| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In their most common form, many elements also contain the same number of neutrons as protons. The most common form of carbon, for example, has six neutrons as well as six protons, for a total of 12 subatomic particles in its nucleus. An element’s mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. So the most common form of carbon’s mass number is 12. (Electrons have so little mass that they do not appreciably contribute to the mass of an atom.) Carbon is a relatively light element. Uranium (U), in contrast, has a mass number of 238 and is referred to as a heavy metal. Its atomic number is 92 (it has 92 protons) but it contains 146 neutrons; it has the most mass of all the naturally occurring elements.
The periodic table of the elements , shown in [link] , is a chart identifying the 92 elements found in nature, as well as several larger, unstable elements discovered experimentally. The elements are arranged in order of their atomic number, with hydrogen and helium at the top of the table, and the more massive elements below. The periodic table is a useful device because for each element, it identifies the chemical symbol, the atomic number, and the mass number, while organizing elements according to their propensity to react with other elements. The number of protons and electrons in an element are equal. The number of protons and neutrons may be equal for some elements, but are not equal for all.
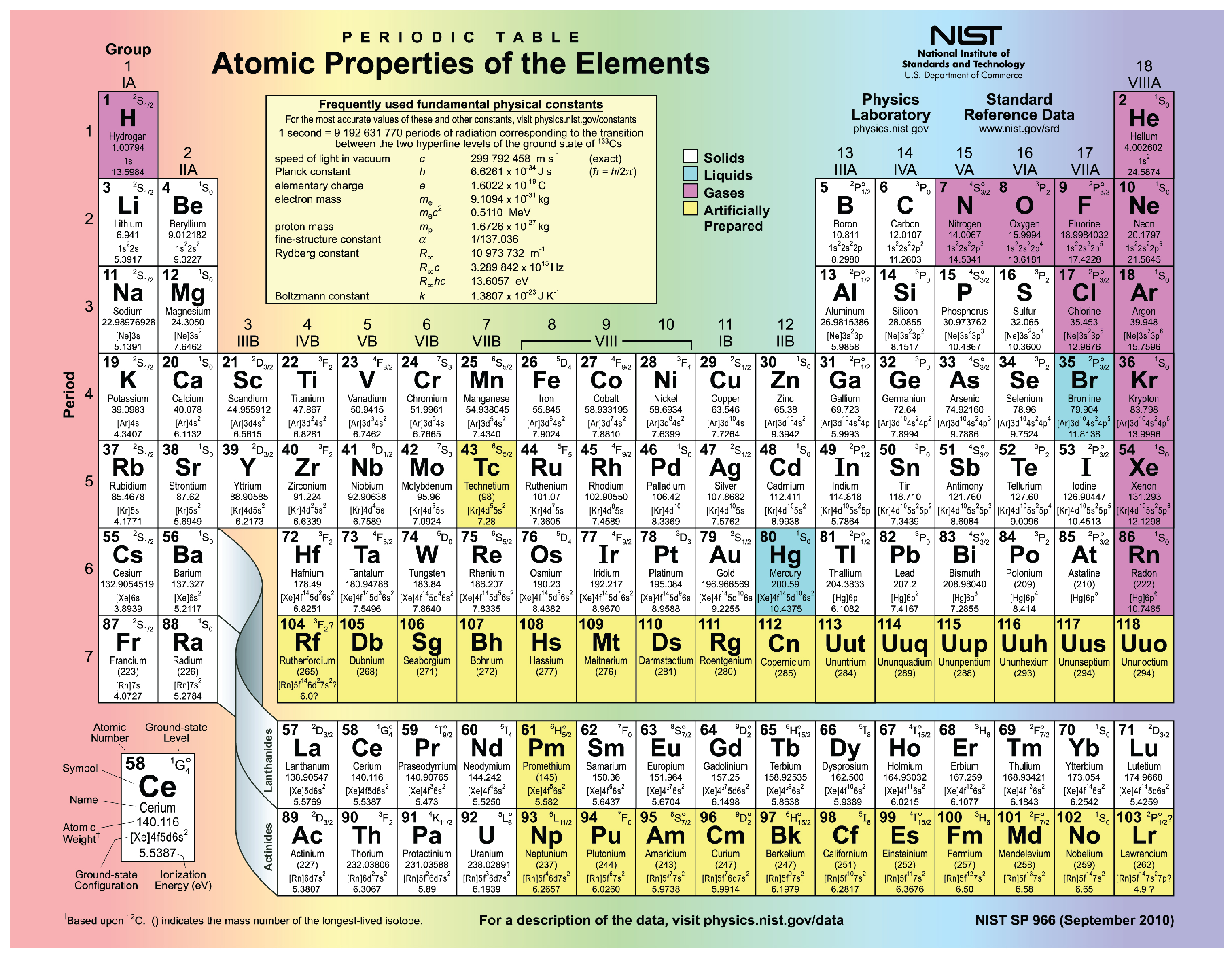
Visit this website to view the periodic table. In the periodic table of the elements, elements in a single column have the same number of electrons that can participate in a chemical reaction. These electrons are known as “valence electrons.” For example, the elements in the first column all have a single valence electron, an electron that can be “donated” in a chemical reaction with another atom. What is the meaning of a mass number shown in parentheses?
Although each element has a unique number of protons, it can exist as different isotopes. An isotope is one of the different forms of an element, distinguished from one another by different numbers of neutrons. The standard isotope of carbon is 12 C, commonly called carbon twelve. 12 C has six protons and six neutrons, for a mass number of twelve. All of the isotopes of carbon have the same number of protons; therefore, 13 C has seven neutrons, and 14 C has eight neutrons. The different isotopes of an element can also be indicated with the mass number hyphenated (for example, C-12 instead of 12 C). Hydrogen has three common isotopes, shown in [link] .
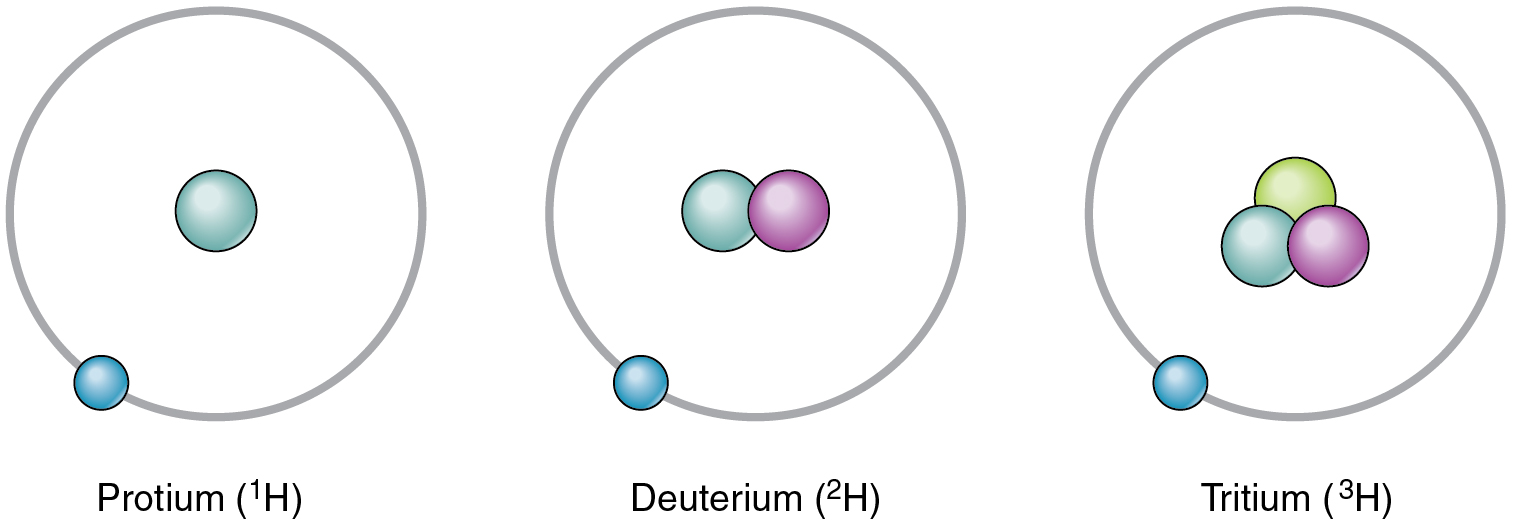
An isotope that contains more than the usual number of neutrons is referred to as a heavy isotope. An example is 14 C. Heavy isotopes tend to be unstable, and unstable isotopes are radioactive. A radioactive isotope is an isotope whose nucleus readily decays, giving off subatomic particles and electromagnetic energy. Different radioactive isotopes (also called radioisotopes) differ in their half-life, the time it takes for half of any size sample of an isotope to decay. For example, the half-life of tritium—a radioisotope of hydrogen—is about 12 years, indicating it takes 12 years for half of the tritium nuclei in a sample to decay. Excessive exposure to radioactive isotopes can damage human cells and even cause cancer and birth defects, but when exposure is controlled, some radioactive isotopes can be useful in medicine. For more information, see the Career Connections.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?