| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Carbon’s affinity for covalent bonding means that many distinct and relatively stable organic molecules nevertheless readily form larger, more complex molecules. Any large molecule is referred to as macromolecule (macro- = “large”), and the organic compounds in this section all fit this description. However, some macromolecules are made up of several “copies” of single units called monomer (mono- = “one”; -mer = “part”). Like beads in a long necklace, these monomers link by covalent bonds to form long polymers (poly- = “many”). There are many examples of monomers and polymers among the organic compounds.
Monomers form polymers by engaging in dehydration synthesis (see [link] ). As was noted earlier, this reaction results in the release of a molecule of water. Each monomer contributes: One gives up a hydrogen atom and the other gives up a hydroxyl group. Polymers are split into monomers by hydrolysis (-lysis = “rupture”). The bonds between their monomers are broken, via the donation of a molecule of water, which contributes a hydrogen atom to one monomer and a hydroxyl group to the other.
The term carbohydrate means “hydrated carbon.” Recall that the root hydro- indicates water. A carbohydrate is a molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; in most carbohydrates, hydrogen and oxygen are found in the same two-to-one relative proportions they have in water. In fact, the chemical formula for a “generic” molecule of carbohydrate is (CH 2 O) n .
Carbohydrates are referred to as saccharides, a word meaning “sugars.” Three forms are important in the body. Monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrates. Disaccharides (di- = “two”) are made up of two monomers. Polysaccharides are the polymers, and can consist of hundreds to thousands of monomers.
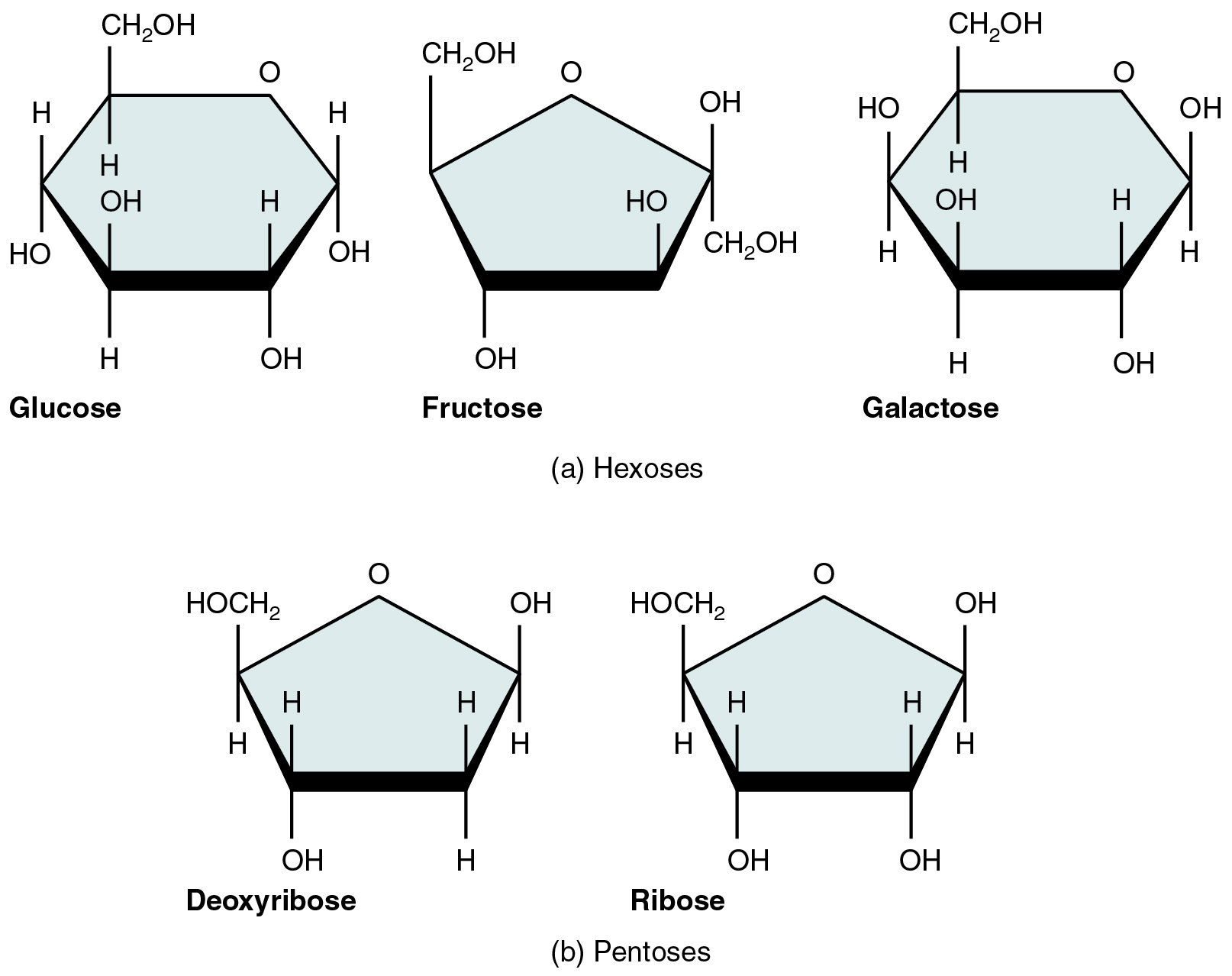
A monosaccharide is a monomer of carbohydrates. Five monosaccharides are important in the body. Three of these are the hexose sugars, so called because they each contain six atoms of carbon. These are glucose, fructose, and galactose, shown in [link] a . The remaining monosaccharides are the two pentose sugars, each of which contains five atoms of carbon. They are ribose and deoxyribose, shown in [link] b .
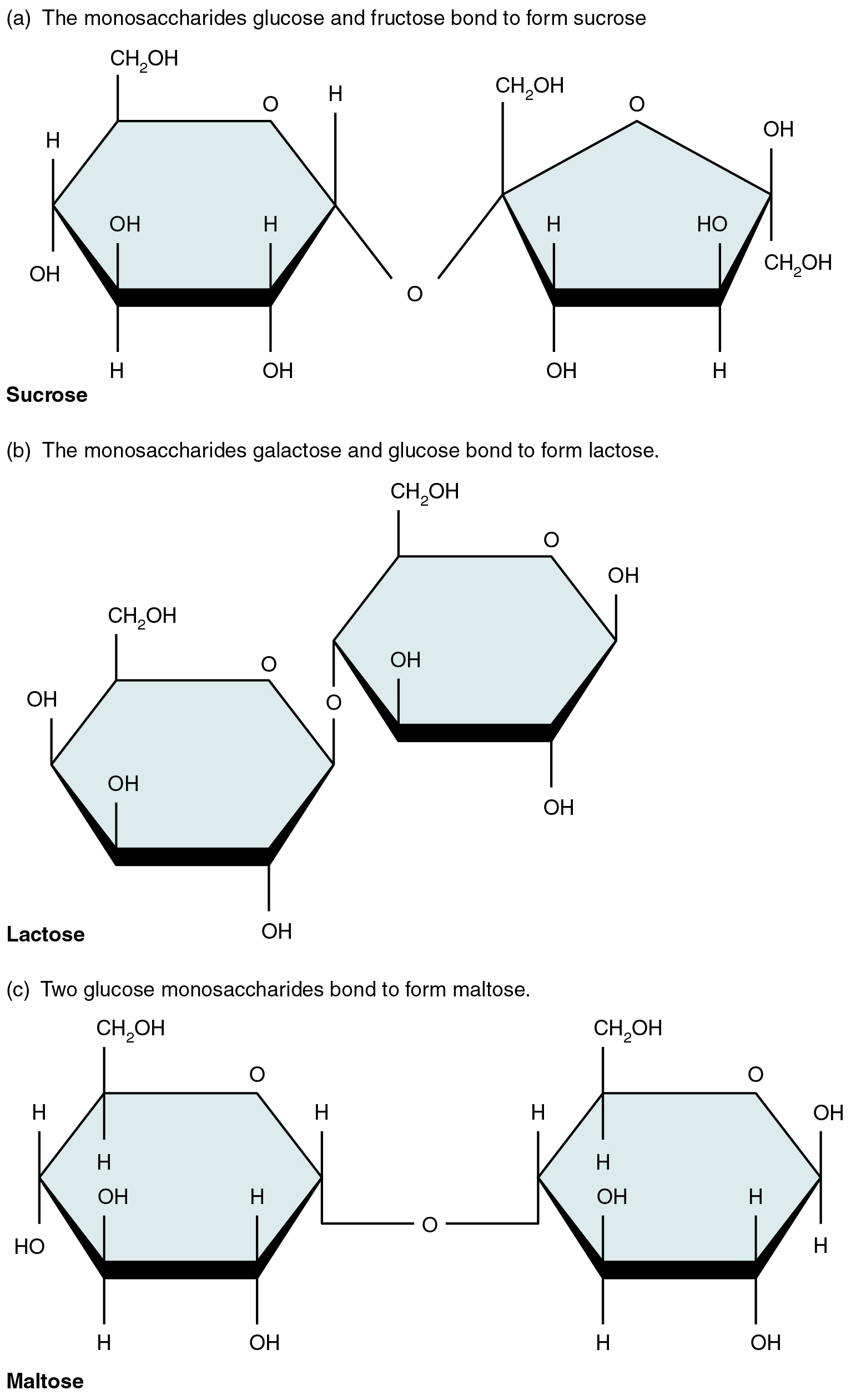
A disaccharide is a pair of monosaccharides. Disaccharides are formed via dehydration synthesis, and the bond linking them is referred to as a glycosidic bond (glyco- = “sugar”). Three disaccharides (shown in [link] ) are important to humans. These are sucrose, commonly referred to as table sugar; lactose, or milk sugar; and maltose, or malt sugar. As you can tell from their common names, you consume these in your diet; however, your body cannot use them directly. Instead, in the digestive tract, they are split into their component monosaccharides via hydrolysis.
Watch this video to observe the formation of a disaccharide. What happens when water encounters a glycosidic bond?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?