| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mucosal tissues are major barriers to the entry of pathogens into the body. The IgA (and sometimes IgM) antibodies in mucus and other secretions can bind to the pathogen, and in the cases of many viruses and bacteria, neutralize them. Neutralization is the process of coating a pathogen with antibodies, making it physically impossible for the pathogen to bind to receptors. Neutralization, which occurs in the blood, lymph, and other body fluids and secretions, protects the body constantly. Neutralizing antibodies are the basis for the disease protection offered by vaccines. Vaccinations for diseases that commonly enter the body via mucous membranes, such as influenza, are usually formulated to enhance IgA production.
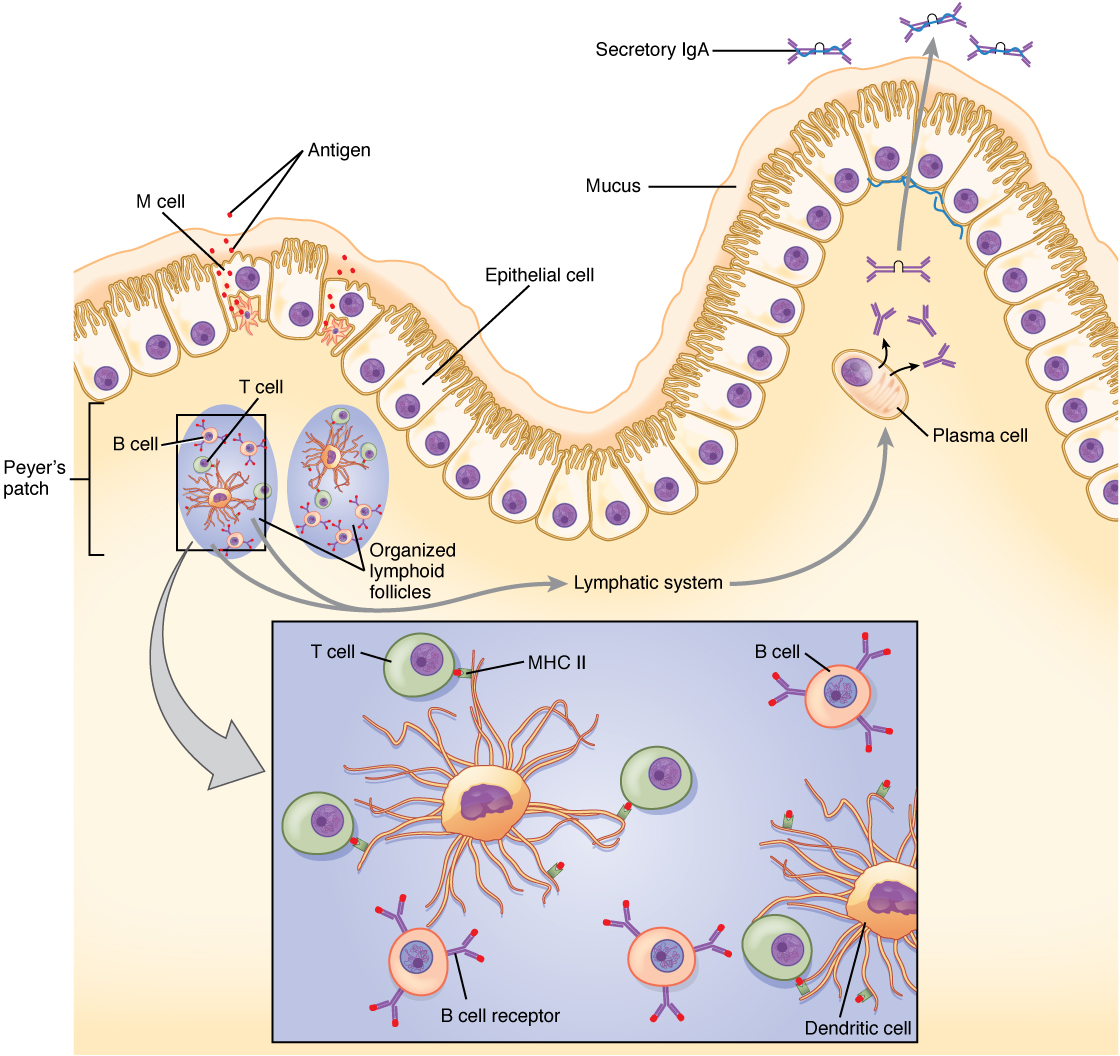
Immune responses in some mucosal tissues such as the Peyer’s patches (see [link] ) in the small intestine take up particulate antigens by specialized cells known as microfold or M cells ( [link] ). These cells allow the body to sample potential pathogens from the intestinal lumen. Dendritic cells then take the antigen to the regional lymph nodes, where an immune response is mounted.
The body fights bacterial pathogens with a wide variety of immunological mechanisms, essentially trying to find one that is effective. Bacteria such as Mycobacterium leprae , the cause of leprosy, are resistant to lysosomal enzymes and can persist in macrophage organelles or escape into the cytosol. In such situations, infected macrophages receiving cytokine signals from Th1 cells turn on special metabolic pathways. Macrophage oxidative metabolism is hostile to intracellular bacteria, often relying on the production of nitric oxide to kill the bacteria inside the macrophage.
Fungal infections, such as those from Aspergillus , Candida , and Pneumocystis , are largely opportunistic infections that take advantage of suppressed immune responses. Most of the same immune mechanisms effective against bacteria have similar effects on fungi, both of which have characteristic cell wall structures that protect their cells.
Worm parasites such as helminths are seen as the primary reason why the mucosal immune response, IgE-mediated allergy and asthma, and eosinophils evolved. These parasites were at one time very common in human society. When infecting a human, often via contaminated food, some worms take up residence in the gastrointestinal tract. Eosinophils are attracted to the site by T cell cytokines, which release their granule contents upon their arrival. Mast cell degranulation also occurs, and the fluid leakage caused by the increase in local vascular permeability is thought to have a flushing action on the parasite, expelling its larvae from the body. Furthermore, if IgE labels the parasite, the eosinophils can bind to it by its Fc receptor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?