| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
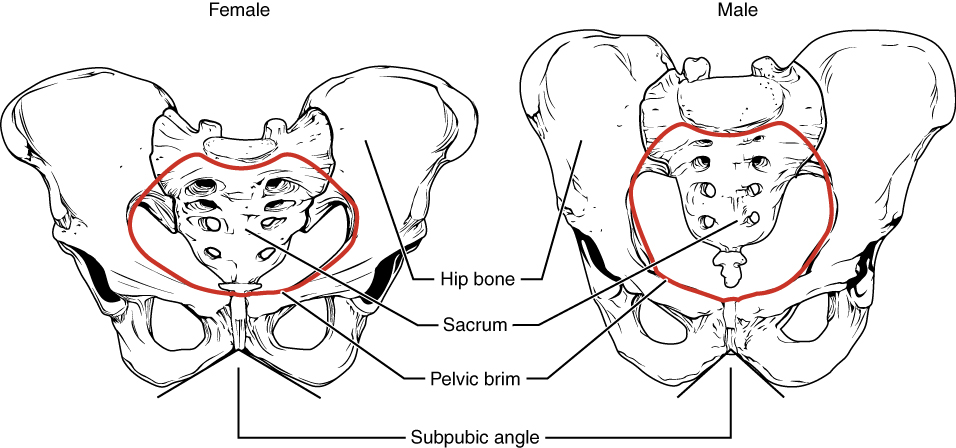
The differences between the adult female and male pelvis relate to function and body size. In general, the bones of the male pelvis are thicker and heavier, adapted for support of the male’s heavier physical build and stronger muscles. The greater sciatic notch of the male hip bone is narrower and deeper than the broader notch of females. Because the female pelvis is adapted for childbirth, it is wider than the male pelvis, as evidenced by the distance between the anterior superior iliac spines (see [link] ). The ischial tuberosities of females are also farther apart, which increases the size of the pelvic outlet. Because of this increased pelvic width, the subpubic angle is larger in females (greater than 80 degrees) than it is in males (less than 70 degrees). The female sacrum is wider, shorter, and less curved, and the sacral promontory projects less into the pelvic cavity, thus giving the female pelvic inlet (pelvic brim) a more rounded or oval shape compared to males. The lesser pelvic cavity of females is also wider and more shallow than the narrower, deeper, and tapering lesser pelvis of males. Because of the obvious differences between female and male hip bones, this is the one bone of the body that allows for the most accurate sex determination. [link] provides an overview of the general differences between the female and male pelvis.
| Overview of Differences between the Female and Male Pelvis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Female pelvis | Male pelvis | |
| Pelvic weight | Bones of the pelvis are lighter and thinner | Bones of the pelvis are thicker and heavier |
| Pelvic inlet shape | Pelvic inlet has a round or oval shape | Pelvic inlet is heart-shaped |
| Lesser pelvic cavity shape | Lesser pelvic cavity is shorter and wider | Lesser pelvic cavity is longer and narrower |
| Subpubic angle | Subpubic angle is greater than 80 degrees | Subpubic angle is less than 70 degrees |
| Pelvic outlet shape | Pelvic outlet is rounded and larger | Pelvic outlet is smaller |
While forensic pathologists are responsible for determining whether the cause of someone’s death was natural, a suicide, accidental, or a homicide, there are times when uncovering the cause of death is more complex, and other skills are needed. Forensic anthropology brings the tools and knowledge of physical anthropology and human osteology (the study of the skeleton) to the task of investigating a death. A forensic anthropologist assists medical and legal professionals in identifying human remains. The science behind forensic anthropology involves the study of archaeological excavation; the examination of hair; an understanding of plants, insects, and footprints; the ability to determine how much time has elapsed since the person died; the analysis of past medical history and toxicology; the ability to determine whether there are any postmortem injuries or alterations of the skeleton; and the identification of the decedent (deceased person) using skeletal and dental evidence.
Due to the extensive knowledge and understanding of excavation techniques, a forensic anthropologist is an integral and invaluable team member to have on-site when investigating a crime scene, especially when the recovery of human skeletal remains is involved. When remains are bought to a forensic anthropologist for examination, he or she must first determine whether the remains are in fact human. Once the remains have been identified as belonging to a person and not to an animal, the next step is to approximate the individual’s age, sex, race, and height. The forensic anthropologist does not determine the cause of death, but rather provides information to the forensic pathologist, who will use all of the data collected to make a final determination regarding the cause of death.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?