| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
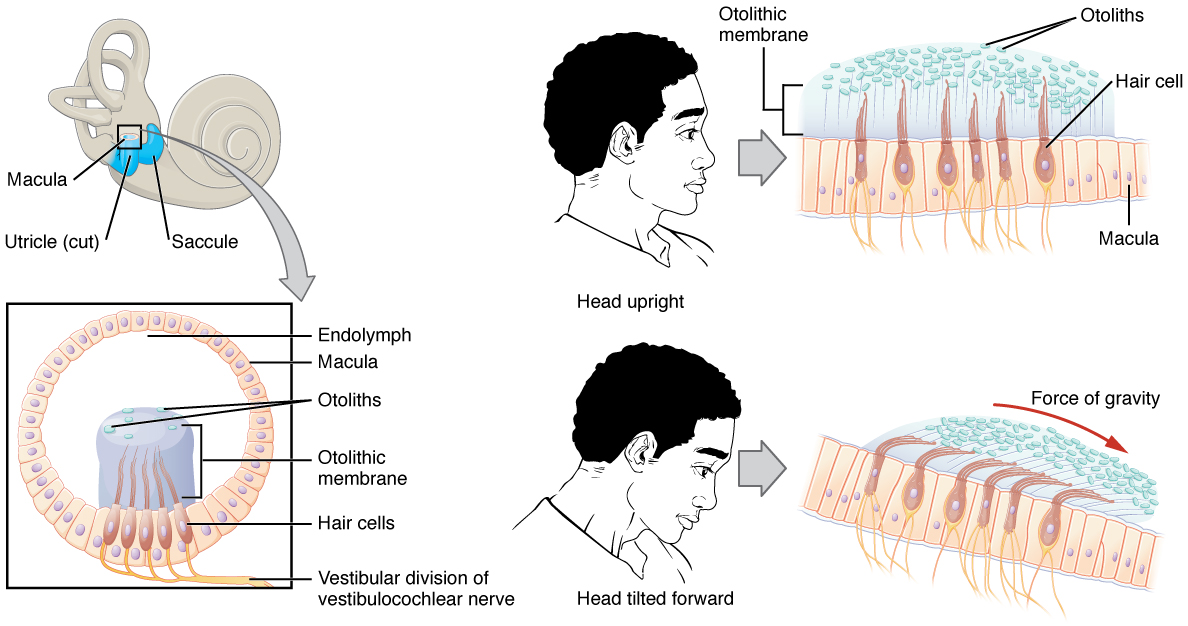
Along with audition, the inner ear is responsible for encoding information about equilibrium , the sense of balance. A similar mechanoreceptor—a hair cell with stereocilia—senses head position, head movement, and whether our bodies are in motion. These cells are located within the vestibule of the inner ear. Head position is sensed by the utricle and saccule , whereas head movement is sensed by the semicircular canals . The neural signals generated in the vestibular ganglion are transmitted through the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain stem and cerebellum.
The utricle and saccule are both largely composed of macula tissue (plural = maculae). The macula is composed of hair cells surrounded by support cells. The stereocilia of the hair cells extend into a viscous gel called the otolithic membrane ( [link] ). On top of the otolithic membrane is a layer of calcium carbonate crystals, called otoliths. The otoliths essentially make the otolithic membrane top-heavy. The otolithic membrane moves separately from the macula in response to head movements. Tilting the head causes the otolithic membrane to slide over the macula in the direction of gravity. The moving otolithic membrane, in turn, bends the sterocilia, causing some hair cells to depolarize as others hyperpolarize. The exact position of the head is interpreted by the brain based on the pattern of hair-cell depolarization.
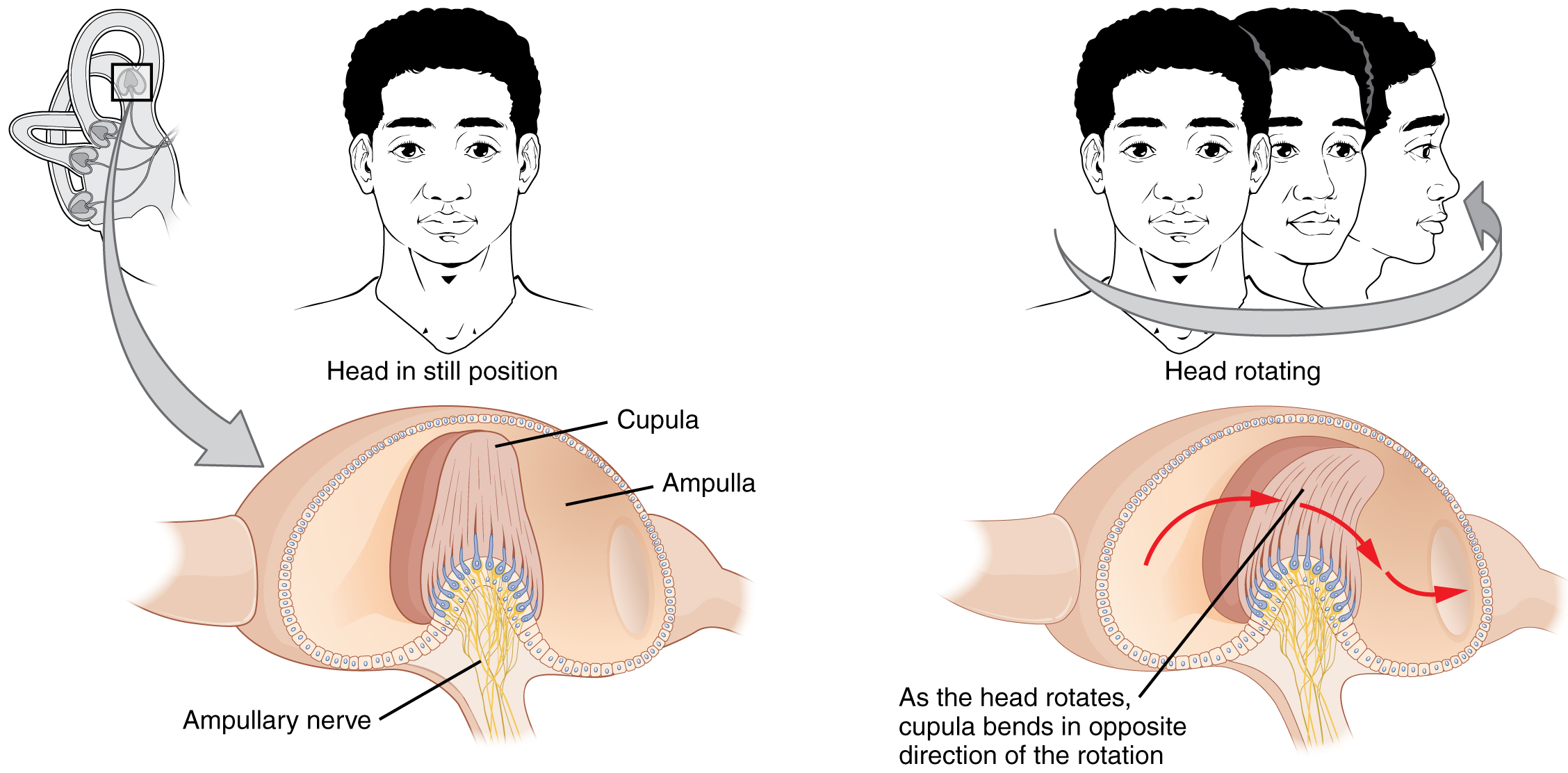
The semicircular canals are three ring-like extensions of the vestibule. One is oriented in the horizontal plane, whereas the other two are oriented in the vertical plane. The anterior and posterior vertical canals are oriented at approximately 45 degrees relative to the sagittal plane ( [link] ). The base of each semicircular canal, where it meets with the vestibule, connects to an enlarged region known as the ampulla . The ampulla contains the hair cells that respond to rotational movement, such as turning the head while saying “no.” The stereocilia of these hair cells extend into the cupula , a membrane that attaches to the top of the ampulla. As the head rotates in a plane parallel to the semicircular canal, the fluid lags, deflecting the cupula in the direction opposite to the head movement. The semicircular canals contain several ampullae, with some oriented horizontally and others oriented vertically. By comparing the relative movements of both the horizontal and vertical ampullae, the vestibular system can detect the direction of most head movements within three-dimensional (3-D) space.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?