| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
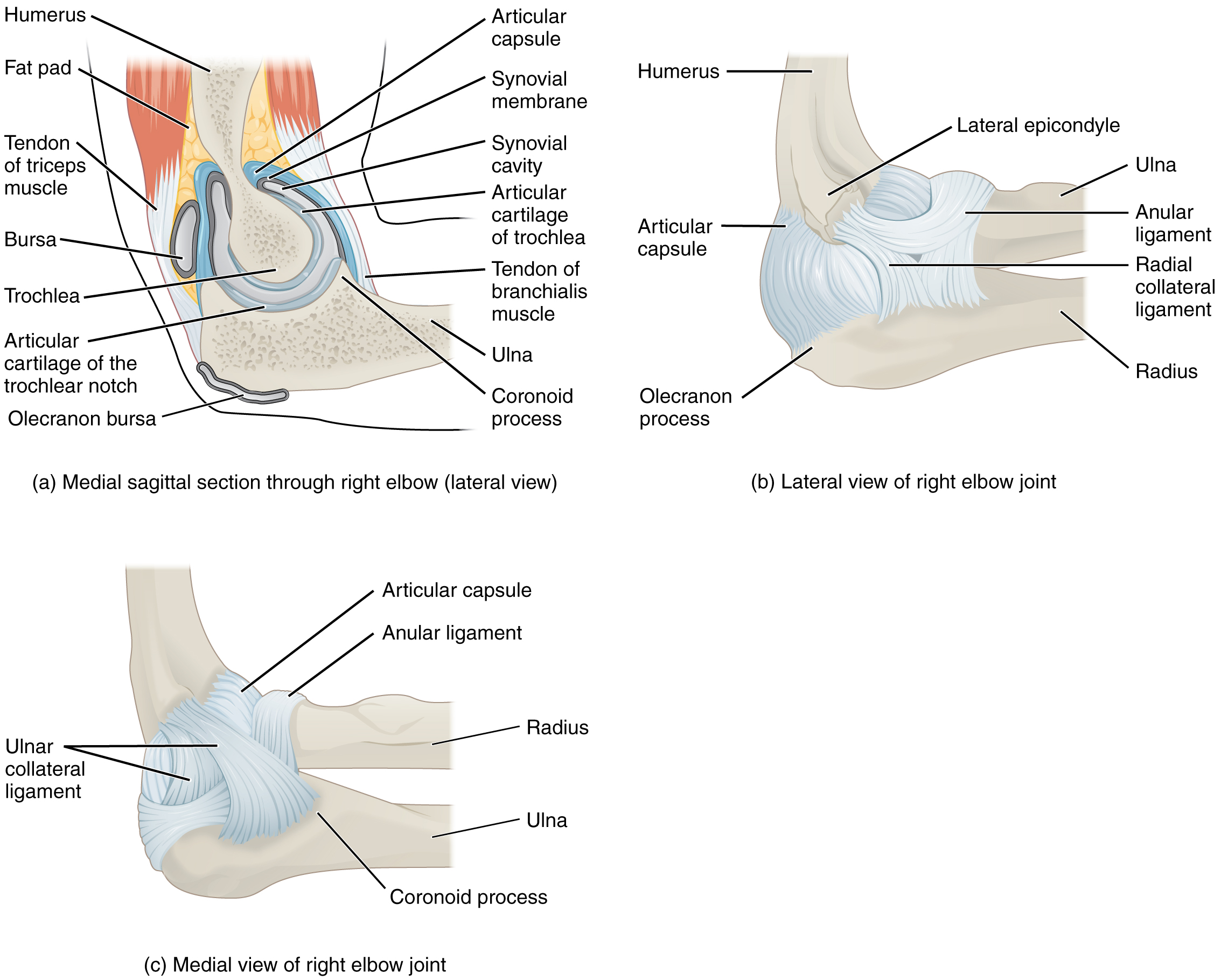
Watch this animation to learn more about the anatomy of the elbow joint. Which structures provide the main stability for the elbow?
Watch this video to learn more about the anatomy of the elbow joint, including bones, joints, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. What are the functions of the articular cartilage?
The hip joint is a multiaxial ball-and-socket joint between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the hip bone ( [link] ). The hip carries the weight of the body and thus requires strength and stability during standing and walking. For these reasons, its range of motion is more limited than at the shoulder joint.
The acetabulum is the socket portion of the hip joint. This space is deep and has a large articulation area for the femoral head, thus giving stability and weight bearing ability to the joint. The acetabulum is further deepened by the acetabular labrum , a fibrocartilage lip attached to the outer margin of the acetabulum. The surrounding articular capsule is strong, with several thickened areas forming intrinsic ligaments. These ligaments arise from the hip bone, at the margins of the acetabulum, and attach to the femur at the base of the neck. The ligaments are the iliofemoral ligament , pubofemoral ligament , and ischiofemoral ligament , all of which spiral around the head and neck of the femur. The ligaments are tightened by extension at the hip, thus pulling the head of the femur tightly into the acetabulum when in the upright, standing position. Very little additional extension of the thigh is permitted beyond this vertical position. These ligaments thus stabilize the hip joint and allow you to maintain an upright standing position with only minimal muscle contraction. Inside of the articular capsule, the ligament of the head of the femur (ligamentum teres) spans between the acetabulum and femoral head. This intracapsular ligament is normally slack and does not provide any significant joint support, but it does provide a pathway for an important artery that supplies the head of the femur.
The hip is prone to osteoarthritis, and thus was the first joint for which a replacement prosthesis was developed. A common injury in elderly individuals, particularly those with weakened bones due to osteoporosis, is a “broken hip,” which is actually a fracture of the femoral neck. This may result from a fall, or it may cause the fall. This can happen as one lower limb is taking a step and all of the body weight is placed on the other limb, causing the femoral neck to break and producing a fall. Any accompanying disruption of the blood supply to the femoral neck or head can lead to necrosis of these areas, resulting in bone and cartilage death. Femoral fractures usually require surgical treatment, after which the patient will need mobility assistance for a prolonged period, either from family members or in a long-term care facility. Consequentially, the associated health care costs of “broken hips” are substantial. In addition, hip fractures are associated with increased rates of morbidity (incidences of disease) and mortality (death). Surgery for a hip fracture followed by prolonged bed rest may lead to life-threatening complications, including pneumonia, infection of pressure ulcers (bedsores), and thrombophlebitis (deep vein thrombosis; blood clot formation) that can result in a pulmonary embolism (blood clot within the lung).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?