| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hemopoiesis begins when the hemopoietic stem cell is exposed to appropriate chemical stimuli collectively called hemopoietic growth factors , which prompt it to divide and differentiate. One daughter cell remains a hemopoietic stem cell, allowing hemopoiesis to continue. The other daughter cell becomes either of two types of more specialized stem cells ( [link] ):
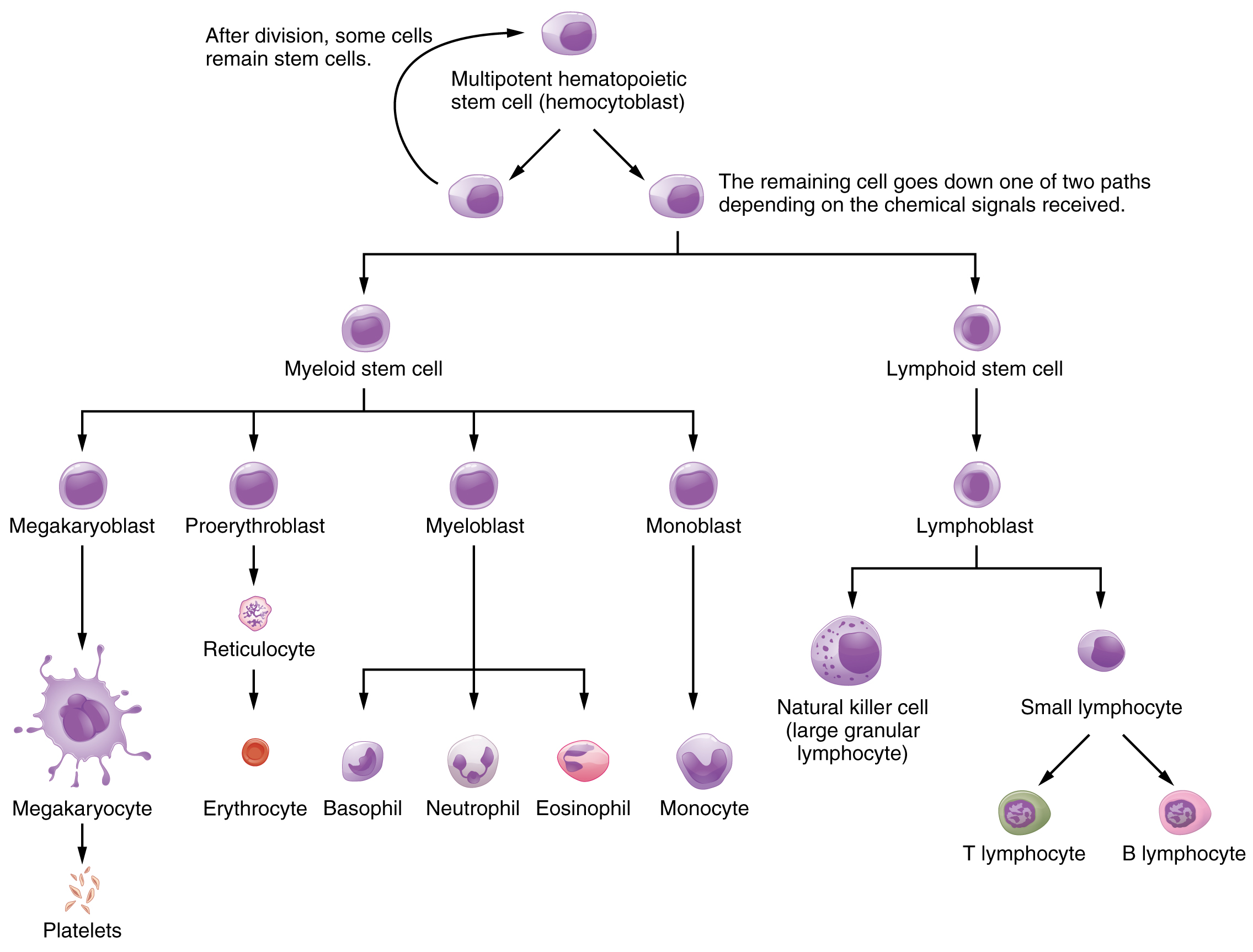
Lymphoid and myeloid stem cells do not immediately divide and differentiate into mature formed elements. As you can see in [link] , there are several intermediate stages of precursor cells (literally, forerunner cells), many of which can be recognized by their names, which have the suffix -blast. For instance, megakaryoblasts are the precursors of megakaryocytes, and proerythroblasts become reticulocytes, which eject their nucleus and most other organelles before maturing into erythrocytes.
Development from stem cells to precursor cells to mature cells is again initiated by hemopoietic growth factors. These include the following:
With the development of synthetic EPO in the 1980s, it became possible to provide additional RBCs by artificially stimulating RBC production in the bone marrow. Originally developed to treat patients suffering from anemia, renal failure, or cancer treatment, large quantities of EPO can be generated by recombinant DNA technology. Synthetic EPO is injected under the skin and can increase hematocrit for many weeks. It may also induce polycythemia and raise hematocrit to 70 or greater. This increased viscosity raises the resistance of the blood and forces the heart to pump more powerfully; in extreme cases, it has resulted in death. Other drugs such as cobalt II chloride have been shown to increase natural EPO gene expression. Blood doping has become problematic in many sports, especially cycling. Lance Armstrong, winner of seven Tour de France and many other cycling titles, was stripped of his victories and admitted to blood doping in 2013.
Watch this video to see doctors discuss the dangers of blood doping in sports. What are the some potential side effects of blood doping?
Sometimes, a healthcare provider will order a bone marrow biopsy , a diagnostic test of a sample of red bone marrow, or a bone marrow transplant , a treatment in which a donor’s healthy bone marrow—and its stem cells—replaces the faulty bone marrow of a patient. These tests and procedures are often used to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of various severe forms of anemia, such as thalassemia major and sickle cell anemia, as well as some types of cancer, specifically leukemia.
In the past, when a bone marrow sample or transplant was necessary, the procedure would have required inserting a large-bore needle into the region near the iliac crest of the pelvic bones (os coxae). This location was preferred, since its location close to the body surface makes it more accessible, and it is relatively isolated from most vital organs. Unfortunately, the procedure is quite painful.
Now, direct sampling of bone marrow can often be avoided. In many cases, stem cells can be isolated in just a few hours from a sample of a patient’s blood. The isolated stem cells are then grown in culture using the appropriate hemopoietic growth factors, and analyzed or sometimes frozen for later use.
For an individual requiring a transplant, a matching donor is essential to prevent the immune system from destroying the donor cells—a phenomenon known as tissue rejection. To treat patients with bone marrow transplants, it is first necessary to destroy the patient’s own diseased marrow through radiation and/or chemotherapy. Donor bone marrow stem cells are then intravenously infused. From the bloodstream, they establish themselves in the recipient’s bone marrow.
Through the process of hemopoiesis, the formed elements of blood are continually produced, replacing the relatively short-lived erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. Hemopoiesis begins in the red bone marrow, with hemopoietic stem cells that differentiate into myeloid and lymphoid lineages. Myeloid stem cells give rise to most of the formed elements. Lymphoid stem cells give rise only to the various lymphocytes designated as B and T cells, and NK cells. Hemopoietic growth factors, including erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, colony-stimulating factors, and interleukins, promote the proliferation and differentiation of formed elements.
Watch this video to see doctors discuss the dangers of blood doping in sports. What are the some potential side effects of blood doping?
Side effects can include heart disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and virus transmission.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?