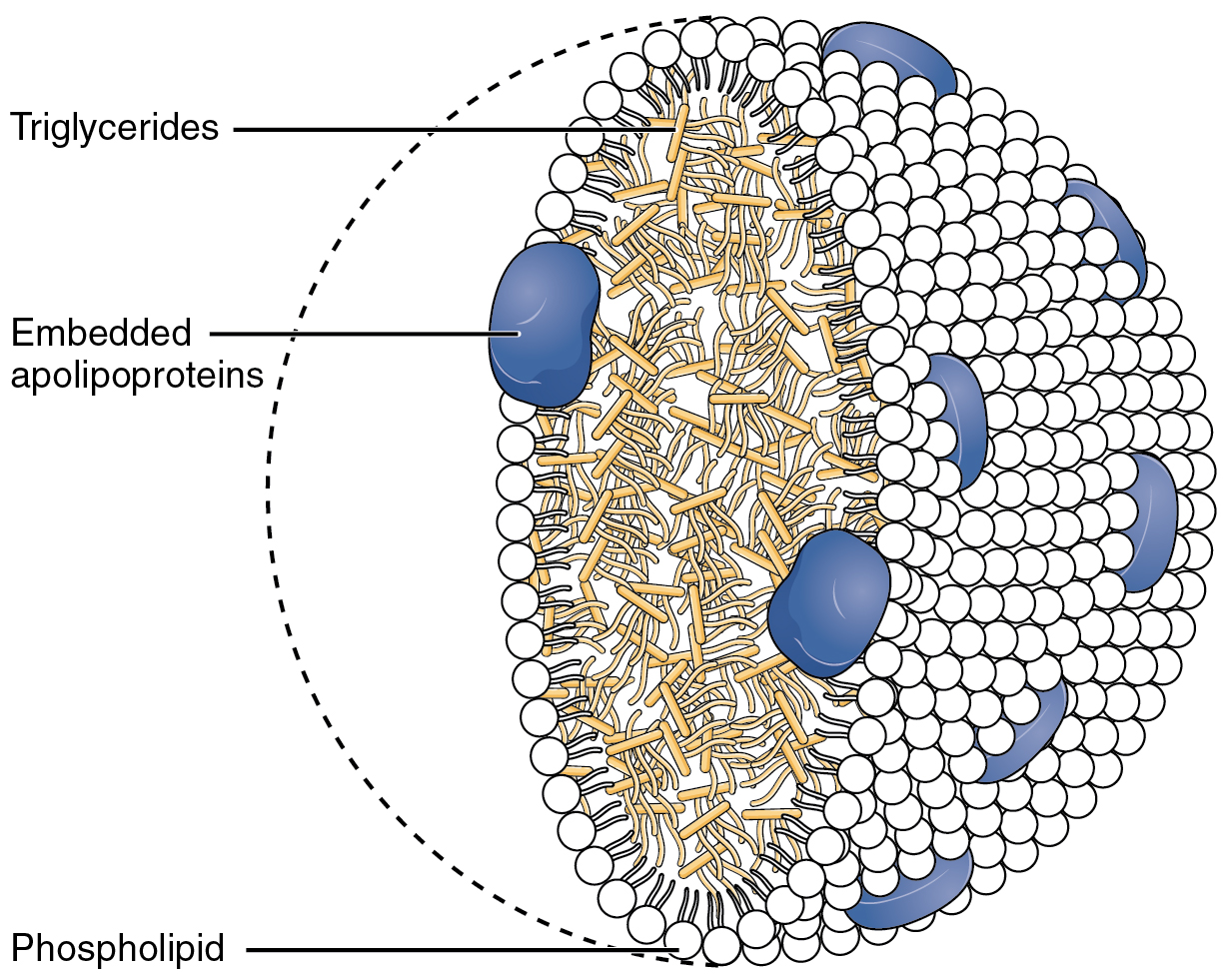
Together, the pancreatic lipases and bile salts break down triglycerides into free fatty acids. These fatty acids can be transported across the intestinal membrane. However, once they cross the membrane, they are recombined to again form triglyceride molecules. Within the intestinal cells, these triglycerides are packaged along with cholesterol molecules in phospholipid vesicles called chylomicrons ( [link] ). The chylomicrons enable fats and cholesterol to move within the aqueous environment of your lymphatic and circulatory systems. Chylomicrons leave the enterocytes by exocytosis and enter the lymphatic system via lacteals in the villi of the intestine. From the lymphatic system, the chylomicrons are transported to the circulatory system. Once in the circulation, they can either go to the liver or be stored in fat cells (adipocytes) that comprise adipose (fat) tissue found throughout the body.
To obtain energy from fat, triglycerides must first be broken down by hydrolysis into their two principal components, fatty acids and glycerol. This process, called lipolysis , takes place in the cytoplasm. The resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β-oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Krebs cycle. The glycerol that is released from triglycerides after lipolysis directly enters the glycolysis pathway as DHAP. Because one triglyceride molecule yields three fatty acid molecules with as much as 16 or more carbons in each one, fat molecules yield more energy than carbohydrates and are an important source of energy for the human body. Triglycerides yield more than twice the energy per unit mass when compared to carbohydrates and proteins. Therefore, when glucose levels are low, triglycerides can be converted into acetyl CoA molecules and used to generate ATP through aerobic respiration.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?