| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
View this animation to see how a blow to the head may produce a contrecoup (counterblow) fracture of the basilar portion of the occipital bone on the base of the skull. Why may a basilar fracture be life threatening?
The facial bones of the skull form the upper and lower jaws, the nose, nasal cavity and nasal septum, and the orbit. The facial bones include 14 bones, with six paired bones and two unpaired bones. The paired bones are the maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior nasal conchae bones. The unpaired bones are the vomer and mandible bones. Although classified with the brain-case bones, the ethmoid bone also contributes to the nasal septum and the walls of the nasal cavity and orbit.
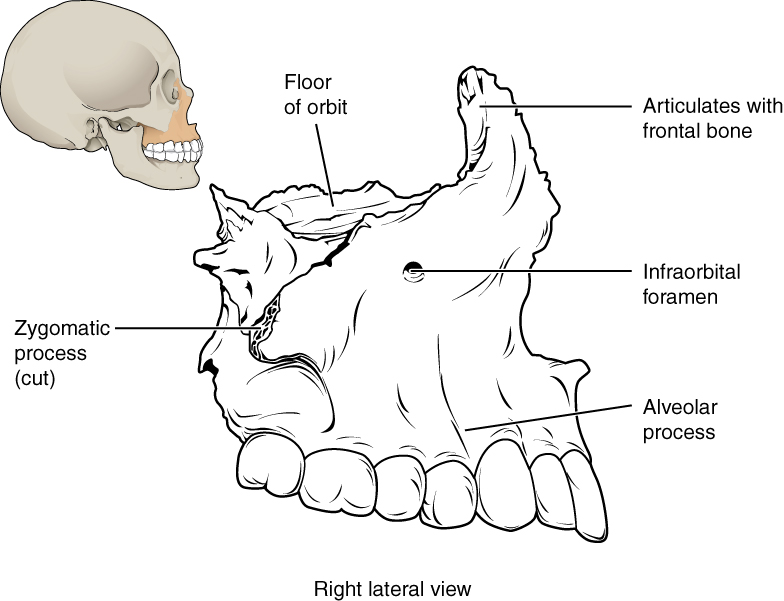
The maxillary bone , often referred to simply as the maxilla (plural = maxillae), is one of a pair that together form the upper jaw, much of the hard palate, the medial floor of the orbit, and the lateral base of the nose (see [link] ). The curved, inferior margin of the maxillary bone that forms the upper jaw and contains the upper teeth is the alveolar process of the maxilla ( [link] ). Each tooth is anchored into a deep socket called an alveolus. On the anterior maxilla, just below the orbit, is the infraorbital foramen. This is the point of exit for a sensory nerve that supplies the nose, upper lip, and anterior cheek. On the inferior skull, the palatine process from each maxillary bone can be seen joining together at the midline to form the anterior three-quarters of the hard palate (see [link] a ). The hard palate is the bony plate that forms the roof of the mouth and floor of the nasal cavity, separating the oral and nasal cavities.
The palatine bone is one of a pair of irregularly shaped bones that contribute small areas to the lateral walls of the nasal cavity and the medial wall of each orbit. The largest region of each of the palatine bone is the horizontal plate . The plates from the right and left palatine bones join together at the midline to form the posterior quarter of the hard palate (see [link] a ). Thus, the palatine bones are best seen in an inferior view of the skull and hard palate.
Cleft lip is a common development defect that affects approximately 1:1000 births, most of which are male. This defect involves a partial or complete failure of the right and left portions of the upper lip to fuse together, leaving a cleft (gap).
A more severe developmental defect is cleft palate, which affects the hard palate. The hard palate is the bony structure that separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity. It is formed during embryonic development by the midline fusion of the horizontal plates from the right and left palatine bones and the palatine processes of the maxilla bones. Cleft palate affects approximately 1:2500 births and is more common in females. It results from a failure of the two halves of the hard palate to completely come together and fuse at the midline, thus leaving a gap between them. This gap allows for communication between the nasal and oral cavities. In severe cases, the bony gap continues into the anterior upper jaw where the alveolar processes of the maxilla bones also do not properly join together above the front teeth. If this occurs, a cleft lip will also be seen. Because of the communication between the oral and nasal cavities, a cleft palate makes it very difficult for an infant to generate the suckling needed for nursing, thus leaving the infant at risk for malnutrition. Surgical repair is required to correct cleft palate defects.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?