| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
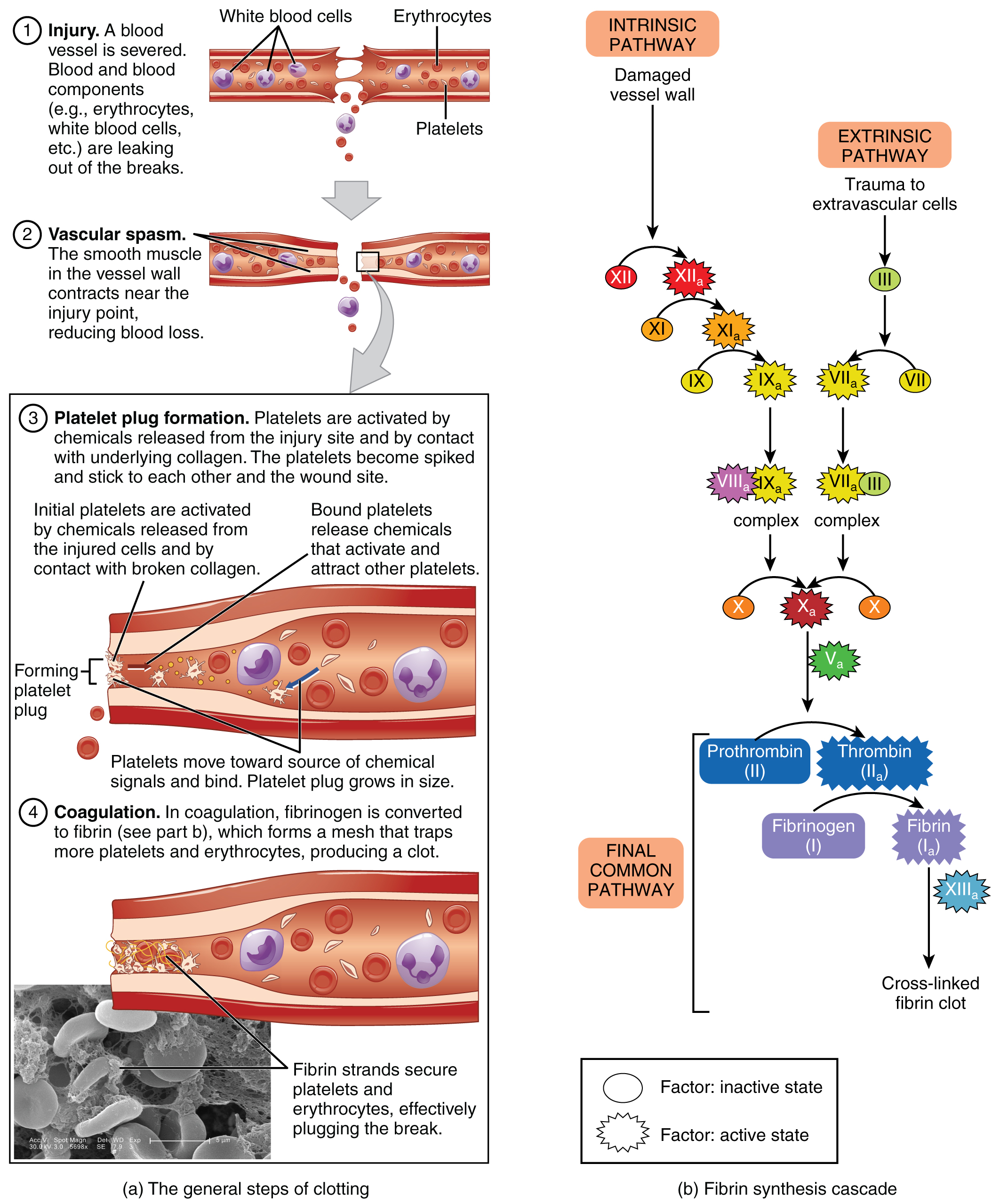
In the coagulation cascade, chemicals called clotting factors (or coagulation factors) prompt reactions that activate still more coagulation factors. The process is complex, but is initiated along two basic pathways:
Both of these merge into a third pathway, referred to as the common pathway (see [link] b ). All three pathways are dependent upon the 12 known clotting factors, including Ca 2+ and vitamin K ( [link] ). Clotting factors are secreted primarily by the liver and the platelets. The liver requires the fat-soluble vitamin K to produce many of them. Vitamin K (along with biotin and folate) is somewhat unusual among vitamins in that it is not only consumed in the diet but is also synthesized by bacteria residing in the large intestine. The calcium ion, considered factor IV, is derived from the diet and from the breakdown of bone. Some recent evidence indicates that activation of various clotting factors occurs on specific receptor sites on the surfaces of platelets.
The 12 clotting factors are numbered I through XIII according to the order of their discovery. Factor VI was once believed to be a distinct clotting factor, but is now thought to be identical to factor V. Rather than renumber the other factors, factor VI was allowed to remain as a placeholder and also a reminder that knowledge changes over time.
| Clotting Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor number | Name | Type of molecule | Source | Pathway(s) |
| I | Fibrinogen | Plasma protein | Liver | Common; converted into fibrin |
| II | Prothrombin | Plasma protein | Liver* | Common; converted into thrombin |
| III | Tissue thromboplastin or tissue factor | Lipoprotein mixture | Damaged cells and platelets | Extrinsic |
| IV | Calcium ions | Inorganic ions in plasma | Diet, platelets, bone matrix | Entire process |
| V | Proaccelerin | Plasma protein | Liver, platelets | Extrinsic and intrinsic |
| VI | Not used | Not used | Not used | Not used |
| VII | Proconvertin | Plasma protein | Liver * | Extrinsic |
| VIII | Antihemolytic factor A | Plasma protein factor | Platelets and endothelial cells | Intrinsic; deficiency results in hemophilia A |
| IX | Antihemolytic factor B (plasma thromboplastin component) | Plasma protein | Liver* | Intrinsic; deficiency results in hemophilia B |
| X | Stuart–Prower factor (thrombokinase) | Protein | Liver* | Extrinsic and intrinsic |
| XI | Antihemolytic factor C (plasma thromboplastin antecedent) | Plasma protein | Liver | Intrinsic; deficiency results in hemophilia C |
| XII | Hageman factor | Plasma protein | Liver | Intrinsic; initiates clotting in vitro also activates plasmin |
| XIII | Fibrin-stabilizing factor | Plasma protein | Liver, platelets | Stabilizes fibrin; slows fibrinolysis |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?