| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
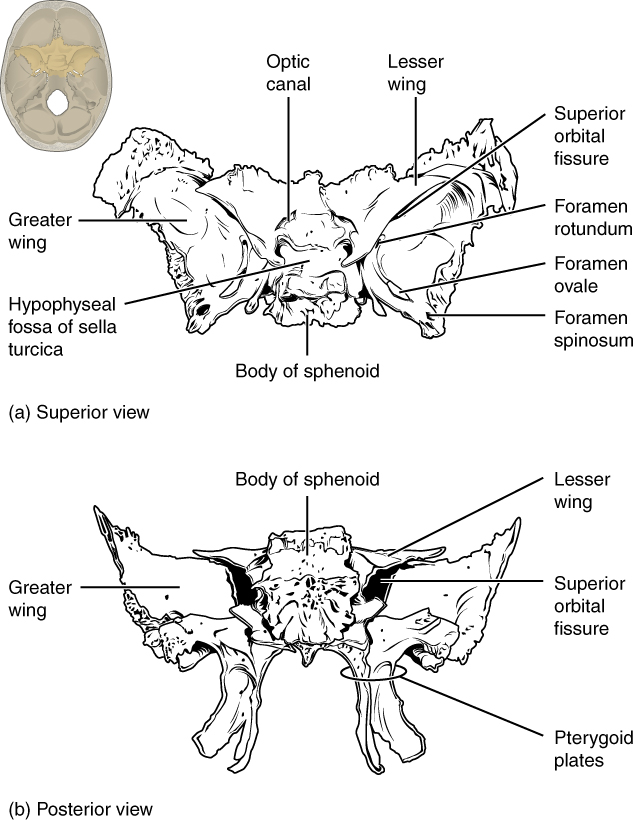
On the inferior aspect of the skull, each half of the sphenoid bone forms two thin, vertically oriented bony plates. These are the medial pterygoid plate and lateral pterygoid plate (pterygoid = “wing-shaped”). The right and left medial pterygoid plates form the posterior, lateral walls of the nasal cavity. The somewhat larger lateral pterygoid plates serve as attachment sites for chewing muscles that fill the infratemporal space and act on the mandible.
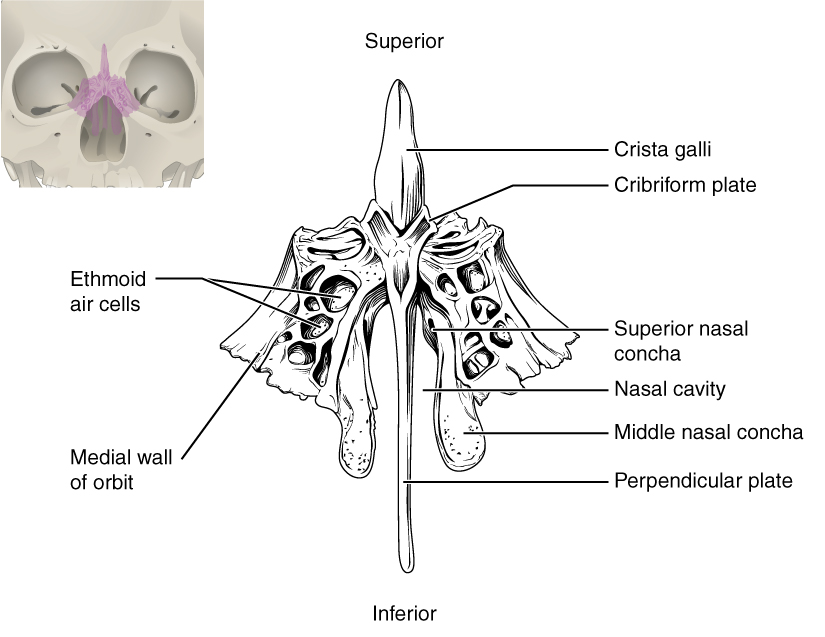
The ethmoid bone is a single, midline bone that forms the roof and lateral walls of the upper nasal cavity, the upper portion of the nasal septum, and contributes to the medial wall of the orbit ( [link] and [link] ). On the interior of the skull, the ethmoid also forms a portion of the floor of the anterior cranial cavity (see [link] b ).
Within the nasal cavity, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the upper portion of the nasal septum. The ethmoid bone also forms the lateral walls of the upper nasal cavity. Extending from each lateral wall are the superior nasal concha and middle nasal concha, which are thin, curved projections that extend into the nasal cavity ( [link] ).
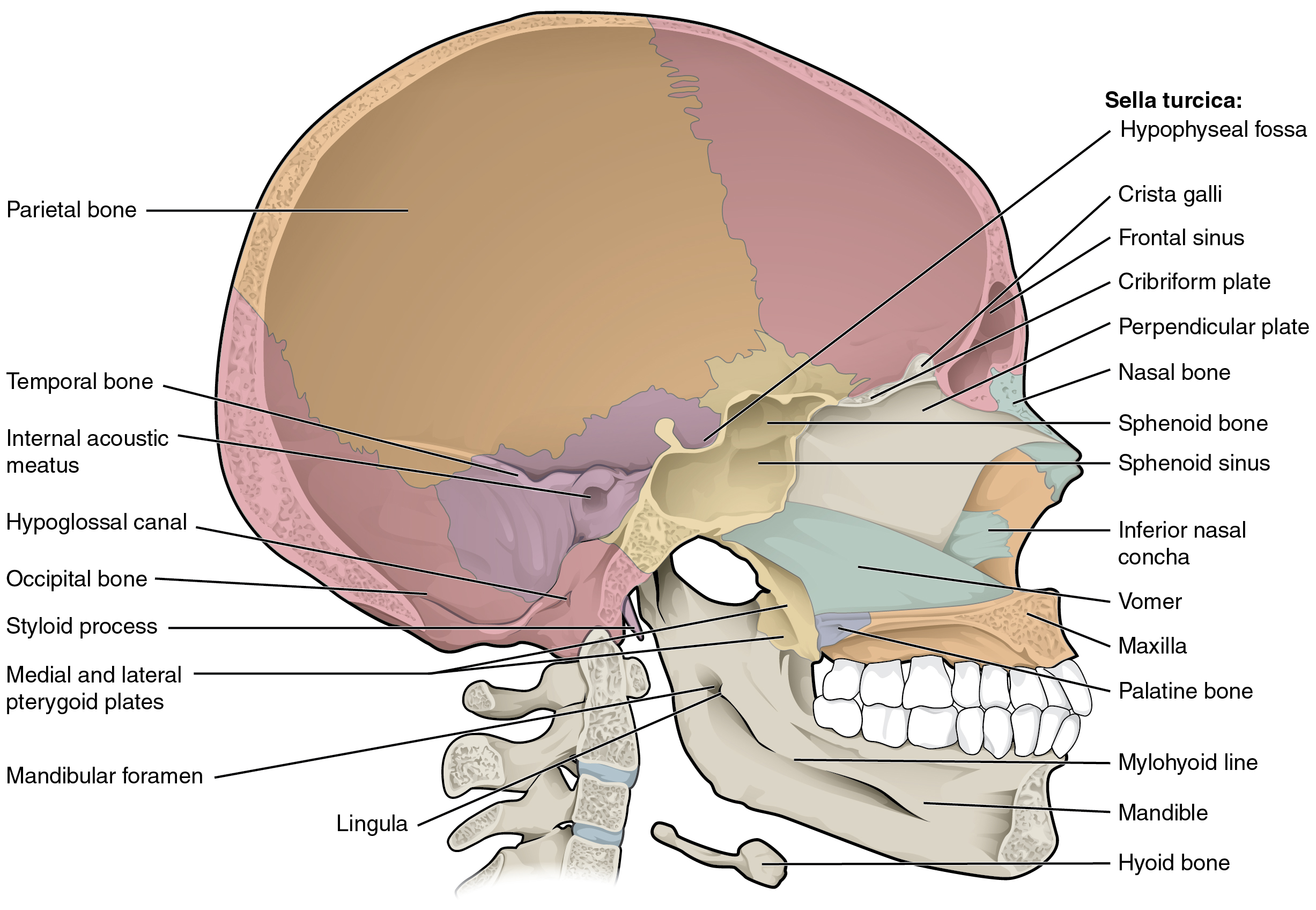
In the cranial cavity, the ethmoid bone forms a small area at the midline in the floor of the anterior cranial fossa. This region also forms the narrow roof of the underlying nasal cavity. This portion of the ethmoid bone consists of two parts, the crista galli and cribriform plates. The crista galli (“rooster’s comb or crest”) is a small upward bony projection located at the midline. It functions as an anterior attachment point for one of the covering layers of the brain. To either side of the crista galli is the cribriform plate (cribrum = “sieve”), a small, flattened area with numerous small openings termed olfactory foramina. Small nerve branches from the olfactory areas of the nasal cavity pass through these openings to enter the brain.
The lateral portions of the ethmoid bone are located between the orbit and upper nasal cavity, and thus form the lateral nasal cavity wall and a portion of the medial orbit wall. Located inside this portion of the ethmoid bone are several small, air-filled spaces that are part of the paranasal sinus system of the skull.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?