| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The primary motor cortex is arranged in a similar fashion to the primary somatosensory cortex, in that it has a topographical map of the body, creating a motor homunculus (see [link] ). The neurons responsible for musculature in the feet and lower legs are in the medial wall of the precentral gyrus, with the thighs, trunk, and shoulder at the crest of the longitudinal fissure. The hand and face are in the lateral face of the gyrus. Also, the relative space allotted for the different regions is exaggerated in muscles that have greater enervation. The greatest amount of cortical space is given to muscles that perform fine, agile movements, such as the muscles of the fingers and the lower face. The “power muscles” that perform coarser movements, such as the buttock and back muscles, occupy much less space on the motor cortex.
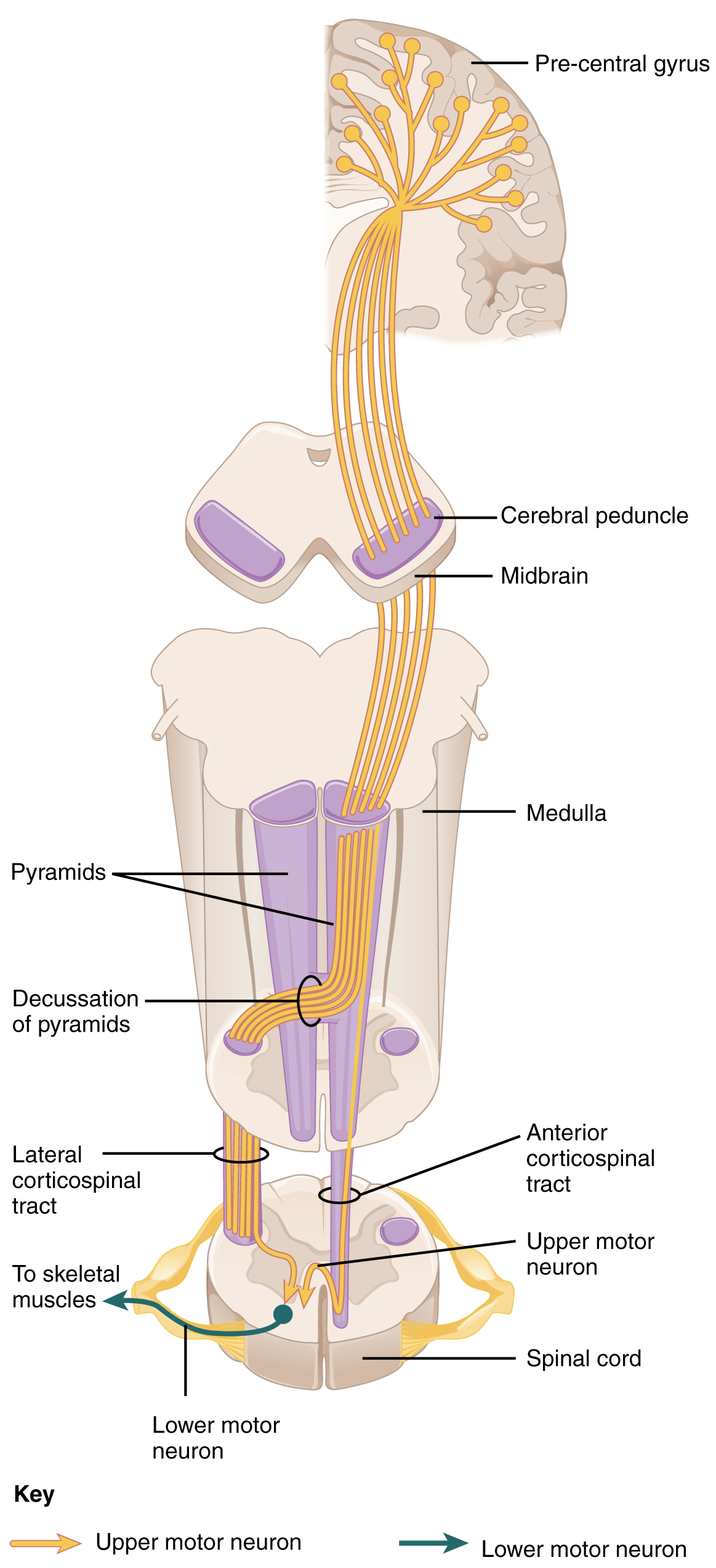
The motor output from the cortex descends into the brain stem and to the spinal cord to control the musculature through motor neurons. Neurons located in the primary motor cortex, named Betz cells , are large cortical neurons that synapse with lower motor neurons in the spinal cord or the brain stem. The two descending pathways travelled by the axons of Betz cells are the corticospinal tract and the corticobulbar tract . Both tracts are named for their origin in the cortex and their targets—either the spinal cord or the brain stem (the term “bulbar” refers to the brain stem as the bulb, or enlargement, at the top of the spinal cord).
These two descending pathways are responsible for the conscious or voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. Any motor command from the primary motor cortex is sent down the axons of the Betz cells to activate upper motor neurons in either the cranial motor nuclei or in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. The axons of the corticobulbar tract are ipsilateral, meaning they project from the cortex to the motor nucleus on the same side of the nervous system. Conversely, the axons of the corticospinal tract are largely contralateral, meaning that they cross the midline of the brain stem or spinal cord and synapse on the opposite side of the body. Therefore, the right motor cortex of the cerebrum controls muscles on the left side of the body, and vice versa.
The corticospinal tract descends from the cortex through the deep white matter of the cerebrum. It then passes between the caudate nucleus and putamen of the basal nuclei as a bundle called the internal capsule . The tract then passes through the midbrain as the cerebral peduncles , after which it burrows through the pons. Upon entering the medulla, the tracts make up the large white matter tract referred to as the pyramids ( [link] ). The defining landmark of the medullary-spinal border is the pyramidal decussation , which is where most of the fibers in the corticospinal tract cross over to the opposite side of the brain. At this point, the tract separates into two parts, which have control over different domains of the musculature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?