| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Decreased blood volume resulting from water loss has two additional effects. First, baroreceptors, blood-pressure receptors in the arch of the aorta and the carotid arteries in the neck, detect a decrease in blood pressure that results from decreased blood volume. The heart is ultimately signaled to increase its rate and/or strength of contractions to compensate for the lowered blood pressure.
Second, the kidneys have a renin-angiotensin hormonal system that increases the production of the active form of the hormone angiotensin II, which helps stimulate thirst, but also stimulates the release of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium in the distal tubules of the nephrons in the kidneys, and water follows this reabsorbed sodium back into the blood.
If adequate fluids are not consumed, dehydration results and a person’s body contains too little water to function correctly. A person who repeatedly vomits or who has diarrhea may become dehydrated, and infants, because their body mass is so low, can become dangerously dehydrated very quickly. Endurance athletes such as distance runners often become dehydrated during long races. Dehydration can be a medical emergency, and a dehydrated person may lose consciousness, become comatose, or die, if his or her body is not rehydrated quickly.
Water loss from the body occurs predominantly through the renal system. A person produces an average of 1.5 liters (1.6 quarts) of urine per day. Although the volume of urine varies in response to hydration levels, there is a minimum volume of urine production required for proper bodily functions. The kidney excretes 100 to 1200 milliosmoles of solutes per day to rid the body of a variety of excess salts and other water-soluble chemical wastes, most notably creatinine, urea, and uric acid. Failure to produce the minimum volume of urine means that metabolic wastes cannot be effectively removed from the body, a situation that can impair organ function. The minimum level of urine production necessary to maintain normal function is about 0.47 liters (0.5 quarts) per day.
The kidneys also must make adjustments in the event of ingestion of too much fluid. Diuresis , which is the production of urine in excess of normal levels, begins about 30 minutes after drinking a large quantity of fluid. Diuresis reaches a peak after about 1 hour, and normal urine production is reestablished after about 3 hours.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) , also known as vasopressin, controls the amount of water reabsorbed from the collecting ducts and tubules in the kidney. This hormone is produced in the hypothalamus and is delivered to the posterior pituitary for storage and release ( [link] ). When the osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect an increase in the concentration of blood plasma, the hypothalamus signals the release of ADH from the posterior pituitary into the blood.
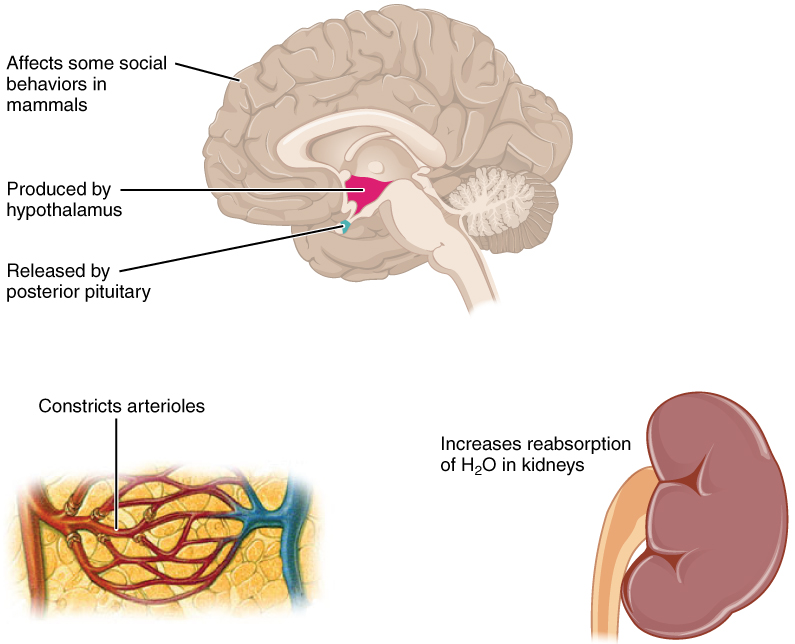
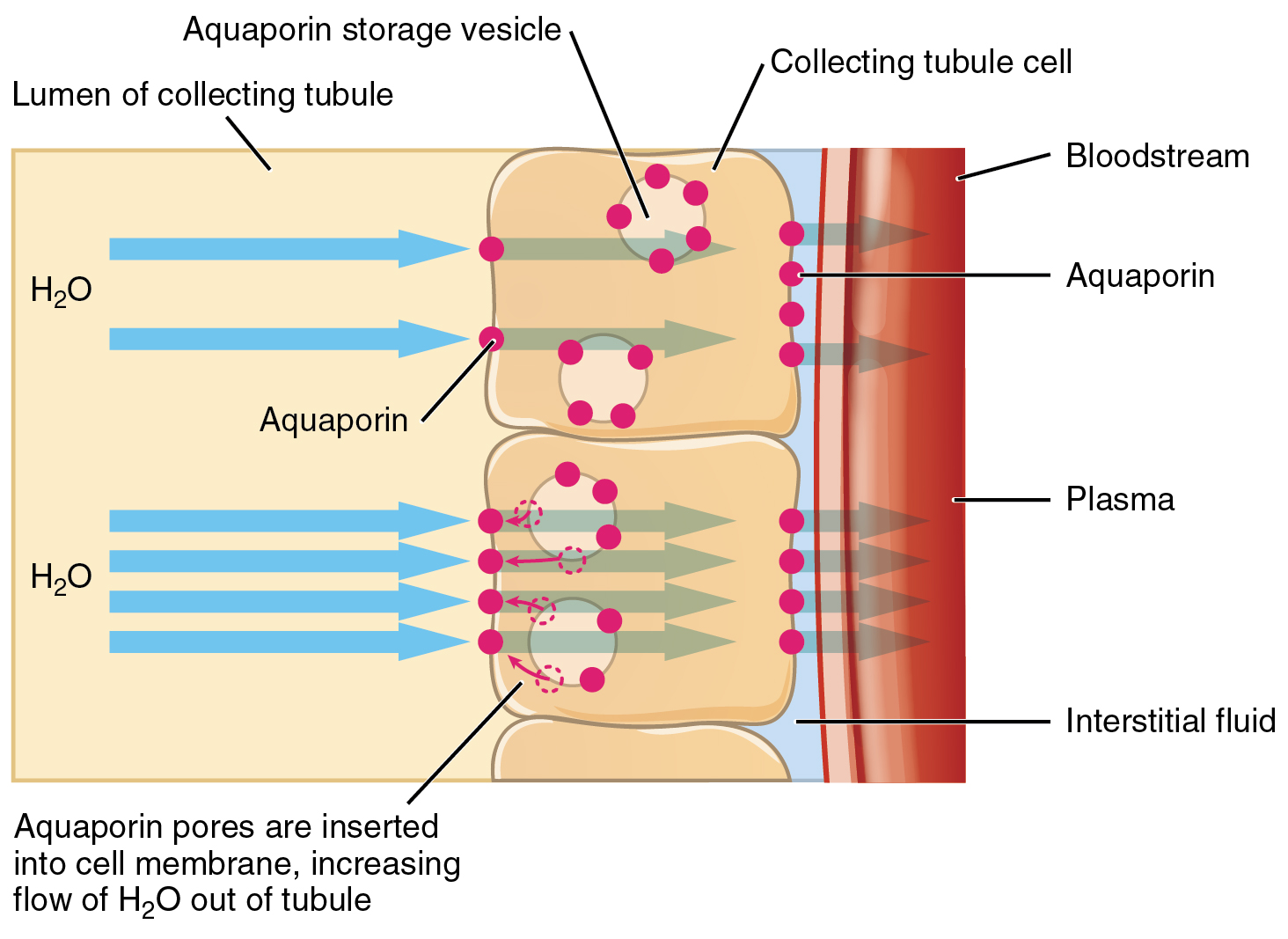
ADH has two major effects. It constricts the arterioles in the peripheral circulation, which reduces the flow of blood to the extremities and thereby increases the blood supply to the core of the body. ADH also causes the epithelial cells that line the renal collecting tubules to move water channel proteins, called aquaporins, from the interior of the cells to the apical surface, where these proteins are inserted into the cell membrane ( [link] ). The result is an increase in the water permeability of these cells and, thus, a large increase in water passage from the urine through the walls of the collecting tubules, leading to more reabsorption of water into the bloodstream. When the blood plasma becomes less concentrated and the level of ADH decreases, aquaporins are removed from collecting tubule cell membranes, and the passage of water out of urine and into the blood decreases.
A diuretic is a compound that increases urine output and therefore decreases water conservation by the body. Diuretics are used to treat hypertension, congestive heart failure, and fluid retention associated with menstruation. Alcohol acts as a diuretic by inhibiting the release of ADH. Additionally, caffeine, when consumed in high concentrations, acts as a diuretic.
Homeostasis requires that water intake and output be balanced. Most water intake comes through the digestive tract via liquids and food, but roughly 10 percent of water available to the body is generated at the end of aerobic respiration during cellular metabolism. Urine produced by the kidneys accounts for the largest amount of water leaving the body. The kidneys can adjust the concentration of the urine to reflect the body’s water needs, conserving water if the body is dehydrated or making urine more dilute to expel excess water when necessary. ADH is a hormone that helps the body to retain water by increasing water reabsorption by the kidneys.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?