| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When a cell differentiates (becomes more specialized), it may undertake major changes in its size, shape, metabolic activity, and overall function. Because all cells in the body, beginning with the fertilized egg, contain the same DNA, how do the different cell types come to be so different? The answer is analogous to a movie script. The different actors in a movie all read from the same script, however, they are each only reading their own part of the script. Similarly, all cells contain the same full complement of DNA, but each type of cell only “reads” the portions of DNA that are relevant to its own function. In biology, this is referred to as the unique genetic expression of each cell.
In order for a cell to differentiate into its specialized form and function, it need only manipulate those genes (and thus those proteins) that will be expressed, and not those that will remain silent. The primary mechanism by which genes are turned “on” or “off” is through transcription factors. A transcription factor is one of a class of proteins that bind to specific genes on the DNA molecule and either promote or inhibit their transcription ( [link] ).
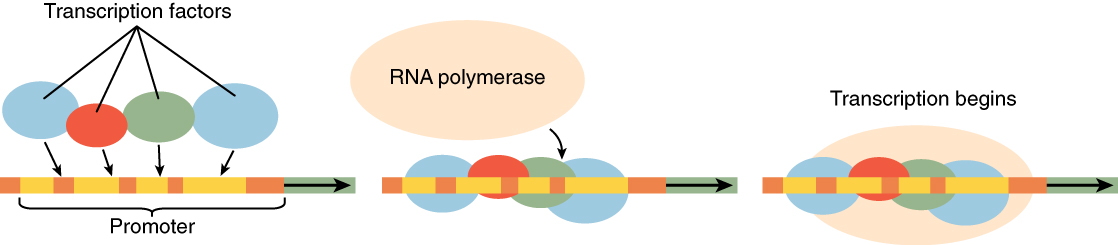
The mechanisms that induce a non-differentiated cell to become a specialized cell are poorly understood. In a laboratory setting, it is possible to induce stem cells to differentiate into specialized cells by changing the physical and chemical conditions of growth. Several sources of stem cells are used experimentally and are classified according to their origin and potential for differentiation. Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are extracted from embryos and are pluripotent. The adult stem cells that are present in many organs and differentiated tissues, such as bone marrow and skin, are multipotent, being limited in differentiation to the types of cells found in those tissues. The stem cells isolated from umbilical cord blood are also multipotent, as are cells from deciduous teeth (baby teeth). Researchers have recently developed induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from mouse and human adult stem cells. These cells are genetically reprogrammed multipotent adult cells that function like embryonic stem cells; they are capable of generating cells characteristic of all three germ layers.
Because of their capacity to divide and differentiate into specialized cells, stem cells offer a potential treatment for diseases such as diabetes and heart disease ( [link] ). Cell-based therapy refers to treatment in which stem cells induced to differentiate in a growth dish are injected into a patient to repair damaged or destroyed cells or tissues. Many obstacles must be overcome for the application of cell-based therapy. Although embryonic stem cells have a nearly unlimited range of differentiation potential, they are seen as foreign by the patient’s immune system and may trigger rejection. Also, the destruction of embryos to isolate embryonic stem cells raises considerable ethical and legal questions.
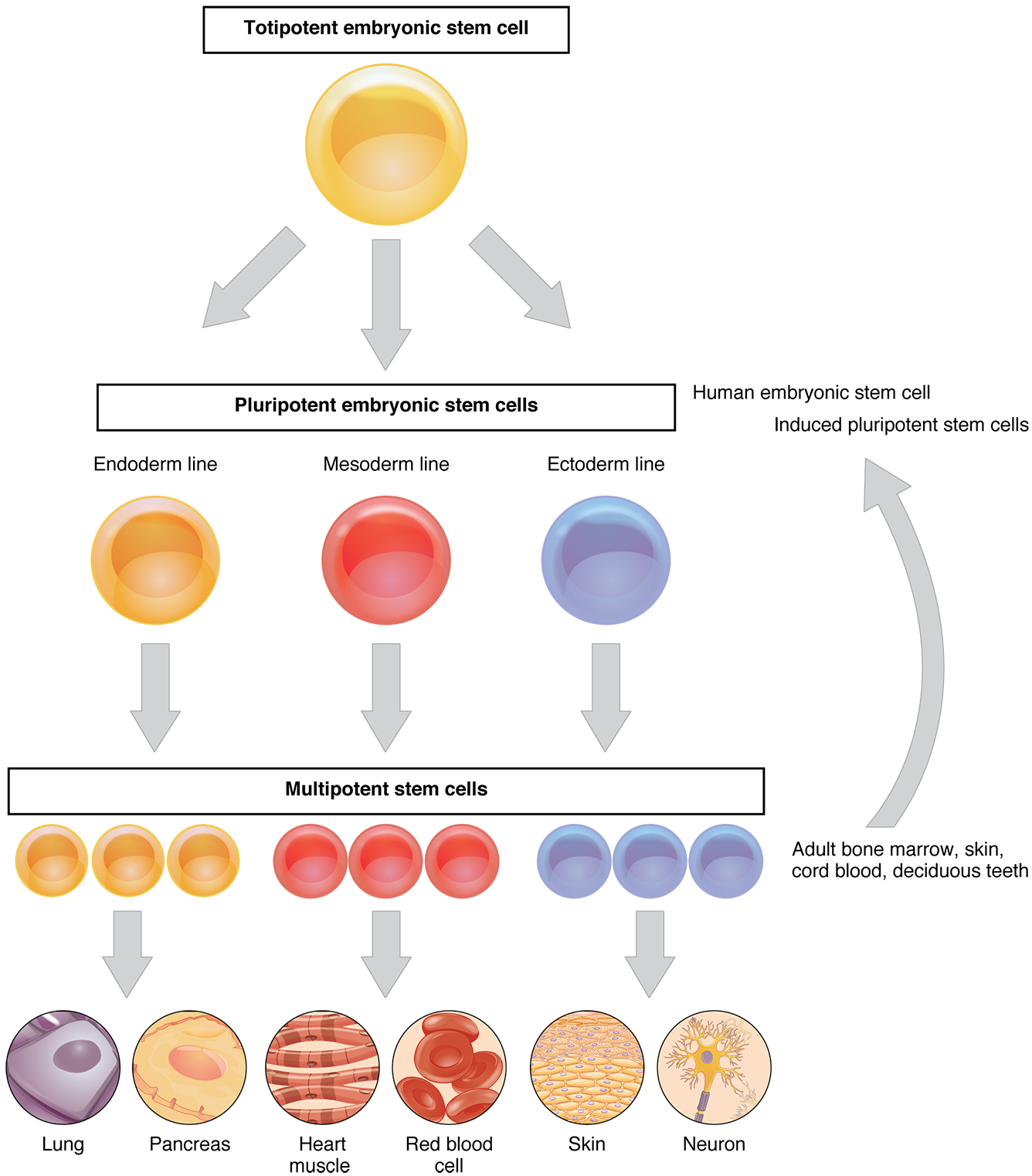
In contrast, adult stem cells isolated from a patient are not seen as foreign by the body, but they have a limited range of differentiation. Some individuals bank the cord blood or deciduous teeth of their child, storing away those sources of stem cells for future use, should their child need it. Induced pluripotent stem cells are considered a promising advance in the field because using them avoids the legal, ethical, and immunological pitfalls of embryonic stem cells.
One of the major areas of research in biology is that of how cells specialize to assume their unique structures and functions, since all cells essentially originate from a single fertilized egg. Cell differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialized as they body develops. A stem cell is an unspecialized cell that can divide without limit as needed and can, under specific conditions, differentiate into specialized cells. Stem cells are divided into several categories according to their potential to differentiate. While all somatic cells contain the exact same genome, different cell types only express some of those genes at any given time. These differences in gene expression ultimately dictate a cell’s unique morphological and physiological characteristics. The primary mechanism that determines which genes will be expressed and which ones will not is through the use of different transcription factor proteins, which bind to DNA and promote or hinder the transcription of different genes. Through the action of these transcription factors, cells specialize into one of hundreds of different cell types in the human body.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?