| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail.
The pharynx is a tube formed by skeletal muscle and lined by mucous membrane that is continuous with that of the nasal cavities (see [link] ). The pharynx is divided into three major regions: the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynx ( [link] ).
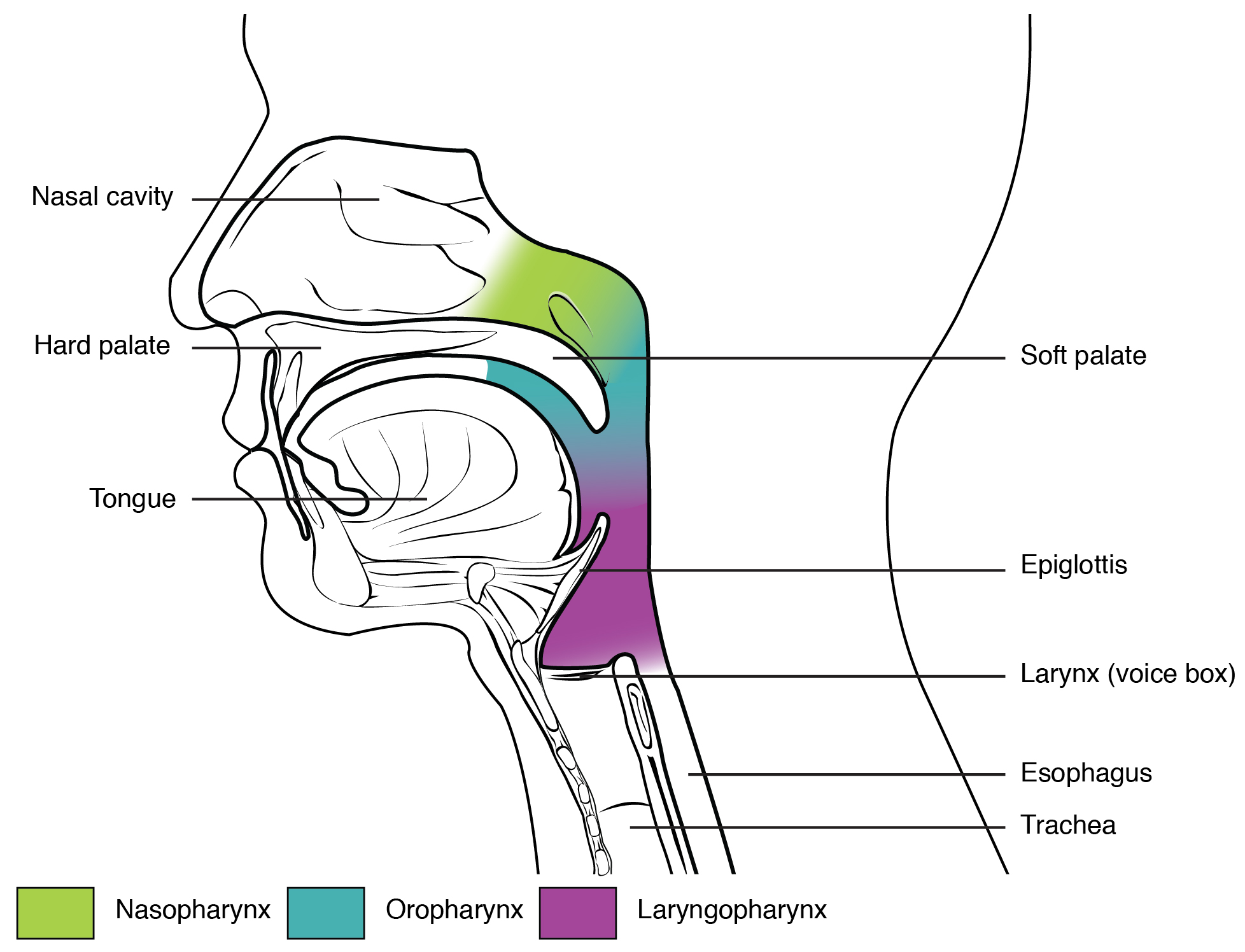
The nasopharynx is flanked by the conchae of the nasal cavity, and it serves only as an airway. At the top of the nasopharynx are the pharyngeal tonsils. A pharyngeal tonsil , also called an adenoid, is an aggregate of lymphoid reticular tissue similar to a lymph node that lies at the superior portion of the nasopharynx. The function of the pharyngeal tonsil is not well understood, but it contains a rich supply of lymphocytes and is covered with ciliated epithelium that traps and destroys invading pathogens that enter during inhalation. The pharyngeal tonsils are large in children, but interestingly, tend to regress with age and may even disappear. The uvula is a small bulbous, teardrop-shaped structure located at the apex of the soft palate. Both the uvula and soft palate move like a pendulum during swallowing, swinging upward to close off the nasopharynx to prevent ingested materials from entering the nasal cavity. In addition, auditory (Eustachian) tubes that connect to each middle ear cavity open into the nasopharynx. This connection is why colds often lead to ear infections.
The oropharynx is a passageway for both air and food. The oropharynx is bordered superiorly by the nasopharynx and anteriorly by the oral cavity. The fauces is the opening at the connection between the oral cavity and the oropharynx. As the nasopharynx becomes the oropharynx, the epithelium changes from pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium to stratified squamous epithelium. The oropharynx contains two distinct sets of tonsils, the palatine and lingual tonsils. A palatine tonsil is one of a pair of structures located laterally in the oropharynx in the area of the fauces. The lingual tonsil is located at the base of the tongue. Similar to the pharyngeal tonsil, the palatine and lingual tonsils are composed of lymphoid tissue, and trap and destroy pathogens entering the body through the oral or nasal cavities.
The laryngopharynx is inferior to the oropharynx and posterior to the larynx. It continues the route for ingested material and air until its inferior end, where the digestive and respiratory systems diverge. The stratified squamous epithelium of the oropharynx is continuous with the laryngopharynx. Anteriorly, the laryngopharynx opens into the larynx, whereas posteriorly, it enters the esophagus.
The larynx is a cartilaginous structure inferior to the laryngopharynx that connects the pharynx to the trachea and helps regulate the volume of air that enters and leaves the lungs ( [link] ). The structure of the larynx is formed by several pieces of cartilage. Three large cartilage pieces—the thyroid cartilage (anterior), epiglottis (superior), and cricoid cartilage (inferior)—form the major structure of the larynx. The thyroid cartilage is the largest piece of cartilage that makes up the larynx. The thyroid cartilage consists of the laryngeal prominence , or “Adam’s apple,” which tends to be more prominent in males. The thick cricoid cartilage forms a ring, with a wide posterior region and a thinner anterior region. Three smaller, paired cartilages—the arytenoids, corniculates, and cuneiforms—attach to the epiglottis and the vocal cords and muscle that help move the vocal cords to produce speech.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?