| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
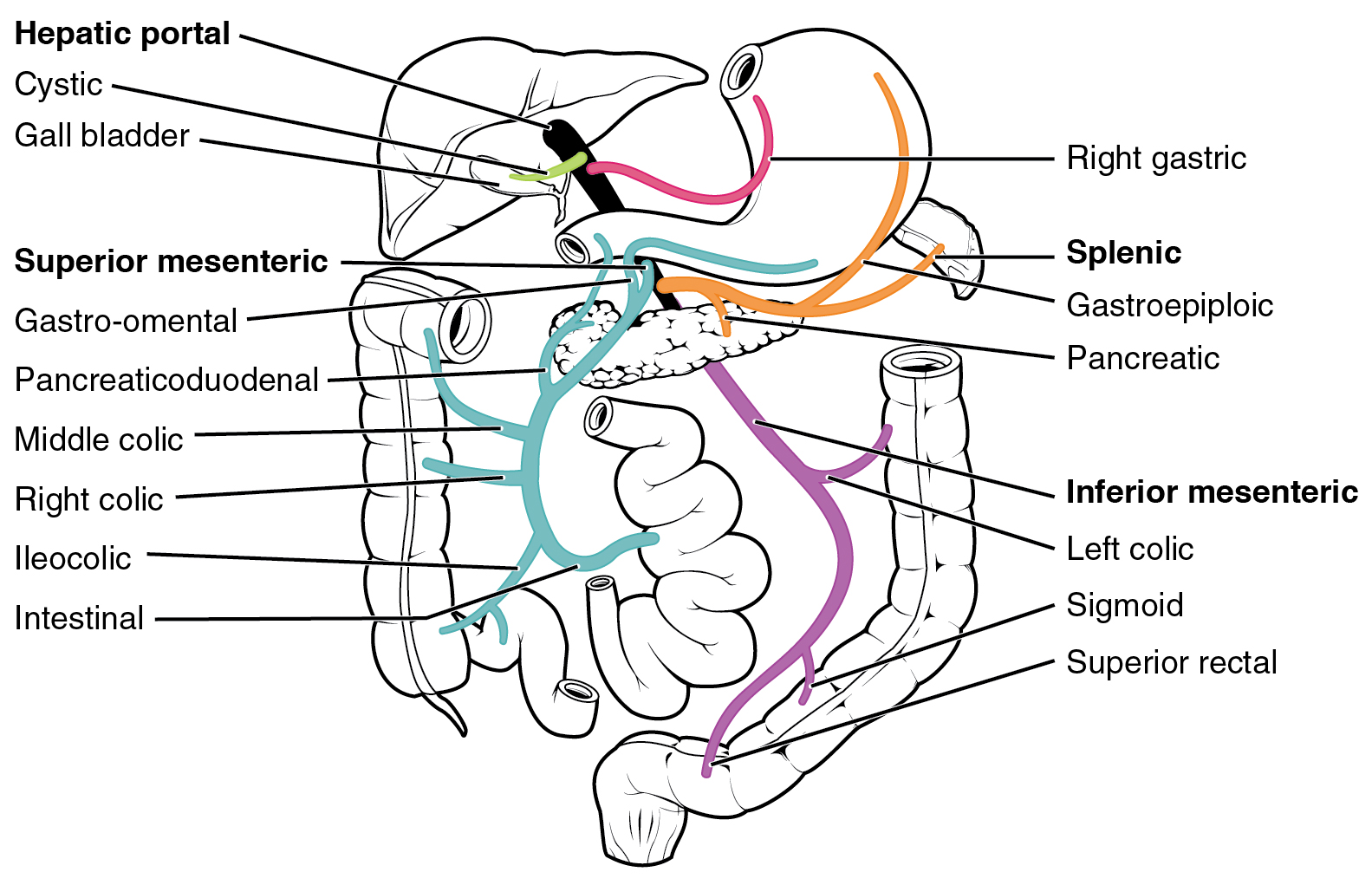
The liver is a complex biochemical processing plant. It packages nutrients absorbed by the digestive system; produces plasma proteins, clotting factors, and bile; and disposes of worn-out cell components and waste products. Instead of entering the circulation directly, absorbed nutrients and certain wastes (for example, materials produced by the spleen) travel to the liver for processing. They do so via the hepatic portal system ( [link] ). Portal systems begin and end in capillaries. In this case, the initial capillaries from the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and spleen lead to the hepatic portal vein and end in specialized capillaries within the liver, the hepatic sinusoids. You saw the only other portal system with the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal vessel in the endocrine chapter.
The hepatic portal system consists of the hepatic portal vein and the veins that drain into it. The hepatic portal vein itself is relatively short, beginning at the level of L2 with the confluence of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins. It also receives branches from the inferior mesenteric vein, plus the splenic veins and all their tributaries. The superior mesenteric vein receives blood from the small intestine, two-thirds of the large intestine, and the stomach. The inferior mesenteric vein drains the distal third of the large intestine, including the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and the rectum. The splenic vein is formed from branches from the spleen, pancreas, and portions of the stomach, and the inferior mesenteric vein. After its formation, the hepatic portal vein also receives branches from the gastric veins of the stomach and cystic veins from the gall bladder. The hepatic portal vein delivers materials from these digestive and circulatory organs directly to the liver for processing.
Because of the hepatic portal system, the liver receives its blood supply from two different sources: from normal systemic circulation via the hepatic artery and from the hepatic portal vein. The liver processes the blood from the portal system to remove certain wastes and excess nutrients, which are stored for later use. This processed blood, as well as the systemic blood that came from the hepatic artery, exits the liver via the right, left, and middle hepatic veins, and flows into the inferior vena cava. Overall systemic blood composition remains relatively stable, since the liver is able to metabolize the absorbed digestive components.
The right ventricle pumps oxygen-depleted blood into the pulmonary trunk and right and left pulmonary arteries, which carry it to the right and left lungs for gas exchange. Oxygen-rich blood is transported by pulmonary veins to the left atrium. The left ventricle pumps this blood into the aorta. The main regions of the aorta are the ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta, which is further divided into the thoracic and abdominal aorta. The coronary arteries branch from the ascending aorta. After oxygenating tissues in the capillaries, systemic blood is returned to the right atrium from the venous system via the superior vena cava, which drains most of the veins superior to the diaphragm, the inferior vena cava, which drains most of the veins inferior to the diaphragm, and the coronary veins via the coronary sinus. The hepatic portal system carries blood to the liver for processing before it enters circulation. Review the figures provided in this section for circulation of blood through the blood vessels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?